 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 Introduction to a large collection of knowledge about the margin attribute of CSS important properties
Introduction to a large collection of knowledge about the margin attribute of CSS important properties
Introduction to a large collection of knowledge about the margin attribute of CSS important properties
The following sharing is inspired by me after learning about margin knowledge in the past few days. I feel that my previous understanding of margin was simply too shallow. Therefore, the following article is written, firstly, for myself to organize my thoughts; secondly, to share the knowledge and avoid misunderstandings about the margin attribute. There may be a lot of content, but it is the essence. I hope you will study patiently.
The following sharing will be divided into the following contents:
1. A brief introduction to the margin attribute
1.1: Margin percentage setting for normal flow
1.2: Margin percentage setting for absolute positioning
2. Elements for which margin cannot be applied
3. Collapsing margins
3.1: Collapsing margins original intention
3.2: Collapsing margins type
3.2.1: Brothers The margins of elements overlap
3.2.2: The margins of parent and child elements overlap
3.2.3: The element’s own margin-bottom and margin-top will also collapse when they are adjacent
4. Margin calculation rules after folding
4.1: The margins participating in the folding are all positive values
4.2: The margins participating in the folding are all negative values
4.3: There are positive values and negative values in the margins involved in folding
5.Collapsing margins solution
1.Simple margin attribute Introduction
Before introducing margin, let’s take a picture of the W3C standard box model so that readers can view the relevant positions.
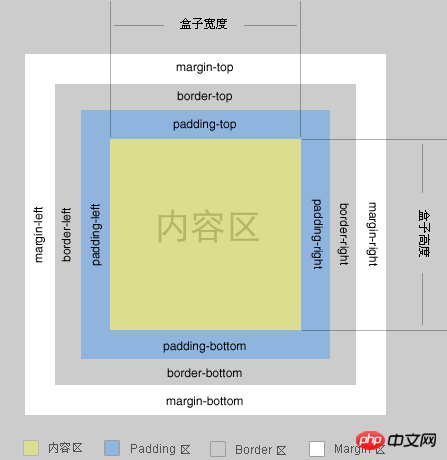
margin, as the name suggests, is called outer margin.
The basic attributes of margin are as follows
a: margin is 'margin-top', 'margin-right', 'margin -bottom', the abbreviation of 'margin-left', indicates the size range of margin.
b: The margin value can be one of the width value, percentage value or 'auto'. Note that margin must have a unit, which can be pixels, inches, millimeters, or ems.
c: The margin percentage value is calculated relative to the width of the parent element.
d: When the margin is margin:10px, it means that the top, right, bottom, and left (counterclockwise) directions are all 10px; when the margin is margin:10px 20px, it means that the top, bottom, and left directions are 10px. is 20px; when the margin is margin:10px 20px 5px, it means the top direction is 10px, the left and right directions are 20px, and the bottom direction is 5px; when the margin is margin:1px 2px 3px 4px, it means the top direction is 1px, and the right direction is 2px. , the bottom direction is 3px, and the left direction is 4px.
Through the brief introduction to margin above, we know that the percentage value of margin is calculated relative to the width of the parent element, but the calculation of margin for ordinary flow and absolutely positioned elements is different.
1.1: Normal flow margin percentage setting
In a normal flow element, the margin percentage value is calculated based on the width of its parent element.
<p class="container">
<p class="content"></p>
</p>.container {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightpink;
margin: 10px;
display: inline-block; <!--设置此值是有原因的,会在下面讲解。-->
}
.container .content {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: lightgreen;
margin: 10%;
}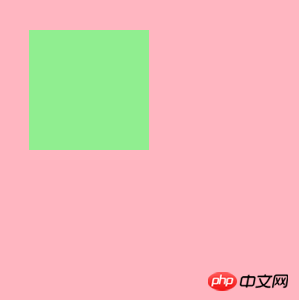
margin are calculated based on the width of the parent element!
