PHP使用traits实现代码复用的例子
PHP 5.4中的traits,是新引入的特性,用于实现代码重用的方法,下面我们就一起来看看PHP使用traits实现代码复用的例子,希望文章可以帮助到各位.
PHP5.4后新增traits实现代码复用机制,Trait和类相似,但不能被实例化,无需继承,只需要在类中使用关键词use引入即可,可引入多个Traits,用','隔开。
(1)Trait简单使用
trait A {
public $var1 = 'test1';
public function test1() {
echo 'trait A::test1()';
}
}
trait B {
public $var2 = 'test2';
public function test2() {
echo 'trait B::test2()';
}
}
class C {
use A,B;
}
$c = new C();
echo $c->var1; //test1
$c->test2(); //trait B::test2()
(2)优先级问题
Trait会覆盖继承的方法,当前类会覆盖Trait方法。
trait A {
public $var1 = 'test';
public function test() {
echo 'A::test()';
}
public function test1() {
echo 'A::test1()';
}
}
class B {
public function test() {
echo 'B::test()';
}
public function test1() {
echo 'B::test1()';
}
}
class C extends B{
use A;
public function test() {
echo 'c::test()';
}
}
$c = new C();
$c->test(); //c::test()
$c->test1(); //A::test1()
(3)多个Trait冲突问题
如果没有解决冲突,会产生致命错误;
可用insteadof来明确使用冲突中哪一个方法;
可用as操作符将其中一个冲突方法另起名;
trait A {
public function test() {
echo 'A::test()';
}
}
trait B {
public function test() {
echo 'B::test()';
}
}
class C {
use A,B {
B::test insteadof A;
B::test as t;
}
}
$c = new C();
$c->test(); //B::test()
$c->t(); //B::test() 可以用as另起名
(4)as可用来修改方法访问控制
trait HelloWorld {
public function sayHello () {
echo 'Hello World!' ;
}
}
// 修改 sayHello 的访问控制
class A {
use HelloWorld { sayHello as protected; }
}
// 给方法一个改变了访问控制的别名
// 原版 sayHello 的访问控制则没有发生变化
class B {
use HelloWorld { sayHello as private myPrivateHello ; }
}
$b = new A();
$b->sayHello(); //Fatal error: Call to protected method A::sayHello() from context ''
(5)Trait中使用Trait
trait A {
public function test1() {
echo 'test1';
}
}
trait B {
public function test2() {
echo 'test2';
}
}
trait C {
use A,B;
}
class D {
use C;
}
$d = new D();
$d->test2(); //test2
(6)Trait支持抽象方法、支持静态方法、不可以直接定义静态变量,但静态变量可被trait方法引用。
trait A {
public function test1() {
static $a = 0;
$a++;
echo $a;
}
abstract public function test2(); //可定义抽象方法
}
class B {
use A;
public function test2() {
}
}
$b = new B();
$b->test1(); //1
$b->test1(); //2
(7)Trait可定义属性,但类中不能定义同样名称属性
trait A {
public $test1;
}
class B {
use A;
public $test2;
}
接着看
trait Drive {
public $carName = 'trait';
public function driving() {
echo "driving {$this->carName}\n";
}
}
class Person {
public function eat() {
echo "eat\n";
}
}
class Student extends Person {
use Drive;
public function study() {
echo "study\n";
}
}
$student = new Student();
$student->study();
$student->eat();
$student->driving();
输出结果如下:
study
eat
driving trait
上面的例子中,Student类通过继承Person,有了eat方法,通过组合Drive,有了driving方法和属性carName。
如果Trait、基类和本类中都存在某个同名的属性或者方法,最终会保留哪一个呢?通过下面的代码测试一下:
trait Drive {
public function hello() {
echo "hello drive\n";
}
