Detailed explanation: Will css loading cause blocking?
JS execution will block the parsing and rendering of the DOM tree, so will css loading block the parsing and rendering of the DOM tree? So, next I will do a test on the parsing and rendering of the DOM tree by css loading.
In order to complete this test, let’s do some popular science first, how to use chrome to set the download speed
1. Open the chrome console (press F12), you can see the picture below , focus on the place where I drew the red circle
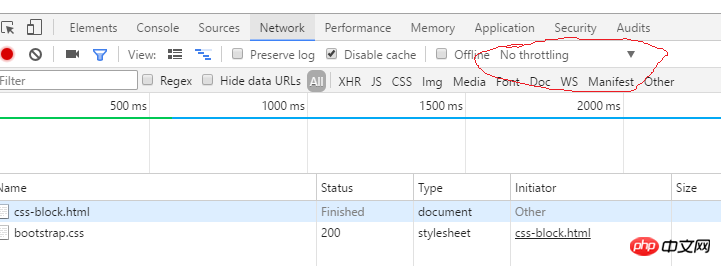
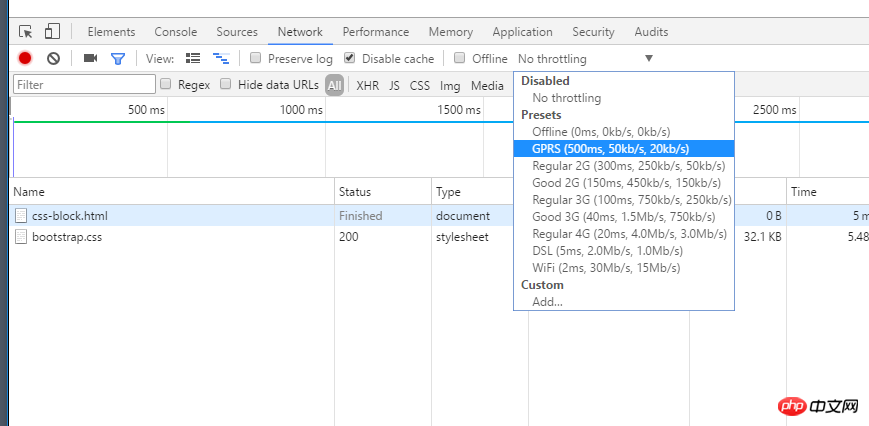
Will css loading block the parsing and rendering of the DOM tree?
Speak in code:<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>css阻塞</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
h1 {
color: red !important
}
</style>
<script>
function h () {
console.log(document.querySelectorAll('h1'))
}
setTimeout(h, 0)
