content"width=640,user-scalable=no" 然后再进行固定尺寸的px设计?
content"width=640,user-scalable=no" 然后再进行固定尺寸的px设计? 竟然也可以达到自适应的布局在手机上面
咱们不都是通常viewport content="width=device-width么 那么上面这种有没有什么坑呢 ,那么以后我是t content="width=device-width css3媒体查询 还是用content"width=640,user-scalable=no"这样的方法呢 我需要兼容手机浏览器和apk的webview
回复内容:
結論:content"width=640,user-scalable=no" 是一個很好的解決方案,荔枝FM,人人都是播客的移動站使用的就是此方案固定宽度,viewport 缩放(轉自MobileWeb 适配总结) 别的不多说了,强烈建议看看前几天刚写的一篇文章:使用Flexible实现手淘H5页面的终端适配 应该能让你找到需要的答案 你在用的可能是:视觉稿、页面宽度、viewport width 使用统一宽度,利用浏览器自身缩放完成适配。页面样式(包括图像元素)完全按照视觉稿的尺寸,使用定值单位 (px、em)即可完成。
优点:存在的问题:
- 开发简单 缩放交给浏览器,完全按视觉稿切图。
- 还原精准 绝对等比例缩放,可以精准还原视觉稿(不考虑清晰度的情况下)。
- 测试方便 在PC端即可完成大部分测试,手机端只需酌情调整一些细节(比如图标、字体混合排列时,因为字体不同造成的对齐问题)。
- 像素丢失 对于一些分辨率较低的手机,可能设备像素还未达到指定的 viewport 宽度,此时屏幕的渲染可能就不准确了。比较常见的是边框“消失”了,不过随着手机硬件的更新,这个问题会越来越少的。
- 缩放失效 某些安卓机不能正常的根据 meta 标签中 width 的值来缩放 viewport,需要配合initial-scale 。
- 文本折行 存在于缩放失效的机型中,某些手机为了便于文本的阅读,在文本到达 viewport 边缘(非元素容器的边缘)时即进行折行,而当 viewport 宽度被修正后,浏览器并没有正确的重绘,所以就发现文本没有占满整行。一些常用的段落性文本标签会存在该问题。
缩放失效问题需通过 js 动态设定 initial-scale。
利用 rem 布局依照某特定宽度设定 rem 值(即 html 的 font-size),页面任何需要弹性适配的元素,尺寸均换算为 rem 进行布局;当页面渲染时,根据页面有效宽度进行计算,调整 rem 的大小,动态缩放以达到适配的效果。利用该方案,还可以根据 devicePixelRatio 设定 initial-scale 来放大 viewport,使页面按照物理像素渲染,提升清晰度。
优点:缺点:
- 清晰度高,能达到物理像素的清晰度。
- 能解决 DPR 引起的“1像素”问题。
- 向后兼容较好,即便屏幕宽度增加、PPI 增加该方案依旧适用。
- 适配 js 需尽可能早进入,减少(避免)viewport 变化引起的重绘。
- 某些Android机会丢掉 rem 小数部分。
- 需要预编译库进行单位转换。
<span class="nt"><meta</span> <span class="na">name=</span><span class="s">"viewport"</span> <span class="na">content=</span><span class="s">"target-densitydpi=device-dpi,width=640,user-scalable=no"</span> <span class="nt">/></span>
<span class="c1">//首先检查浏览器类型</span>
<span class="kd">var</span> <span class="nx">browser</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nx">getBrowser</span><span class="p">();</span>
<span class="k">if</span> <span class="p">(</span><span class="nb">window</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">top</span> <span class="o">===</span> <span class="nb">window</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="kd">var</span> <span class="nx">s</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="nx">t</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="nx">sw</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="k">if</span> <span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">browser</span> <span class="o">===</span> <span class="s1">'Gecko'</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="nx">s</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nx">calcRato</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nb">Math</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">min</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">width</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">height</span><span class="p">));</span>
<span class="nb">document</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">write</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="s1">'<meta name="viewport" content="width='</span> <span class="o">+</span> <span class="mi">100</span> <span class="o">/</span> <span class="nx">s</span> <span class="o">+</span> <span class="s1">'%, user-scalable=no, initial-scale='</span> <span class="o">+</span> <span class="nx">s</span> <span class="o">+</span> <span class="s1">'"/>'</span><span class="p">);</span>
<span class="p">}</span> <span class="k">else</span> <span class="k">if</span> <span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">browser</span> <span class="o">===</span> <span class="s1">'Trident'</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="nb">document</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">write</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="s1">'<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no"/>'</span><span class="p">);</span>
<span class="nb">document</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">documentElement</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">style</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">zoom</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nx">calcRato</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nb">Math</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">min</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">width</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">height</span><span class="p">));</span>
<span class="p">}</span> <span class="k">else</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="nx">t</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nb">document</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">createElement</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="s1">'meta'</span><span class="p">);</span>
