Share a small case of Request object
We will make a page that can remember the name of the visitor. In this small case, you will learn how to use the values of the Cookies, Form and ServerVariables collections of the Request object, and you can also learn how to use the Response object to send Cookies. .
First, let’s take a look at the program code:
<%@LANGUAGE="VBSCRIPT" CODEPAGE="65001"%><!doctype html><html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>用Cookies记住访问者的姓名</title></head><body><%Dim sUserName
sUserName = Trim(Request.Cookies("name"))'判断name是否为空,不为空则输出name的值If sUserName = "" Then
'判断是否是POST刚提交了表单,是的话则获取表单内容输出Cookies
If UCase(Trim(Request.ServerVariables("REQUEST_METHOD"))) = "POST" Then
sUserName = Trim(Request.Form("name"))
Response.Cookies("name") = sUserName
Response.Cookies("name").Expires = DateAdd("d", 1, Now) 'Cookies一天后过期 Response.Write("我已经记住您的姓名了!") Else
'否则显示表单,让用户提交表单%>
<form method="post" action="">
请告诉我您的姓名 : <input name="name" type="text"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form><%
End If Else
Response.Write("您好," & sUserName)End If%></body></html>When running for the first time, Cookies information cannot be obtained, and the form is displayed for the user to submit, as shown below:
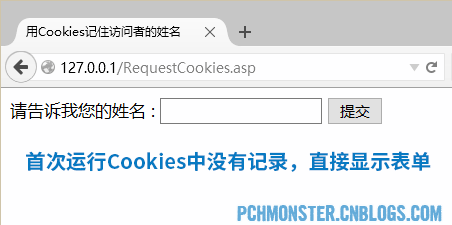
Submit the form, or POST to the current ASP page. Because Cookies still cannot be obtained, the page with successful submission of the form is displayed, as shown below:
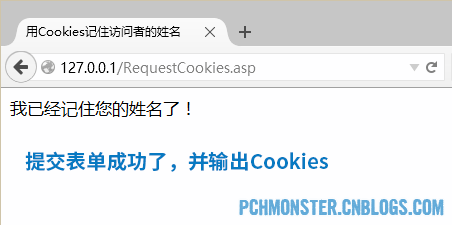
Refresh the current page RequestCookies.asp again, because Cookies can be obtained and the visitor's name is directly displayed.
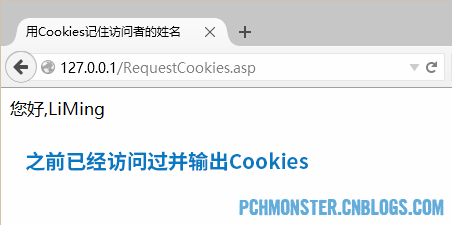
Let’s explain in detail the part that allows the user to enter their name and save it. First, get the value of the ServerVariables variable REQUEST_METHOD. This value identifies the request method of the current page. If it is the POST method, it means that the form is being submitted to this page. At this time, the value of the form must be obtained and the Response.Cookies collection will be used to output cookies to the client. Otherwise, the HTML code for the user to fill in the name will be displayed.
Little knowledge
Trim function removes spaces on both sides of a string, LTrimThe function deletes the spaces on the left side of the string, and the RTrim function deletes the spaces on the right side of the string. The
UCase function converts the specified string to uppercase, and the LCase function converts the specified string to lowercase.
【Related Recommendations】
1. Summary of Asp.net built-in object Request object usage examples
2. Talk about the use of the two objects Request and Response
3. Share the request object in asp Five methods to obtain client data
4. Detailed explanation of ASP.NET system object Request
The above is the detailed content of Share a small case of Request object. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1243
1243
 24
24
 Convert an array or object to a JSON string using PHP's json_encode() function
Nov 03, 2023 pm 03:30 PM
Convert an array or object to a JSON string using PHP's json_encode() function
Nov 03, 2023 pm 03:30 PM
JSON (JavaScriptObjectNotation) is a lightweight data exchange format that has become a common format for data exchange between web applications. PHP's json_encode() function can convert an array or object into a JSON string. This article will introduce how to use PHP's json_encode() function, including syntax, parameters, return values, and specific examples. Syntax The syntax of the json_encode() function is as follows: st
 What does php request mean?
Jul 07, 2021 pm 01:49 PM
What does php request mean?
Jul 07, 2021 pm 01:49 PM
The Chinese meaning of request is "request". It is a global variable in PHP and is an array containing "$_POST", "$_GET" and "$_COOKIE". The "$_REQUEST" variable can obtain data and COOKIE information submitted by POST or GET.
 Use Python's __contains__() function to define the containment operation of an object
Aug 22, 2023 pm 04:23 PM
Use Python's __contains__() function to define the containment operation of an object
Aug 22, 2023 pm 04:23 PM
Use Python's __contains__() function to define the containment operation of an object. Python is a concise and powerful programming language that provides many powerful features to handle various types of data. One of them is to implement the containment operation of objects by defining the __contains__() function. This article will introduce how to use the __contains__() function to define the containment operation of an object, and give some sample code. The __contains__() function is Pytho
 How to use the urllib.request.urlopen() function to send a GET request in Python 3.x
Jul 30, 2023 am 11:28 AM
How to use the urllib.request.urlopen() function to send a GET request in Python 3.x
Jul 30, 2023 am 11:28 AM
How to use the urllib.request.urlopen() function in Python3.x to send a GET request. In network programming, we often need to obtain data from a remote server by sending an HTTP request. In Python, we can use the urllib.request.urlopen() function in the urllib module to send an HTTP request and get the response returned by the server. This article will introduce how to use
 How to convert MySQL query result array to object?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
How to convert MySQL query result array to object?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
Here's how to convert a MySQL query result array into an object: Create an empty object array. Loop through the resulting array and create a new object for each row. Use a foreach loop to assign the key-value pairs of each row to the corresponding properties of the new object. Adds a new object to the object array. Close the database connection.
 Source code exploration: How are objects called in Python?
May 11, 2023 am 11:46 AM
Source code exploration: How are objects called in Python?
May 11, 2023 am 11:46 AM
Wedge We know that objects are created in two main ways, one is through Python/CAPI, and the other is by calling a type object. For instance objects of built-in types, both methods are supported. For example, lists can be created through [] or list(). The former is Python/CAPI and the latter is a calling type object. But for instance objects of custom classes, we can only create them by calling type objects. If an object can be called, then the object is callable, otherwise it is not callable. Determining whether an object is callable depends on whether a method is defined in its corresponding type object. like
 Use Python's __le__() function to define a less than or equal comparison of two objects
Aug 21, 2023 pm 09:29 PM
Use Python's __le__() function to define a less than or equal comparison of two objects
Aug 21, 2023 pm 09:29 PM
Title: Using Python's __le__() function to define a less than or equal comparison of two objects In Python, we can define comparison operations between objects by using special methods. One of them is the __le__() function, which is used to define less than or equal comparisons. The __le__() function is a magic method in Python and is a special function used to implement the "less than or equal" operation. When we compare two objects using the less than or equal operator (<=), Python
 How do PHP functions return objects?
Apr 10, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
How do PHP functions return objects?
Apr 10, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
PHP functions can encapsulate data into a custom structure by returning an object using a return statement followed by an object instance. Syntax: functionget_object():object{}. This allows creating objects with custom properties and methods and processing data in the form of objects.




