sqlite基本sql语句使用
sqlite基本sql语句使用 一,SQLite常见的数据类型 SQLite是无类型的。 这意味着你可以保存任何类型的数据到你所想要保存的任何表的任何列中,无论这列声明的数据类型是什么(只有自动递增Integer Primary Key才有用)。对于SQLite来说对字段不指定类型是完全有
sqlite基本sql语句使用
一,SQLite常见的数据类型
SQLite是无类型的。 这意味着你可以保存任何类型的数据到你所想要保存的任何表的任何列中,无论这列声明的数据类型是什么(只有自动递增Integer Primary Key才有用)。对于SQLite来说对字段不指定类型是完全有效的。 即使SQLite允许忽略数据类型,但是仍然建议在你的Create Table语句中指定数据类型。 因为数据类型对于你和其他的程序员交
流,或者你准备换掉你的数据库引擎是非常有用的。SQLite只支持常见的5种存储类,
NULL
INTEGER --整型
REAL --浮点数
TEXT --文本
BLOB --大二进制对象
以下定义的数据类型都会转到相应的存储类中。
create table tab( --注意其中的注释方式
a VARCHAR(10), --长度不固定且其最大长度为n的字符串
b NVARCHAR(15),
c TEXT, --二进制对象
d INTEGER, --带符号的整型,具体取决于存入数字的范围大小
e FLOAT,
f BOOLEAN,
g CLOB, --使用CHAR来保存数据
h BLOB, --使用二进制对象保存数据,如保存位图
i TIMESTAMP,
j NUMBERIC(10,5),
k VARYING CHARACTER(24),
l NATIONAL VARYING CHARACTER(16), //
j REAL --浮点数字,存储为8-byte IEEE浮点数
);
二, 基本的数据操作
1,建立表
Create table admin(
username text,
age integer);
2,插入数据
insert into 表名(字段列表) values(值列表);
例如:insert into admin values(‘song’,25);
3,查询
select 字段名 from 表名;
select * from admin;
select distinct field from table_name;(distinct去掉重复项,将列中各字段值单个列出)
4,删除数据
Delete from 表名 where 条件子句。
delete from admin form where username=’song’;
5,修改
update 表名 set 字段名=值 where 条件子句。
update admin set username=’zhang’,age=24 where username=’song’ and age=25;
6,按条件分组
select * from 表名 where 条件子句 group by 分组子句 having …order by排子句
例如:
select * from admin;
select * from admin order by id desc(降序) | asc(升序);
select username from admin group by username having count(*)>1;
7,多条件查询语句
select 字段名 from 表名 where 子句1 按 子句二
select * from admin where username=’song’ and age=24;
select * from table_name where field in (‘val1’ , ’val2’ , ‘val3’ );
select * from table_name where field between val1 and val2;
select * from admin limit 5; --限制输出数据记录数量
8,多条件排序
select 字段名 from 表名 order by 字段1 (desc),字段2(desc);
select * from admin order by t1 ,t2 desc;
9,索引
例如 建立复合索引:create index idxT1 on admin(username,age);
各自建立索引:create index idxUsername on admin(username);
create index idxAge on admin(age);
10,外键FOREIGN KEY(UNIQUE | PRIMARY KEY | NOT NULL)的用法()
create table a(
a1 INTEGER PRIMARY KEY | UNIQUE | NOT NULL,
a2 TEXT,
a3 INTEGER );
create table b()(
b1 INTEGER ,
b2 TEXT,
b3 INTEGER,
foreign key(b3) references a(a1));
11,分页
select * from account limit 5 offset 3;
或者 select * from account limit 5,3;
12,模糊查询
SELECT 字段 FROM 表 WHERE 某字段 LIKE 条件
(1)%:表示任意0个或多个字符
(2)_ :表示任意单个字符,匹配单个任意字符,常用来限制表达式的字符长度语句。
(3)[ ]:表示括号内所列字符中的一个(类似正则表达式)
select * from admin where username like ‘[张李王]三’;
表示搜索的是“张三”,“李三”或“王三”
[4]:[^]表示不在括号所列之类的单个字符。
[5]:查询内容包含通配符时,用“[ ]”括起来。
13,删除表 | 索引
drop table [ IF EXISTS] admin;
drop index index_name
14,查询记录数目
select count(*) from table_name;

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Was ist der Unterschied zwischen HQL und SQL im Hibernate-Framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
Was ist der Unterschied zwischen HQL und SQL im Hibernate-Framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
HQL und SQL werden im Hibernate-Framework verglichen: HQL (1. Objektorientierte Syntax, 2. Datenbankunabhängige Abfragen, 3. Typsicherheit), während SQL die Datenbank direkt betreibt (1. Datenbankunabhängige Standards, 2. Komplexe ausführbare Datei). Abfragen und Datenmanipulation).