public function driving() {
echo "driving from drive\n";
}
}
class Person {
public function hello() {
echo "hello person\n";
}
public function driving() {
echo "driving from person\n";
}
}
class Student extends Person {
use Drive;
public function hello() {
echo "hello student\n";
}
}
$student = new Student();
$student->hello();
$student->driving();
输出结果如下:
hello student
driving from drive
因此得出结论:当方法或属性同名时,当前类中的方法会覆盖 trait的 方法,而 trait 的方法又覆盖了基类中的方法。
如果要组合多个Trait,通过逗号分隔 Trait名称:
use Trait1, Trait2;
如果多个Trait中包含同名方法或者属性时,会怎样呢?答案是当组合的多个Trait包含同名属性或者方法时,需要明确声明解决冲突,否则会产生一个致命错误。
trait Trait1 {
public function hello() {
echo "Trait1::hello\n";
}
public function hi() {
echo "Trait1::hi\n";
}
}
trait Trait2 {
public function hello() {
echo "Trait2::hello\n";
}
public function hi() {
echo "Trait2::hi\n";
}
}
class Class1 {
use Trait1, Trait2;
}
输出结果如下:
PHP Fatal error: Trait method hello has not been applied, because there are collisions with other trait methods on Class1 in ~/php54/trait_3.php on line 20
使用insteadof和as操作符来解决冲突,insteadof是使用某个方法替代另一个,而as是给方法取一个别名,具体用法请看代码:
trait Trait1 {
public function hello() {
echo "Trait1::hello\n";
}
public function hi() {
echo "Trait1::hi\n";
}
}
trait Trait2 {
public function hello() {
echo "Trait2::hello\n";
}
public function hi() {
echo "Trait2::hi\n";
}
}
class Class1 {
use Trait1, Trait2 {
Trait2::hello insteadof Trait1;
Trait1::hi insteadof Trait2;
}
}
class Class2 {
use Trait1, Trait2 {
Trait2::hello insteadof Trait1;
Trait1::hi insteadof Trait2;
Trait2::hi as hei;
Trait1::hello as hehe;
}
}
$Obj1 = new Class1();
$Obj1->hello();
$Obj1->hi();
echo "\n";
$Obj2 = new Class2();
$Obj2->hello();
$Obj2->hi();
$Obj2->hei();
$Obj2->hehe();
输出结果如下:
Trait2::hello
Trait1::hi
Trait2::hello
Trait1::hi
Trait2::hi
Trait1::hello
as关键词还有另外一个用途,那就是修改方法的访问控制:
trait Hello {
public function hello() {
echo "hello,trait\n";
}
}
class Class1 {
use Hello {
hello as protected;
}
}
class Class2 {
use Hello {
Hello::hello as private hi;
}
}
$Obj1 = new Class1();
$Obj1->hello(); # 报致命错误,因为hello方法被修改成受保护的
$Obj2 = new Class2();
$Obj2->hello(); # 原来的hello方法仍然是公共的
$Obj2->hi(); # 报致命错误,因为别名hi方法被修改成私有的
Trait 也能组合Trait,Trait中支持抽象方法、静态属性及静态方法,测试代码如下:
trait Hello {
public function sayHello() {
echo "Hello\n";
}
}
trait World {
use Hello;
public function sayWorld() {
echo "World\n";
}
abstract public function getWorld();
public function inc() {
static $c = 0;
$c = $c + 1;
echo "$c\n";
}
public static function doSomething() {
echo "Doing something\n";
}
}
class HelloWorld {
use World;
public function getWorld() {
return 'get World';
}
}
$Obj = new HelloWorld();
$Obj->sayHello();
$Obj->sayWorld();
echo $Obj->getWorld() . "\n";
