HTML <div> and <span>
HTML block-level elements <div> and inline elements <span>
##The width of block-level elements fills the entire visible area of the browser, Generally, there can only be one block-level element in a line The width of an inline element is generally based on the text content within the element. Multiple inline elements can be placed within a block-level element
Example
Let’s first look at the characteristics of the block-level element <div> and the inline element <span><!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>php中文网(php.cn)</title> </head> <body> <div style="border: 1px solid red;"> hello </div> <span style="border: 1px solid blue;">world</span> </body> </html>Program running results:
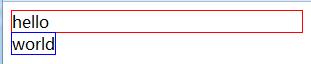
##Block-level elements<div>
Block-level elements will occupy one line by default. , the width will automatically fill the width of the parent element. Therefore, multiple cross-level elements are displayed on multiple lines from top to bottom.Block-level elements: div, p, form, ul, li, ol, dl, table…
Inline element<span>
Inline elements: span, strong, em, br, img, input, label, select, textarea, cite……
HTML grouping tag
##We learned earlier There are so many tags. In the next section, we will teach you how to use those tags to make a simple web page layout Tag Description ## <div> defines the area of the document, block-level <span> Used to combine inline elements in the document, inline elements (inline)