</script>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是红色的</h1>
</body>
</html>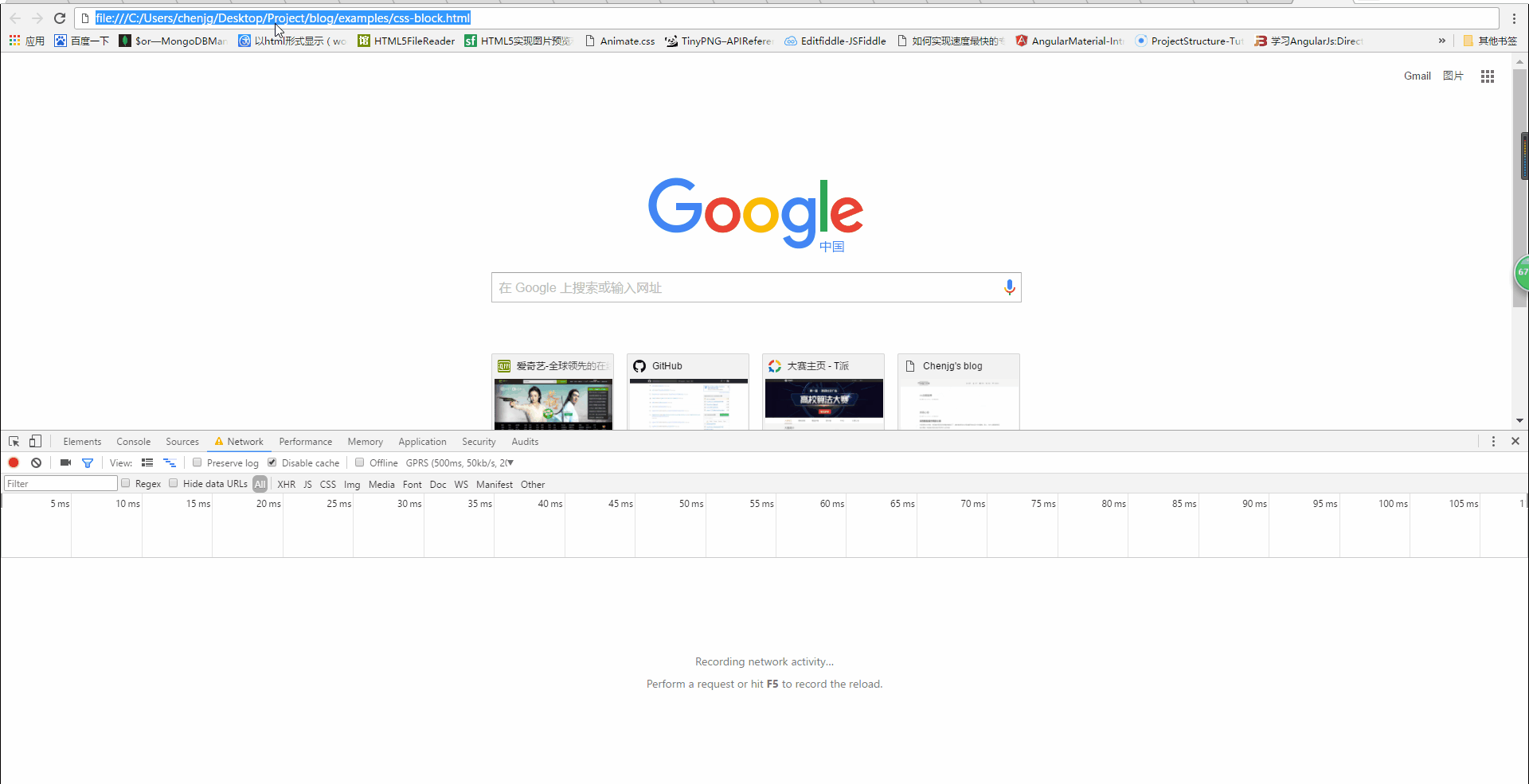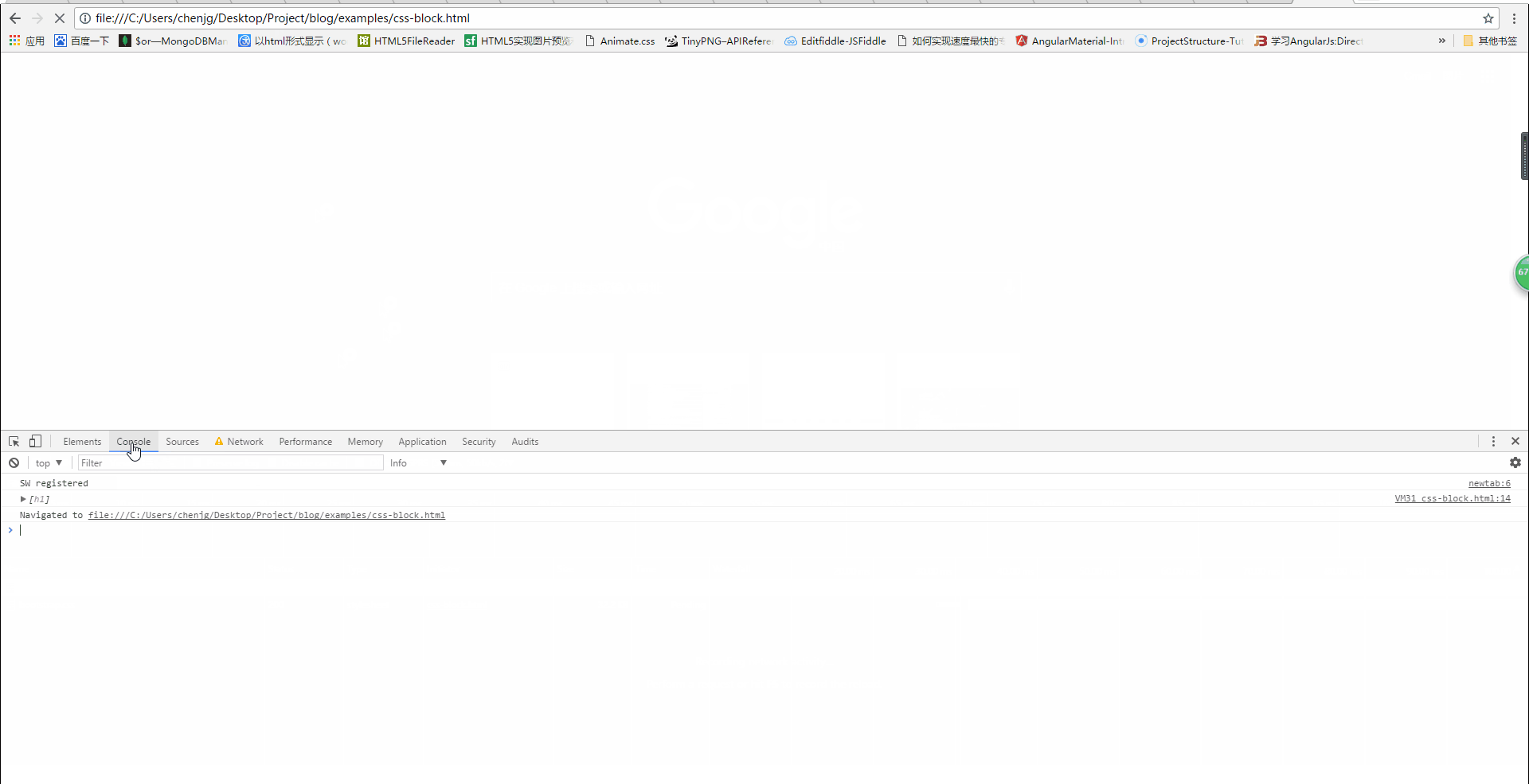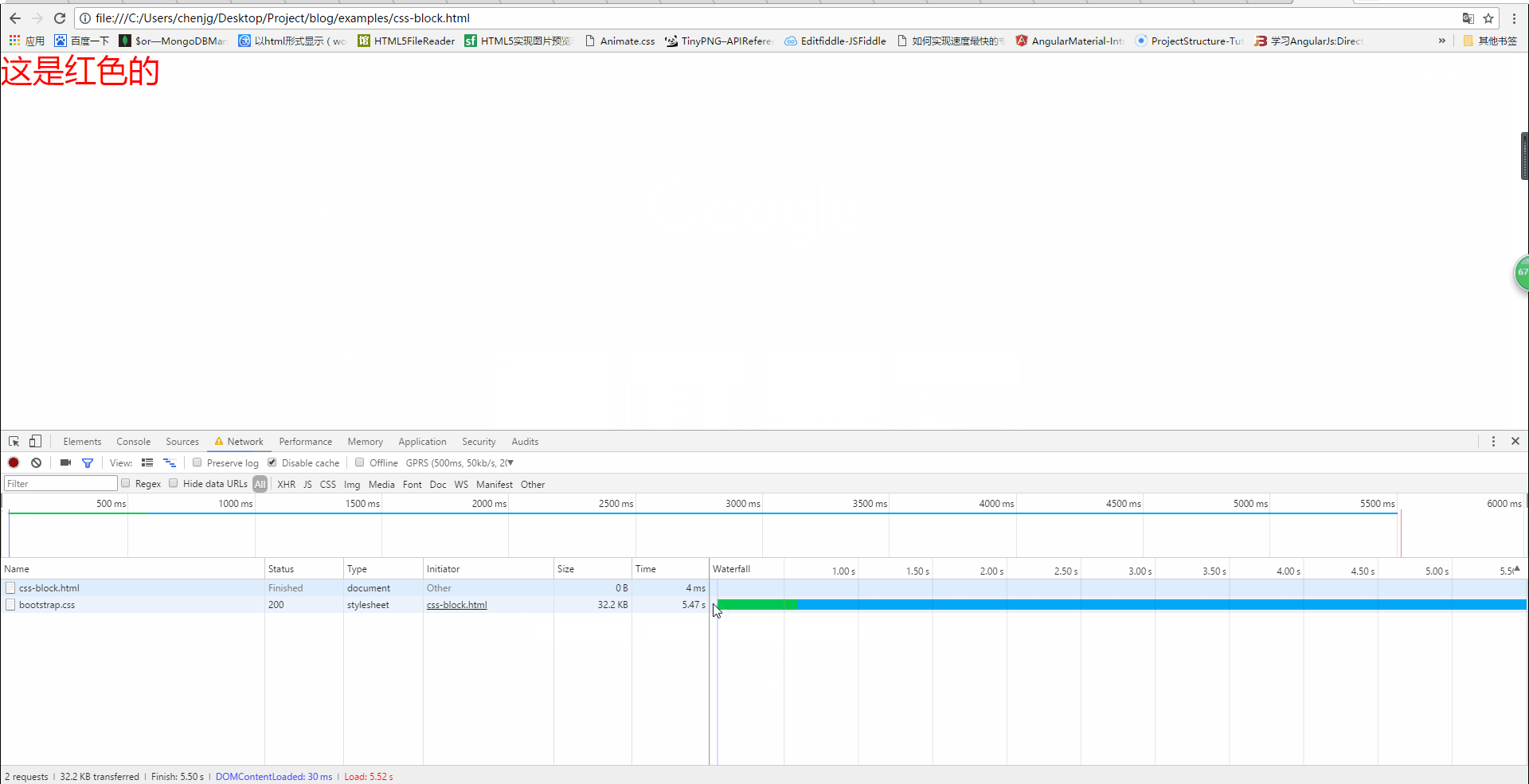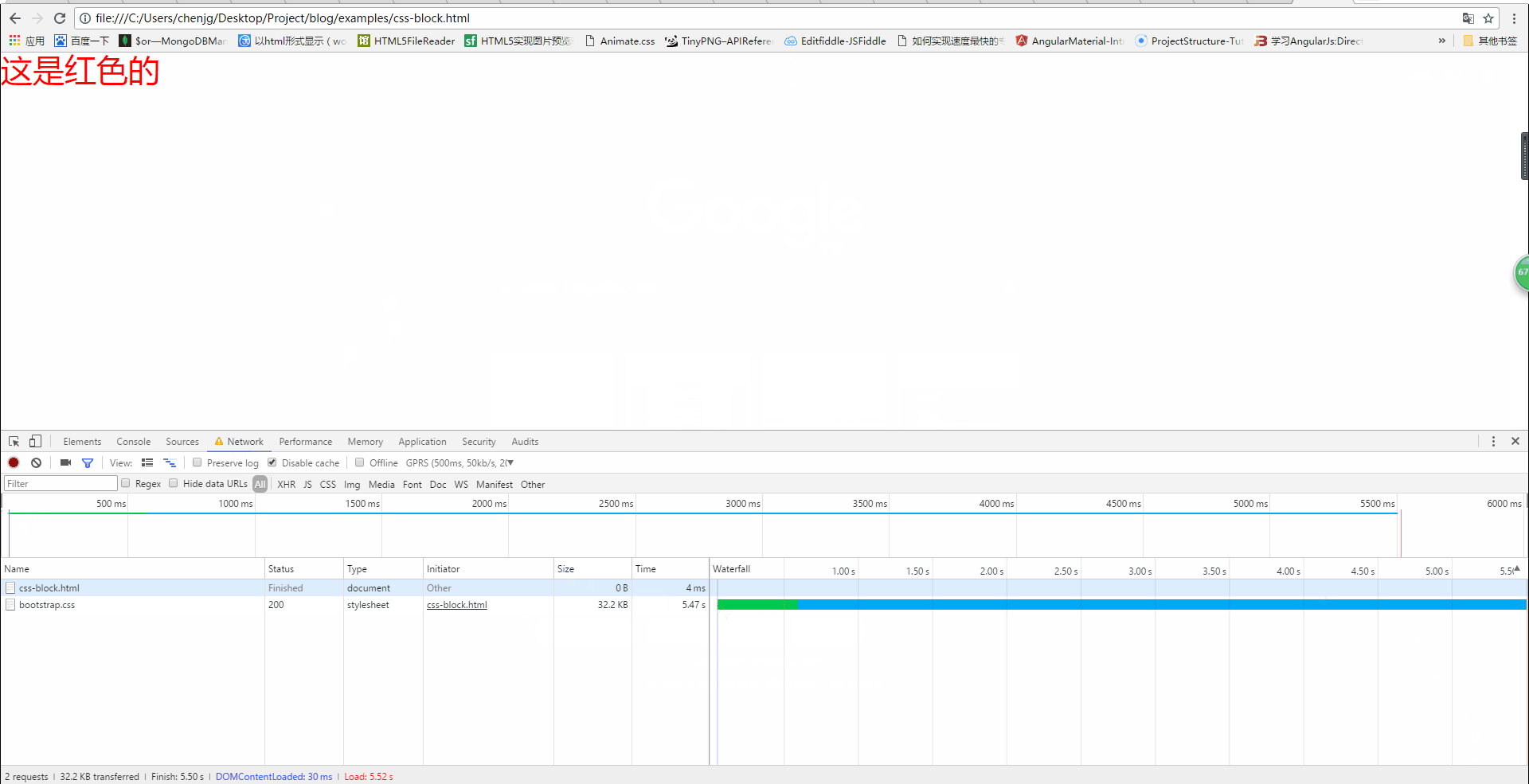
Will css block DOM tree parsing?
We can see from the above picture that when the css has not been loaded, h1 is not displayed, but at this time the console output is as follows 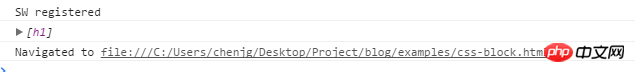
Will css loading block DOM tree rendering?