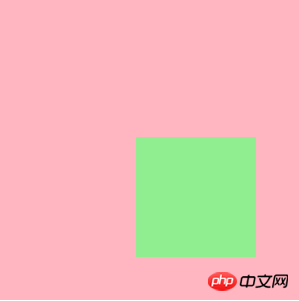
1.2: Absolute positioning margin percentage setting
In an absolutely positioned element, if the parent element is set to relative/absolute/fixed, the margin percentage value It is calculated based on the width of the parent element; if the parent element is not set to relative/absolute/fixed, the margin percentage value is calculated based on the width of the entire page..container {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightpink;
display: inline-block;
}
.container .content {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: lightgreen;
position: absolute; /*增加了改该属性*/
margin: 10%;
}
2. Margin cannot be applied to elements
有以下元素设置 margin 值是没有效果的。
a:行内元素垂直 margin 值不起作用。
b:margin 非 table 类型的元素,以及 table 类型中 table-caption, table-cell 和 inline-table 这3类。例如 TD TR TH 等,margin 是不适用的。
c:对于行内非替换元素(例如 SPAN),垂直方向的 margin 不起作用。
3.外边距折叠 (Collapsing margins)
Collapsing margins,即外边距折叠,指的是相邻的两个或多个外边距 (margin) 会合并成一个外边距。margin 折叠 必须发生在普通流元素中。
3.1:Collapsing margins 初衷
Collapsing margins 的初衷就是为了让段落显示的更加好看。以由几个段落组成的典型文本页面为例。第一个段落上面的空间等于段落的上外边距。如果没有外边距合并,后续所有段落之间的外边距都将是相邻上外边距和下外边距的和。这意味着段落之间的空间是页面顶部的两倍。如果发生外边距合并,段落之间的上外边距和下外边距就合并在一起,这样各处的距离就一致了。
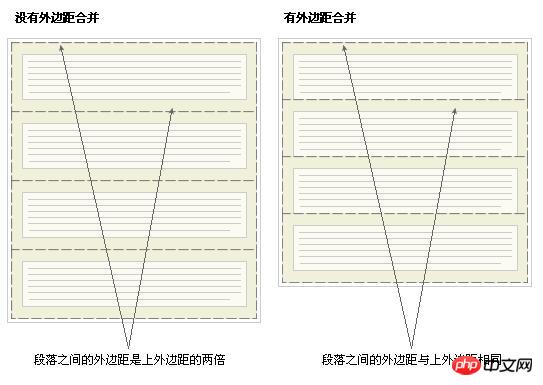
此图来源于 W3C
3.2:Collapsing margins 类型
3.2.1:兄弟元素的 margin 重叠
<p class="container"></p> <p class="an-container"></p>
.container {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
background-color: lightpink;
}
.an-container {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
margin-top: 10px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
3.2.2:父子元素的 margin 重叠
两个或多个外边距没有被非空内容、padding、border 或 clear 分隔开。
这些 margin 都处于普通流中。
margin-top 重叠:在没有被分隔的情况下,一个元素的 margin-top 会和它普通流中的第一个子元素(非浮动元素等)的 margin-top 相邻。
<p class="container">
<p class="an-container"></p>
</p>.container {
width: 150px;
margin-top: 10px;
background-color: lightpink;
}
.container .an-container {
background-color: lightgreen;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
margin-bottom 重叠:在没有被分隔的情况下,只有在父元素的 height 是 "auto" 的情况下,它的 margin-bottom 才会和它普通流中的最后一个子元素(非浮动元素等)的 margin-bottom 相邻。就是说,父元素的height值不能是固定高度值。如果父元素固定高度,那么margin-bottom会无效的。代码同上。
3.2.3:元素自身的 margin-bottom 和 margin-top 相邻时也会折叠
<p style="border:1px solid red; width:100px;">
<p style="margin-top: 100px;margin-bottom: 50px;"></p>
</p>
以上代码运行后,我们讲得到的是红色边框的正方形,方框的宽高都应该是 100px,高度不应该是 150px。
4.折叠后 margin 的计算规则
4.1:参与折叠的 margin 都是正值
<p style="height:50px; margin-bottom:50px; width:50px; background-color: red;">A</p> <p style="height:50px; margin-top:100px; width:50px; background-color: green;">B</p>
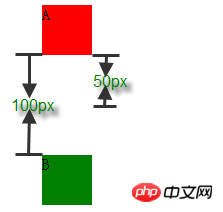
在 margin 都是正数的情况下,取其中 margin 较大的值为最终 margin 值。
4.2:参与折叠的 margin 都是负值
<p style="height:100px; margin-bottom:-75px; width:100px; background-color: red;">A</p> <p style="height:100px; margin-top:-50px; margin-left:50px; width:100px; background-color: green;">B</p>
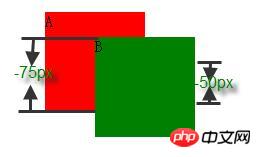
当 margin 都是负值的时候,取的是其中绝对值较大的,然后,从 0 位置,负向位移。
4.3:参与折叠的 margin 中有正值,有负值
<p style="height:50px; margin-bottom:-50px; width:50px; background-color: red;">A</p> <p style="height:50px; margin-top:100px; width:50px; background-color: green;">B</p>
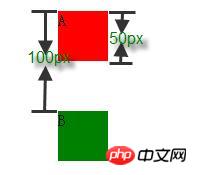
如果,相邻的 margin 中有正值,同时存在负值会怎样呢?有正有负,先取出负 margin 中绝对值中最大的,然后,和正 margin 值中最大的 margin 相加。其实也就是正负相加就可以了。
上面的例子最终的 margin 应该是 100 + (-50) = 50px。
5.Collapsing margins 解决方法
解决方法有如下:
a:浮动元素、inline-block 元素、绝对定位元素的 margin 不会和垂直方向上其他元素的 margin 折叠 ( 针对 兄弟元素)
注意: 浮动元素 , inline-block元素 , 绝对定位元素 都属于 BFC元素。
b:创建了块级格式化上下文(BFC, blocking formatting context )的父元素,比如说overflow:hidden,不和它的子元素发生 margin 折叠 (针对 父子元素)。
c:给父元素添加以下内容之一都可以避免发生 margin 重叠 。如 添加内容 , 添加 padding , 添加 border。
虽然有方法解决这个问题。但是目前最好的解决方案是回避这个问题。也就是,不要给指定元素添加具有指定宽度的内边距或外边距,而是尝试将内边距或外边距添加到元素的父元素和子元素。
以上这篇CSS重要属性之 margin 属性知识大整合(必看篇)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持PHP中文网。
更多CSS重要属性之 margin 属性知识大合集介绍相关文章请关注PHP中文网!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1668
1668
 14
14
 1426
1426
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1255
1255
 24
24
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text



