
We are familiar with margin. This article mainly introduces the usage of margin in CSS and the analysis of common problems. The introduction in the article is very detailed and has certain reference and learning value for everyone. Friends who need it can follow Let’s take a look together.
1. Introduction
marginWe are generally used to calling it margins. We can set the margins in four directions respectively. No more details here. Describe the assignment syntax in detail.
Actually, the margins we usually set are physical-level settings, and margins also include start, end, before, after, etc. These are mainly logical-level settings. If you are interested, Google it yourself. .
When setting margin, we must know:
For block-level elements, how effective is margin in four directions;
For inline elements, margin is only effective in the horizontal direction.
2. Box model
Speaking of margin, I have to talk about the box model:
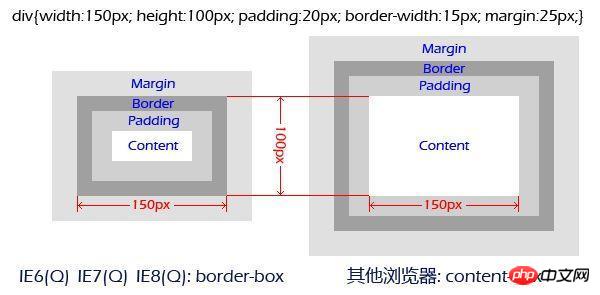
1. Content => padding => border => margin
The reason why the box model needs to be understood from the inside and outside is mainly because the standards of the box model are different. It determines what the width we set in CSS is. At this time, everyone will think of those calculation formulas. In fact, with the arrival of CSS3, we can set the standard of the box model through box-sizing:
2. border-box: width is calculated from border;
3. content-box: width is calculated from content;
4. padding-box: has been calculated from removed from the standard.
Here’s another picture, are you already aware of it?
##3. Margin overlap problem
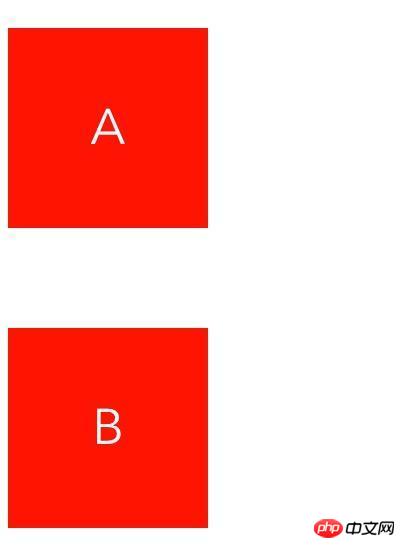
This kind of problem mainly occurs on block elements and not floating elements (it is not described clearly here, and will be discussed in detail later). Let’s take a look at what happened.1. Occurs in adjacent sibling elements
.a {
margin: 50px 0;
}
.b {
margin: 100px 0;
}
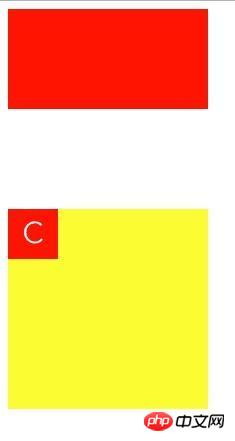
2. Occurs at the parent-child node
p(class="b")
p(class="a")
p(class="c") C .a {
margin: 20px 0;
}
.b {
margin: 100px 0;
}
4. Magical negative margin value
We set the margin in four directions for a block element What happens: .item {
margin: 0 200px;
height: 200px;
} .item {
position: absolute;
background: red;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
margin-top: -100px;
margin-left: -100px;
}5. Margin and float
For these two troublesome attributes, Together, let me just say, it was a real blast. I said above that "this problem mainly occurs on block elements and not floating elements". Here are two more points: .clearfix::before, .clearfix::after {
content: " ";
display: table;
}
.clearfix::after {
clear: both;
}学完本文相信大家对css 中margin属性有更深的认识,大家赶紧收藏起来吧。
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Analysis of usage and common problems of margin in CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