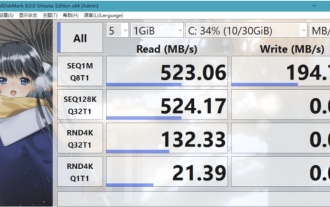 Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark ist ein kleines HDD-Benchmark-Tool für Festplatten, das schnell sequentielle und zufällige Lese-/Schreibgeschwindigkeiten misst. Lassen Sie sich als Nächstes vom Redakteur CrystalDiskMark und die Verwendung von CrystalDiskMark vorstellen ). Zufällige I/O-Leistung. Es ist eine kostenlose Windows-Anwendung und bietet eine benutzerfreundliche Oberfläche und verschiedene Testmodi zur Bewertung verschiedener Aspekte der Festplattenleistung. Sie wird häufig in Hardware-Reviews verwendet
 Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 ist eine Software, die Ihnen jederzeit Musik aller Art mit verlustfreier Klangqualität bietet Spielen Sie das erweiterte Audio auf dem Computer ab, um ein bequemeres und effizienteres Musikwiedergabeerlebnis zu ermöglichen. Das Interface-Design ist einfach, klar und benutzerfreundlich. Es nimmt einen minimalistischen Designstil an, ohne übermäßige Dekoration Es unterstützt außerdem eine Vielzahl von Skins und Themes, personalisiert Einstellungen nach Ihren eigenen Vorlieben und erstellt einen exklusiven Musikplayer, der die Wiedergabe mehrerer Audioformate unterstützt. Außerdem unterstützt es die Audio-Gain-Funktion zum Anpassen der Lautstärke Passen Sie die Lautstärke entsprechend Ihrem Hörzustand an, um Hörschäden durch zu hohe Lautstärke zu vermeiden. Als nächstes lass mich dir helfen
 Verwendung der Divisionsoperation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Verwendung der Divisionsoperation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
„Verwendung der Divisionsoperation in OracleSQL“ In OracleSQL ist die Divisionsoperation eine der häufigsten mathematischen Operationen. Während der Datenabfrage und -verarbeitung können uns Divisionsoperationen dabei helfen, das Verhältnis zwischen Feldern zu berechnen oder die logische Beziehung zwischen bestimmten Werten abzuleiten. In diesem Artikel wird die Verwendung der Divisionsoperation in OracleSQL vorgestellt und spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. 1. Zwei Arten von Divisionsoperationen in OracleSQL In OracleSQL können Divisionsoperationen auf zwei verschiedene Arten durchgeführt werden.