From the above picture, we can also see that when the css has not been loaded, the page displays a white screen. It is not until the css is loaded that the red font is displayed, that is Said that although the following content was parsed, it was not rendered. Therefore, css loading will block DOM tree rendering.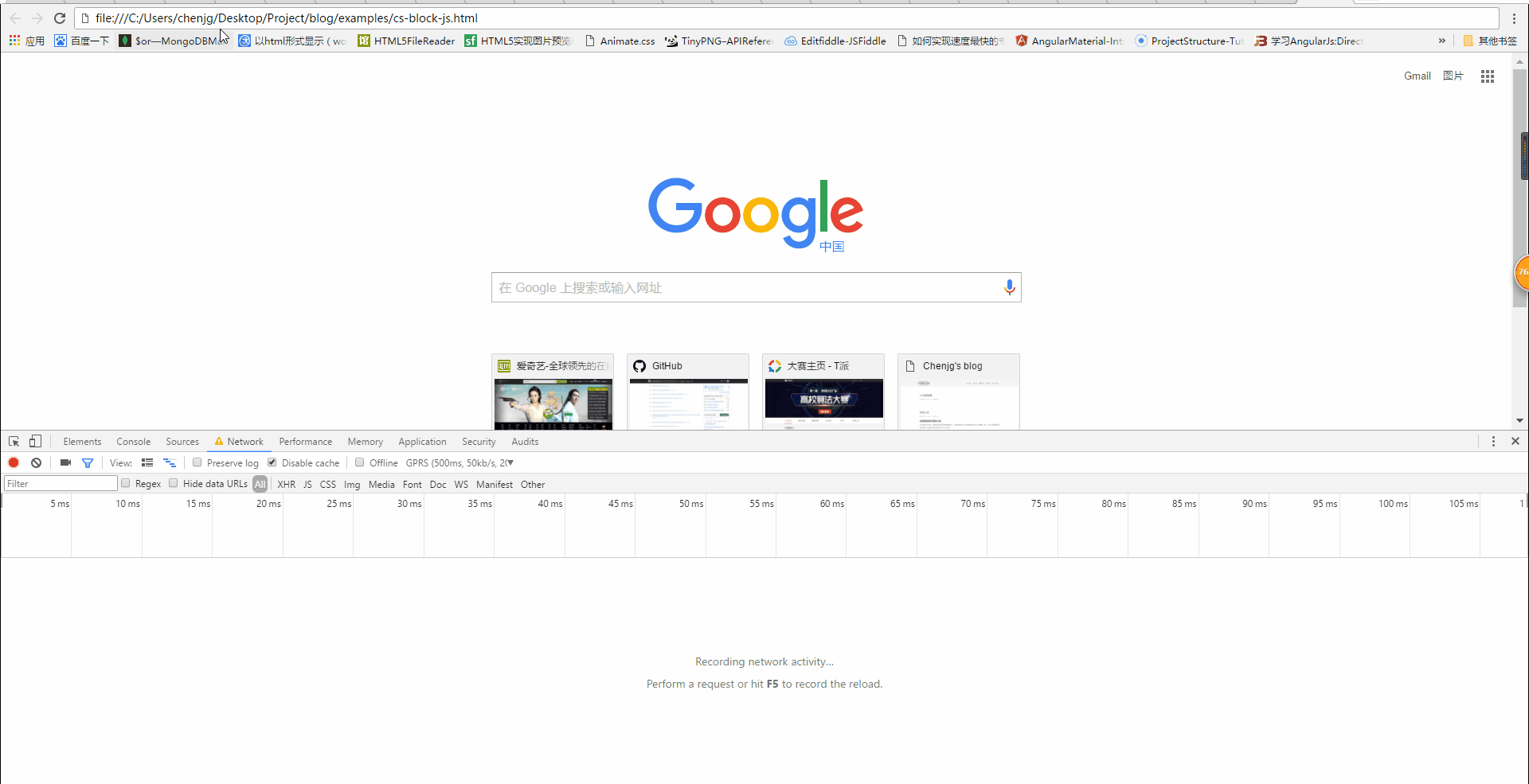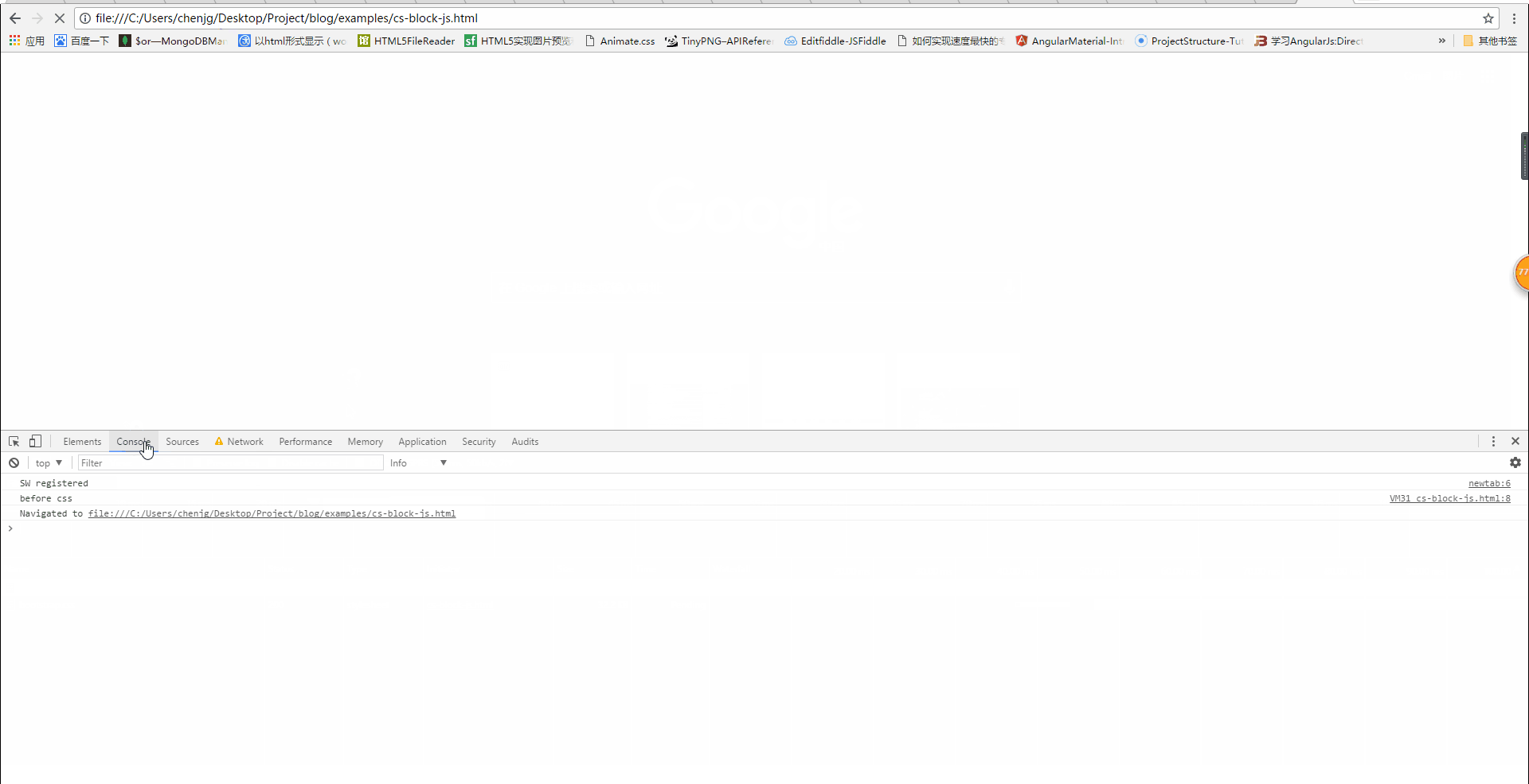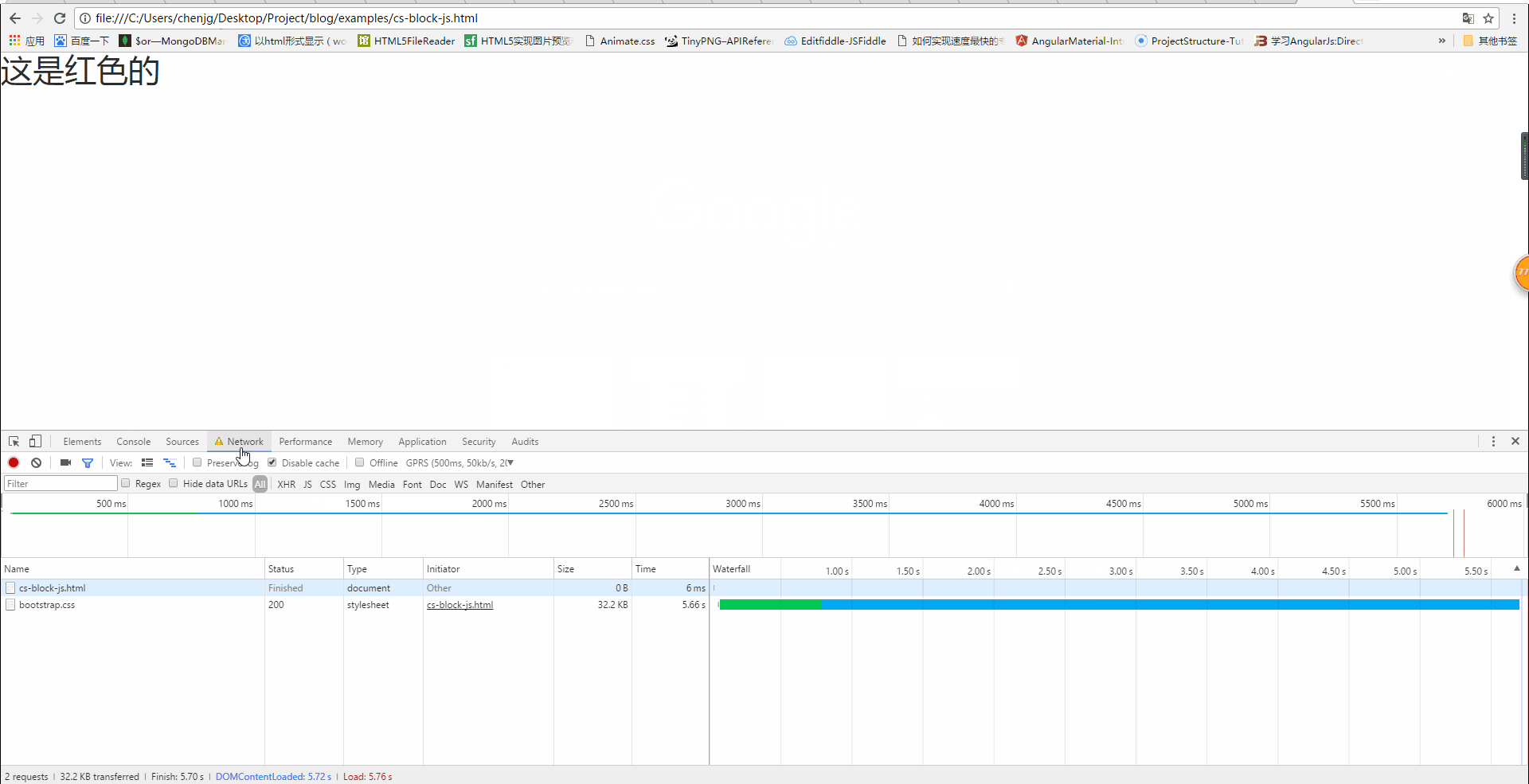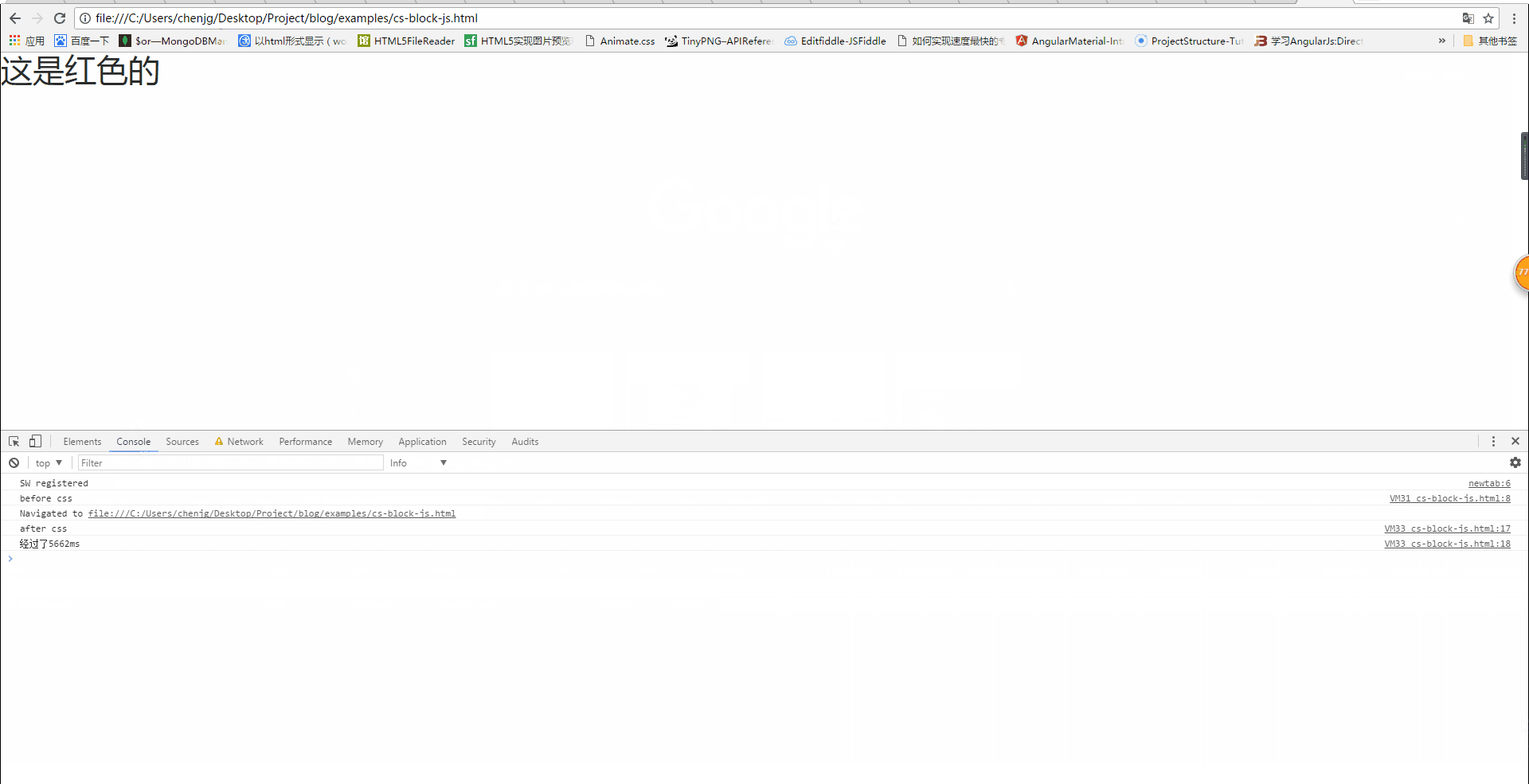
Will css loading block js running?