HelloWorld::doSomething();
$Obj->inc();
$Obj->inc();
输出结果如下:
Hello
World
get World
Doing something
1
2

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1382
1382
 52
52
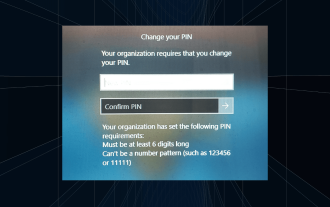 Lösung: Ihre Organisation verlangt von Ihnen, dass Sie Ihre PIN ändern
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
Lösung: Ihre Organisation verlangt von Ihnen, dass Sie Ihre PIN ändern
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
Auf dem Anmeldebildschirm wird die Meldung „Ihre Organisation hat Sie gebeten, Ihre PIN zu ändern“ angezeigt. Dies geschieht, wenn das PIN-Ablauflimit auf einem Computer erreicht wird, der organisationsbasierte Kontoeinstellungen verwendet und die Kontrolle über persönliche Geräte hat. Wenn Sie Windows jedoch über ein persönliches Konto einrichten, sollte die Fehlermeldung im Idealfall nicht erscheinen. Obwohl dies nicht immer der Fall ist. Die meisten Benutzer, die auf Fehler stoßen, melden dies über ihre persönlichen Konten. Warum fordert mich meine Organisation auf, meine PIN unter Windows 11 zu ändern? Es ist möglich, dass Ihr Konto mit einer Organisation verknüpft ist. Ihr primärer Ansatz sollte darin bestehen, dies zu überprüfen. Die Kontaktaufnahme mit Ihrem Domain-Administrator kann hilfreich sein! Darüber hinaus können falsch konfigurierte lokale Richtlinieneinstellungen oder falsche Registrierungsschlüssel Fehler verursachen. Im Augenblick
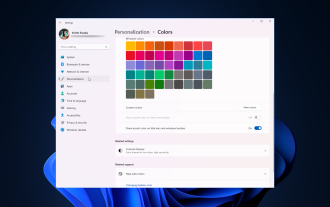 So passen Sie die Fensterrahmeneinstellungen unter Windows 11 an: Farbe und Größe ändern
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
So passen Sie die Fensterrahmeneinstellungen unter Windows 11 an: Farbe und Größe ändern
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Windows 11 bringt frisches und elegantes Design in den Vordergrund; die moderne Benutzeroberfläche ermöglicht es Ihnen, feinste Details, wie zum Beispiel Fensterränder, zu personalisieren und zu ändern. In diesem Leitfaden besprechen wir Schritt-für-Schritt-Anleitungen, die Ihnen dabei helfen, eine Umgebung zu erstellen, die Ihrem Stil im Windows-Betriebssystem entspricht. Wie ändere ich die Fensterrahmeneinstellungen? Drücken Sie +, um die Einstellungen-App zu öffnen. WindowsIch gehe zu Personalisierung und klicke auf Farbeinstellungen. Farbänderung Fensterränder Einstellungen Fenster 11" Breite="643" Höhe="500" > Suchen Sie die Option Akzentfarbe auf Titelleiste und Fensterrändern anzeigen und schalten Sie den Schalter daneben um. Um Akzentfarben im Startmenü und in der Taskleiste anzuzeigen Um die Designfarbe im Startmenü und in der Taskleiste anzuzeigen, aktivieren Sie „Design im Startmenü und in der Taskleiste anzeigen“.