 Vergleich und Unterschiede der SQL-Syntax zwischen Oracle und DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Vergleich und Unterschiede der SQL-Syntax zwischen Oracle und DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Oracle und DB2 sind zwei häufig verwendete relationale Datenbankverwaltungssysteme, die jeweils über ihre eigene, einzigartige SQL-Syntax und -Eigenschaften verfügen. In diesem Artikel werden die SQL-Syntax von Oracle und DB2 verglichen und unterschieden und spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. Datenbankverbindung Verwenden Sie in Oracle die folgende Anweisung, um eine Verbindung zur Datenbank herzustellen: CONNECTusername/password@database. In DB2 lautet die Anweisung zum Herstellen einer Verbindung zur Datenbank wie folgt: CONNECTTOdataba
 Ausführliche Erläuterung der Funktion „Tag festlegen' in den dynamischen SQL-Tags von MyBatis
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Ausführliche Erläuterung der Funktion „Tag festlegen' in den dynamischen SQL-Tags von MyBatis
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation der dynamischen SQL-Tags von MyBatis: Detaillierte Erläuterung der Verwendung von Set-Tags. MyBatis ist ein hervorragendes Persistenzschicht-Framework. Es bietet eine Fülle dynamischer SQL-Tags und kann Datenbankoperationsanweisungen flexibel erstellen. Unter anderem wird das Set-Tag zum Generieren der SET-Klausel in der UPDATE-Anweisung verwendet, die sehr häufig bei Aktualisierungsvorgängen verwendet wird. In diesem Artikel wird die Verwendung des Set-Tags in MyBatis ausführlich erläutert und seine Funktionalität anhand spezifischer Codebeispiele demonstriert. Was ist Set-Tag? Set-Tag wird in MyBati verwendet
 So verwenden Sie NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
So verwenden Sie NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox ist eine von chinesischen Internetnutzern weit verbreitete E-Mail-Adresse und hat mit seinen stabilen und effizienten Diensten schon immer das Vertrauen der Benutzer gewonnen. NetEase Mailbox Master ist eine E-Mail-Software, die speziell für Mobiltelefonbenutzer entwickelt wurde. Sie vereinfacht das Senden und Empfangen von E-Mails erheblich und macht unsere E-Mail-Verarbeitung komfortabler. Wie Sie NetEase Mailbox Master verwenden und welche spezifischen Funktionen es bietet, wird Ihnen der Herausgeber dieser Website im Folgenden ausführlich vorstellen und hofft, Ihnen weiterzuhelfen! Zunächst können Sie die NetEase Mailbox Master-App im Mobile App Store suchen und herunterladen. Suchen Sie im App Store oder im Baidu Mobile Assistant nach „NetEase Mailbox Master“ und befolgen Sie dann die Anweisungen zur Installation. Nachdem der Download und die Installation abgeschlossen sind, öffnen wir das NetEase-E-Mail-Konto und melden uns an. Die Anmeldeschnittstelle ist wie unten dargestellt
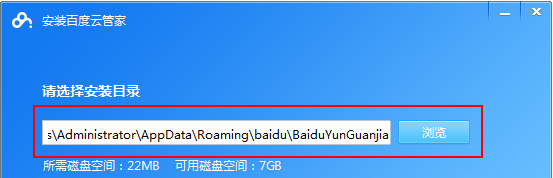 So verwenden Sie die Baidu Netdisk-App
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
So verwenden Sie die Baidu Netdisk-App
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud-Speicher sind heutzutage aus unserem täglichen Leben und Arbeiten nicht mehr wegzudenken. Als einer der führenden Cloud-Speicherdienste in China hat Baidu Netdisk mit seinen leistungsstarken Speicherfunktionen, der effizienten Übertragungsgeschwindigkeit und dem komfortablen Bedienerlebnis die Gunst einer großen Anzahl von Benutzern gewonnen. Und egal, ob Sie wichtige Dateien sichern, Informationen teilen, Videos online ansehen oder Musik hören möchten, Baidu Cloud Disk kann Ihre Anforderungen erfüllen. Viele Benutzer verstehen jedoch möglicherweise nicht die spezifische Verwendung der Baidu Netdisk-App. Dieses Tutorial führt Sie daher im Detail in die Verwendung der Baidu Netdisk-App ein. Wenn Sie immer noch verwirrt sind, folgen Sie bitte diesem Artikel, um mehr im Detail zu erfahren. So verwenden Sie Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation Wählen Sie beim Herunterladen und Installieren der Baidu Cloud-Software zunächst die benutzerdefinierte Installationsoption aus.