<span class="nx">t</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">name</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="s1">'viewport'</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="nx">t</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">content</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="s1">'width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1'</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="nb">document</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">head</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">appendChild</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">t</span><span class="p">);</span>
<span class="nx">sw</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nb">Math</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">min</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">width</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">height</span><span class="p">);</span>
<span class="k">if</span> <span class="p">(</span><span class="nb">Math</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">min</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">width</span> <span class="o">/</span> <span class="nb">window</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">innerWidth</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="nx">screen</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">height</span> <span class="o">/</span> <span class="nb">window</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">innerHeight</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="o">></span> <span class="mi">1</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="nb">document</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">documentElement</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">style</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">zoom</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nx">calcRato</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">sw</span> <span class="o">/</span> <span class="nx">devicePixelRatio</span><span class="p">);</span>
<span class="p">}</span> <span class="k">else</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="nx">s</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nx">calcRato</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">sw</span><span class="p">);</span>
<span class="nx">t</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">content</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="s1">'width='</span> <span class="o">+</span> <span class="mi">100</span> <span class="o">/</span> <span class="nx">s</span> <span class="o">+</span> <span class="s1">'%, user-scalable=no, initial-scale='</span> <span class="o">+</span> <span class="nx">s</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="p">}</span>
<span class="p">}</span>
<span class="p">}</span>
<span class="kd">function</span> <span class="nx">calcRato</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">sw</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="c1">//离散放大级别</span>
<span class="kd">var</span> <span class="nx">step</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="mf">0.125</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="c1">//基准宽度为320px</span>
<span class="kd">var</span> <span class="nx">zoom</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nx">sw</span> <span class="o">/</span> <span class="mi">320</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="c1">//放大时不使用线性算法</span>
<span class="k">if</span> <span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">zoom</span> <span class="o">></span> <span class="mi">1</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="nx">zoom</span> <span class="o">=</span> <span class="nb">Math</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">floor</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nb">Math</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="nx">sqrt</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="nx">zoom</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="o">/</span> <span class="nx">step</span><span class="p">)</span> <span class="o">*</span> <span class="nx">step</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="p">}</span>
<span class="k">return</span> <span class="nx">zoom</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="p">}</span>

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Was bedeutet die Breite von HTML?
Jun 03, 2021 pm 02:15 PM
Was bedeutet die Breite von HTML?
Jun 03, 2021 pm 02:15 PM
In HTML5 bedeutet „Breite“ die Breite des Inhaltsbereichs. Sie können innere Ränder, Ränder und äußere Ränder außerhalb des Inhaltsbereichs hinzufügen Element.
