Common functions of data tables for beginners in PHP
mysql_query()
##mysql_query()
Associates with the specified connection identifier The current number of activities in the database sends a query. If link_identifier is not specified, the last opened connection is used. If there is no open connection, this method will try to call #mysql_connect() function without parameters to establish it. A connect and use it. Query results will be cached. This function is used to execute sql statements
mysql_fetch_array()Get a row from the result set as an association Array, or numeric array, or both
Returns an array generated based on the rows fetched from the result set, or false if there are no more rowsSyntax: mysql_fetch_array(data,array_type )Detailed explanation: $sql = "sql statement"; $info = mysql_query($sql); //Execute sql statement $row =mysql_fetch_array($info ); //Get the result set of sql Print_r($row);Example:
First we create a table in the database. The data table has id username password 3 fields, and then fill in some contentThe code is as follows: 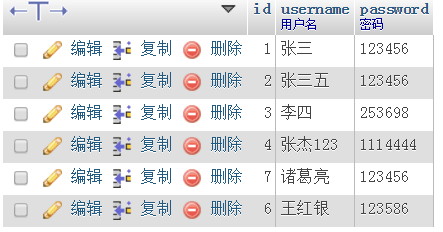
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>数据表操作 查询</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$con = mysql_connect('localhost','root','root') or die('连接服务器失败');
mysql_select_db('php') or die('连接数据库失败');
mysql_set_charset('utf8');
$sql = "select * from `user`"; //查询数据库user这张表的所有内容
$info = mysql_query($sql); //执行sqL语句
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($info)){
echo "<pre>";
print_r($row);
echo "</pre>";
}
?>
</body>
</html>mysql_fetch_array() is an extended version of mysql_fetch_row(). In addition to storing data in an array as a numerical index, you can also store data as an associative index, using the field name as the key. Tip: It is important to point out that using mysql_fetch_array() is not significantly slower than using mysql_fetch_row(), and it also obviously provides more values## The #mysql_fetch_row() function obtains a row from the result set as a numeric array
##The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>数据表操作 查询</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$con = mysql_connect('localhost','root','root') or die('连接服务器失败');
mysql_select_db('php') or die('连接数据库失败');
mysql_set_charset('utf8');
$sql = "select * from `user`"; //查询数据库user这张表的所有内容
$info = mysql_query($sql); //执行sqL语句
while($row = mysql_fetch_row($info)){
echo "<pre>";
print_r($row);
echo "</pre>";
}
?>
</body>
</html>Note: mysql_fetch_row() obtains a row of data from the result set associated with the result identifier data and returns it as an array. Each result column is stored in a cell of the array, starting at offset 0.
Calling mysql_fetch_row() in sequence will return the next row in the result set, or FALSE if there are no more rows
##mysql_result() function
mysql_result() function returns the value of a field in the result set. If successful, the function returns the field value. If it fails, return falseSyntax: mysql_result(data,row,field)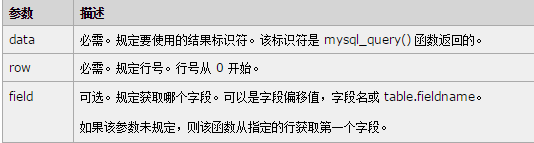
The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>数据表操作查询</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$con = mysql_connect('localhost','root','root') or die('连接服务器失败');
mysql_select_db('php') or die('连接数据库失败');
mysql_set_charset('utf8');
$sql = "select * from `user`"; //查询数据库user这张表的所有内容
$info = mysql_query($sql); //执行sqL语句
$row =mysql_result($info, 1);
echo $row;
?>
</body>
</html>