From the above inference, we can conclude that css loading will not block DOM tree parsing, but it will block DOM tree rendering. So, will css loading block js execution?Similarly, verify through code.<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>css阻塞</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<script>
console.log('before css')
var startDate = new Date()
</script>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是红色的</h1>
<script>
var endDate = new Date()
console.log('after css')
console.log('经过了' + (endDate -startDate) + 'ms')
</script>
</body>
</html>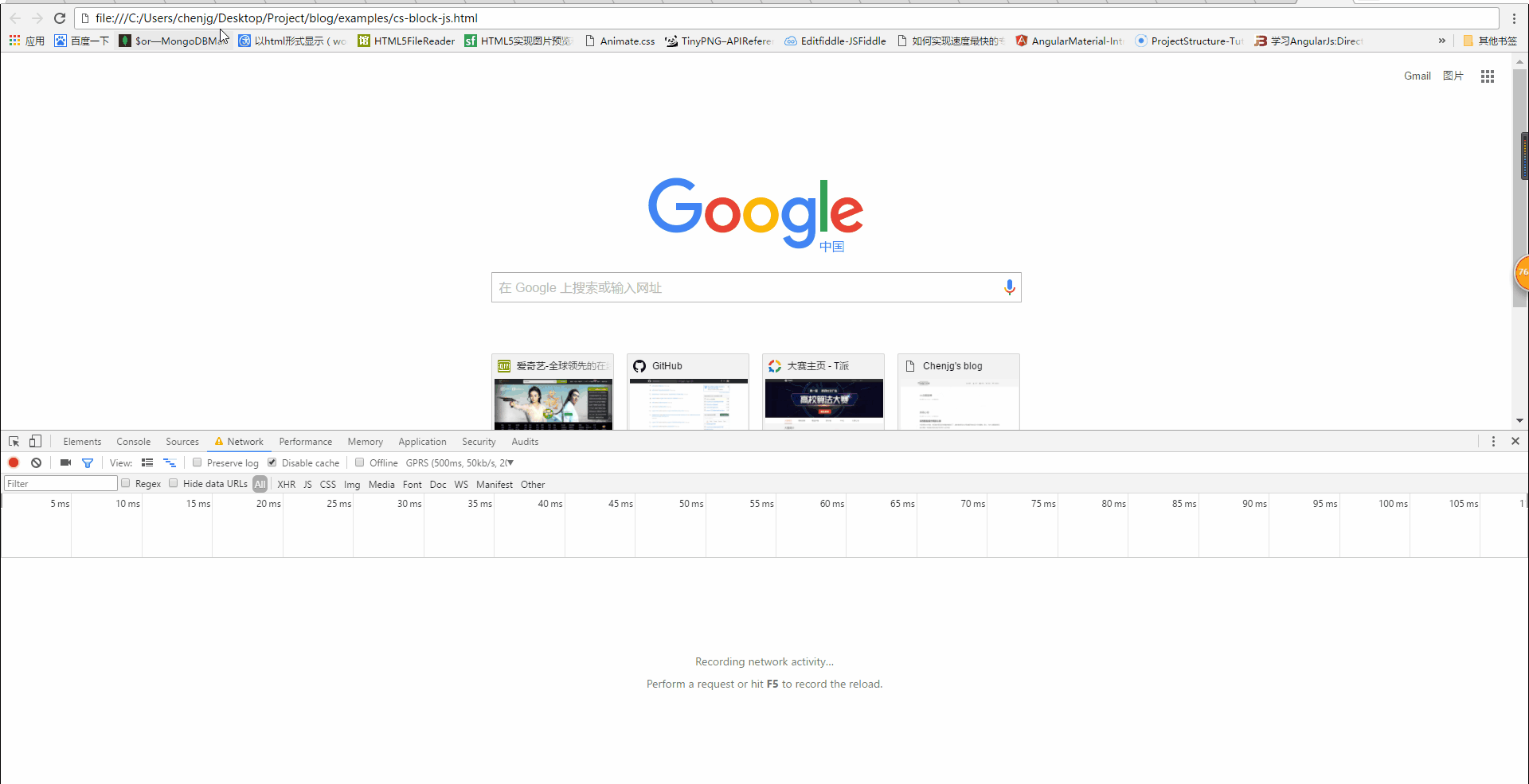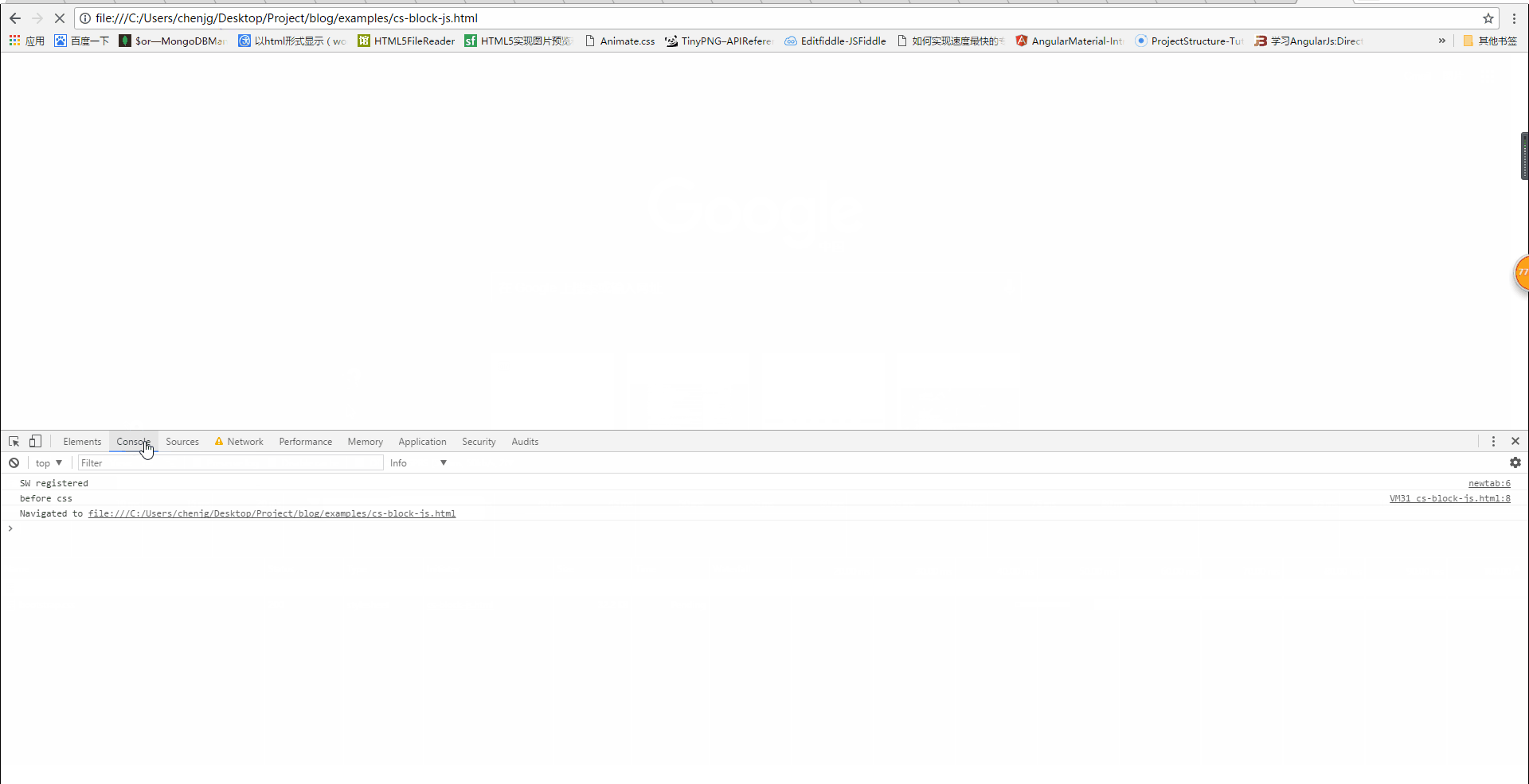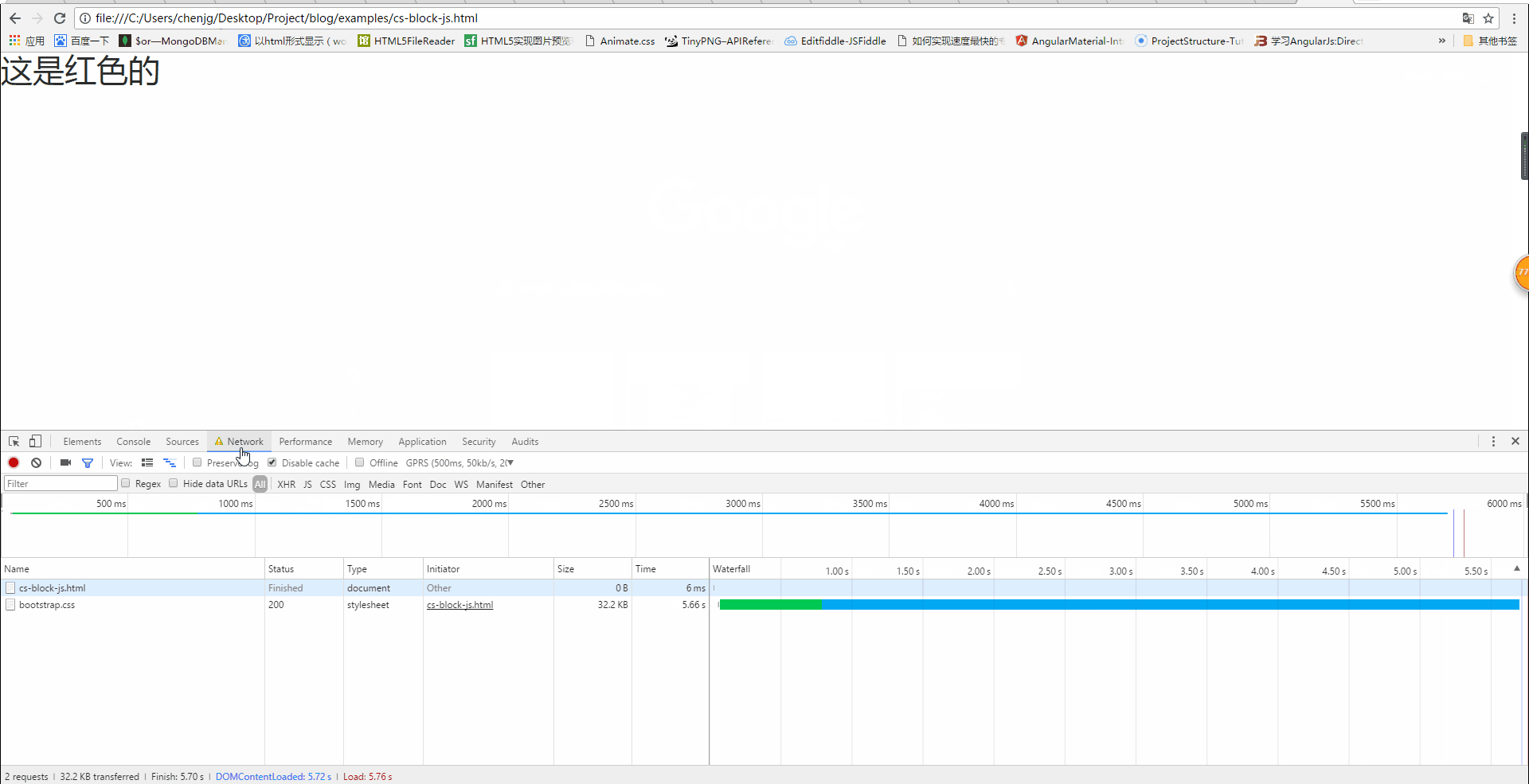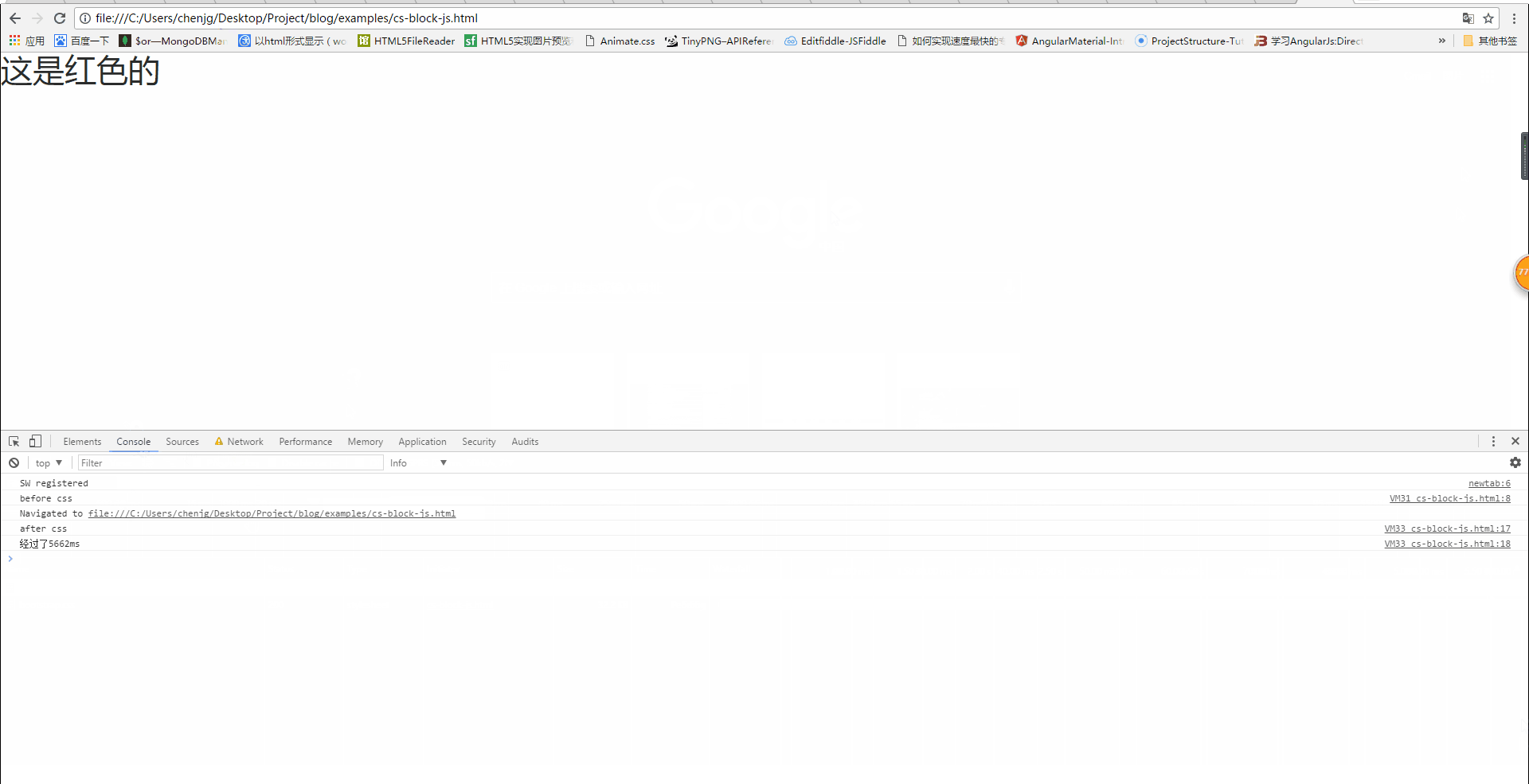
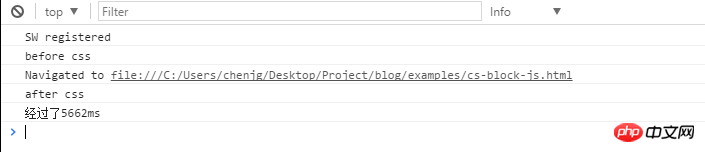
From the above, we can The following conclusions are drawn:
1.css loading will not block the parsing of the DOM tree
2.css loading will block the rendering of the DOM tree3.css loading will block the execution of subsequent js statements
Therefore, in order to avoid letting users see a long white screen time, we should improve the css loading speed as much as possible. For example, we can use the following methods:
1. Use CDN (because CDN will select the nearest node with cached content to provide you with resources based on your network conditions, so it can reduce loading time)
2. Compress css (can Use many packaging tools, such as webpack, gulp, etc., you can also turn on gzip compression)
3. Use cache reasonably (setting cache-control, expires, and E-tag are good, but you should pay attention to one problem, After the file is updated, you need to avoid the impact of caching. One solution is to add a version number after the file name)
4. Reduce the number of http requests, merge multiple css files, or simply directly. Written as inline style (one disadvantage of inline style is that it cannot be cached)
The above content is a detailed explanation of the blocking caused by css loading. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
Related recommendations:
Detailed explanation of the use of hover selector in CSS
Why sometimes DIV CSS fails to load
Judge to execute subsequent code example after css is loaded_javascript skills
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation: Will css loading cause blocking?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1659
1659
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1231
1231
 24
24
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text