 Lösen Sie das Problem ausgelasteter Geräte unter Linux
Jan 02, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
Lösen Sie das Problem ausgelasteter Geräte unter Linux
Jan 02, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
Bei der Verwaltung von umount-Geräten unter Linux kommt es häufig zu „Gerät ist ausgelastet“. Dann gibt es wahrscheinlich einen Benutzer oder Prozess, der dieses Verzeichnis verwendet. #umount/mntumount:/mnt:deviceisbusyumount:/mnt:deviceisbusy Anschließend müssen Sie den Befehl „fuser“ verwenden, um die Prozess-ID und den Eigentümer des Prozesses anzuzeigen, z. B.: #fuser-mu/mnt/mnt:25781c(root)#kill- 925781#umount/mnt ist so
 So lösen Sie das Problem der Docker-Mounting-Verzeichnisberechtigungen
Feb 29, 2024 am 10:04 AM
So lösen Sie das Problem der Docker-Mounting-Verzeichnisberechtigungen
Feb 29, 2024 am 10:04 AM
In Docker kann das Berechtigungsproblem des Mount-Verzeichnisses normalerweise durch die folgende Methode gelöst werden: Hinzufügen berechtigungsbezogener Optionen bei Verwendung des Parameters -v zur Angabe des Mount-Verzeichnisses. Sie können die Berechtigungen des gemounteten Verzeichnisses angeben, indem Sie nach dem gemounteten Verzeichnis Folgendes hinzufügen: ro oder :rw, was jeweils Lese- und Lese-/Schreibberechtigungen angibt. Beispiel: dockerrun-v/host/path:/container/path:roimage_name Definieren Sie die USER-Direktive in der Docker-Datei, um den Benutzer anzugeben, der im Container ausgeführt wird, um sicherzustellen, dass Vorgänge innerhalb des Containers den Berechtigungsanforderungen entsprechen. Zum Beispiel: FROMimage_name#CreateanewuserRUNuseradd-ms/bin/
 Wie deaktiviere ich Geräte im WIN10 Home Edition-System?
Jan 17, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Wie deaktiviere ich Geräte im WIN10 Home Edition-System?
Jan 17, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Das Betriebssystem Windows 10 ist heute zweifellos eines der einflussreichsten Betriebssysteme. Es verfügt über äußerst leistungsstarke Geräteverwaltungsfunktionen. Zu dieser leistungsstarken Funktion gehört sicherlich das Aktivieren und Deaktivieren von Geräten. So deaktivieren Sie das Gerät im WIN10 Home Edition-System Methode 1: Deaktivieren des Geräts im Geräte-Manager 1. Öffnen wir zunächst den Geräte-Manager! Es gibt drei Methoden: (1) Drücken Sie die Tasten WIN+X auf der Tastatur und wählen Sie Geräte-Manager. (2) Geben Sie im Startmenü direkt „Geräte-Manager“ ein und klicken Sie darauf! (3) Suchen Sie den Geräte-Manager in der Systemsteuerung und wählen Sie ihn aus. 2. Suchen Sie als Nächstes das Gerät, das Sie deaktivieren möchten, in der Geräteliste! Klicken Sie, um es zu deaktivieren. Ps: Hier sehen Sie alle Geräte, die mit dem System verbunden wurden
 Welche Methoden gibt es, um den Breitenwert in CSS auszudrücken?
Nov 13, 2023 pm 05:47 PM
Welche Methoden gibt es, um den Breitenwert in CSS auszudrücken?
Nov 13, 2023 pm 05:47 PM
Zu den Methoden gehören Pixelwert, Prozentsatz, EM-Einheit, REM-Einheit, VW/VH-Einheit, Auto, Fit-Content, Min-Content, Max-Content. Ausführliche Einführung: 1. Pixelwert (px): Der Pixelwert ist fest und seine Breite bleibt unverändert, unabhängig davon, wie sich die Bildschirmauflösung ändert. Beispiel: Breite: 300 Pixel; 2. Prozent (%): Die prozentuale Breite ist relativ zur Breite des übergeordneten Elements. Zum Beispiel: Breite: 50 %, em-Einheit usw.