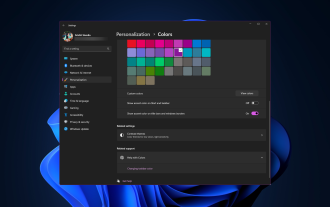 Wie ändere ich die Farbe der Titelleiste unter Windows 11?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Wie ändere ich die Farbe der Titelleiste unter Windows 11?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Standardmäßig hängt die Farbe der Titelleiste unter Windows 11 vom gewählten Dunkel-/Hell-Design ab. Sie können es jedoch in jede gewünschte Farbe ändern. In diesem Leitfaden besprechen wir Schritt-für-Schritt-Anleitungen für drei Möglichkeiten, wie Sie Ihr Desktop-Erlebnis ändern und personalisieren können, um es optisch ansprechend zu gestalten. Ist es möglich, die Farbe der Titelleiste von aktiven und inaktiven Fenstern zu ändern? Ja, Sie können die Farbe der Titelleiste aktiver Fenster mit der App „Einstellungen“ ändern, oder Sie können die Farbe der Titelleiste inaktiver Fenster mit dem Registrierungseditor ändern. Um diese Schritte zu lernen, fahren Sie mit dem nächsten Abschnitt fort. Wie ändere ich die Farbe der Titelleiste in Windows 11? 1. Drücken Sie in der App „Einstellungen“ +, um das Einstellungsfenster zu öffnen. WindowsIch gehe zu „Personalisierung“ und dann
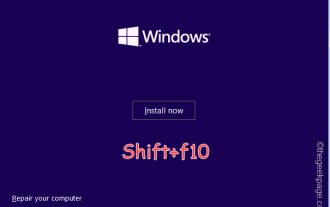 OOBELANGUAGE-Fehlerprobleme bei der Reparatur von Windows 11/10
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
OOBELANGUAGE-Fehlerprobleme bei der Reparatur von Windows 11/10
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Wird auf der Windows Installer-Seite „Ein Problem ist aufgetreten“ zusammen mit der Anweisung „OOBELANGUAGE“ angezeigt? Aufgrund solcher Fehler bricht die Installation von Windows manchmal ab. OOBE bedeutet Out-of-the-Box-Erlebnis. Wie aus der Fehlermeldung hervorgeht, handelt es sich hierbei um ein Problem im Zusammenhang mit der OOBE-Sprachauswahl. Sie müssen sich keine Sorgen machen, Sie können dieses Problem durch eine geschickte Bearbeitung der Registrierung über den OOBE-Bildschirm selbst lösen. Schnelllösung – 1. Klicken Sie unten in der OOBE-App auf die Schaltfläche „Wiederholen“. Dadurch wird der Prozess ohne weitere Probleme fortgesetzt. 2. Verwenden Sie den Netzschalter, um das Herunterfahren des Systems zu erzwingen. Nach dem Neustart des Systems sollte OOBE fortgesetzt werden. 3. Trennen Sie das System vom Internet. Schließen Sie alle Aspekte von OOBE im Offline-Modus ab
 So aktivieren oder deaktivieren Sie die Vorschau von Miniaturansichten in der Taskleiste unter Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
So aktivieren oder deaktivieren Sie die Vorschau von Miniaturansichten in der Taskleiste unter Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Miniaturansichten in der Taskleiste können Spaß machen, aber auch ablenken oder stören. Wenn man bedenkt, wie oft Sie mit der Maus über diesen Bereich fahren, haben Sie möglicherweise ein paar Mal versehentlich wichtige Fenster geschlossen. Ein weiterer Nachteil besteht darin, dass es mehr Systemressourcen verbraucht. Wenn Sie also nach einer Möglichkeit suchen, ressourceneffizienter zu arbeiten, zeigen wir Ihnen, wie Sie es deaktivieren können. Wenn Ihre Hardware-Spezifikationen jedoch dafür geeignet sind und Ihnen die Vorschau gefällt, können Sie sie aktivieren. Wie aktiviere ich die Miniaturvorschau der Taskleiste in Windows 11? 1. Tippen Sie in der App „Einstellungen“ auf die Taste und klicken Sie auf „Einstellungen“. Klicken Sie unter Windows auf „System“ und wählen Sie „Info“. Klicken Sie auf Erweiterte Systemeinstellungen. Navigieren Sie zur Registerkarte „Erweitert“ und wählen Sie unter „Leistung“ die Option „Einstellungen“ aus. Wählen Sie „Visuelle Effekte“