 So lösen Sie die fehlende Funktion zum Finden eines PCI-Geräts in CentOS7
Jan 05, 2024 am 09:08 AM
So lösen Sie die fehlende Funktion zum Finden eines PCI-Geräts in CentOS7
Jan 05, 2024 am 09:08 AM
Bei der Verwendung von XilinxPCIEdemo habe ich einen von xapp1022 bereitgestellten Linux-Treiber kompiliert und eine Fehlermeldung angezeigt, dass die Funktion pci_find_device nicht gefunden werden konnte. In der Beschreibung heißt es, dass dieser Treiber für Fedora ist und die aktuelle Umgebung Centos7 ist. Die einzige im Treiber verwendete Header-Datei ist linux/pci.h, die mit PCI zusammenhängt. Ich habe sie also überprüft und festgestellt, dass sie nicht vorhanden ist. Ich dachte, dass ich möglicherweise eine Bibliothek installieren müsste, und nachdem ich gesucht hatte, fand ich sie: pciutils. Nach der Installation habe ich Folgendes neu kompiliert, aber es ist immer noch fehlgeschlagen. Wenn Sie sich die Header-Datei noch einmal ansehen, gibt es einen zusätzlichen PCI-Ordner, der eine pci.h enthält. In dieser pci.h gibt es viele Funktionsdeklarationen, aber kein pci_find_devi
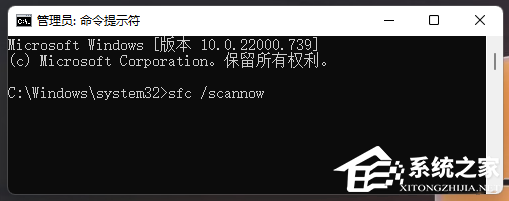 Fünf Möglichkeiten, den Bluescreen „Thread steckt im Gerätetreiber fest' zu beheben
Mar 25, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
Fünf Möglichkeiten, den Bluescreen „Thread steckt im Gerätetreiber fest' zu beheben
Mar 25, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
Einige Benutzer berichteten, dass nach der Installation des März-Win11-Update-Patches KB5035853 von Microsoft ein Bluescreen-of-Death-Fehler auftrat und „ThreadStuckinDeviceDriver“ auf der Systemseite angezeigt wurde. Es wird davon ausgegangen, dass dieser Fehler durch Hardware- oder Treiberprobleme verursacht werden kann. Hier sind fünf Lösungen, die Ihr Computer-Bluescreen-Problem hoffentlich schnell lösen werden. Methode 1: Führen Sie eine Systemdateiprüfung durch. Führen Sie den Befehl [sfc/scannow] in der Eingabeaufforderung aus, mit dem Sie Probleme mit der Systemdateiintegrität erkennen und beheben können. Der Zweck dieses Befehls besteht darin, alle fehlenden oder beschädigten Systemdateien zu scannen und zu reparieren und so zur Gewährleistung der Systemstabilität und des normalen Betriebs beizutragen. Methode 2: 1. Laden Sie das „Blue Screen Repair Tool“ herunter und öffnen Sie es.
 Erklärte CSS-Inhaltseigenschaften: Inhalt, Zähler und Anführungszeichen
Oct 21, 2023 am 10:16 AM
Erklärte CSS-Inhaltseigenschaften: Inhalt, Zähler und Anführungszeichen
Oct 21, 2023 am 10:16 AM
Detaillierte Erläuterung der CSS-Inhaltsattribute: Inhalt, Zähler und Anführungszeichen. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) ist ein unverzichtbarer Bestandteil der Front-End-Entwicklung. Es kann uns helfen, Webseiten zu verschönern und die Benutzererfahrung zu verbessern. In CSS gibt es einige spezielle Eigenschaften, mit denen die Anzeige von Textinhalten gesteuert werden kann, darunter Inhalt, Zähler und Anführungszeichen. In diesem Artikel werden diese Eigenschaften ausführlich erläutert und spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. 1. InhaltsattributInhaltsattribut