 Anleitung zur Anzeigeskalierung unter Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Anleitung zur Anzeigeskalierung unter Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Wir alle haben unterschiedliche Vorlieben, wenn es um die Anzeigeskalierung unter Windows 11 geht. Manche Leute mögen große Symbole, andere mögen kleine Symbole. Wir sind uns jedoch alle einig, dass die richtige Skalierung wichtig ist. Eine schlechte Schriftartenskalierung oder eine Überskalierung von Bildern kann bei der Arbeit ein echter Produktivitätskiller sein. Sie müssen daher wissen, wie Sie sie anpassen können, um die Fähigkeiten Ihres Systems optimal zu nutzen. Vorteile des benutzerdefinierten Zooms: Dies ist eine nützliche Funktion für Personen, die Schwierigkeiten haben, Text auf dem Bildschirm zu lesen. Es hilft Ihnen, mehr gleichzeitig auf dem Bildschirm zu sehen. Sie können benutzerdefinierte Erweiterungsprofile erstellen, die nur für bestimmte Monitore und Anwendungen gelten. Kann dazu beitragen, die Leistung von Low-End-Hardware zu verbessern. Dadurch haben Sie mehr Kontrolle darüber, was auf Ihrem Bildschirm angezeigt wird. So verwenden Sie Windows 11
 10 Möglichkeiten, die Helligkeit unter Windows 11 anzupassen
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
10 Möglichkeiten, die Helligkeit unter Windows 11 anzupassen
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Die Bildschirmhelligkeit ist ein wesentlicher Bestandteil der Nutzung moderner Computergeräte, insbesondere wenn Sie über einen längeren Zeitraum auf den Bildschirm schauen. Es hilft Ihnen, die Belastung Ihrer Augen zu reduzieren, die Lesbarkeit zu verbessern und Inhalte einfach und effizient anzuzeigen. Abhängig von Ihren Einstellungen kann es jedoch manchmal schwierig sein, die Helligkeit zu verwalten, insbesondere unter Windows 11 mit den neuen Änderungen an der Benutzeroberfläche. Wenn Sie Probleme beim Anpassen der Helligkeit haben, finden Sie hier alle Möglichkeiten, die Helligkeit unter Windows 11 zu verwalten. So ändern Sie die Helligkeit unter Windows 11 [10 Möglichkeiten erklärt] Benutzer eines einzelnen Monitors können die folgenden Methoden verwenden, um die Helligkeit unter Windows 11 anzupassen. Hierzu zählen sowohl Desktop-Systeme mit einem einzelnen Monitor als auch Laptops. Lasst uns beginnen. Methode 1: Verwenden Sie das Action Center. Das Action Center ist zugänglich
 So beheben Sie den Aktivierungsfehlercode 0xc004f069 in Windows Server
Jul 22, 2023 am 09:49 AM
So beheben Sie den Aktivierungsfehlercode 0xc004f069 in Windows Server
Jul 22, 2023 am 09:49 AM
Der Aktivierungsprozess unter Windows nimmt manchmal eine plötzliche Wendung und zeigt eine Fehlermeldung mit diesem Fehlercode 0xc004f069 an. Obwohl der Aktivierungsprozess online erfolgt, kann dieses Problem bei einigen älteren Systemen mit Windows Server auftreten. Führen Sie diese ersten Prüfungen durch. Wenn sie Ihnen bei der Aktivierung Ihres Systems nicht weiterhelfen, fahren Sie mit der Hauptlösung fort, um das Problem zu beheben. Problemumgehung – Schließen Sie die Fehlermeldung und das Aktivierungsfenster. Starten Sie dann Ihren Computer neu. Wiederholen Sie den Windows-Aktivierungsprozess noch einmal von Grund auf. Fix 1 – Aktivierung über das Terminal. Aktivieren Sie das Windows Server Edition-System über das CMD-Terminal. Stufe – 1 Überprüfen Sie die Windows Server-Version. Sie müssen überprüfen, welchen W-Typ Sie verwenden




