
Bubble Sort ist einer der einfachsten Sortieralgorithmen in der Informatik. Benannt nach der Art und Weise, wie kleinere Elemente bei jeder Iteration an den Anfang der Liste „sprudeln“, ist es ein hervorragendes Werkzeug, um die Grundlagen von Sortieralgorithmen zu vermitteln. Obwohl es für große Datenmengen nicht besonders effizient ist, ist es aufgrund seiner Einfachheit ein guter Ausgangspunkt für das Verständnis der Funktionsweise von Sortieralgorithmen.
Bubble Sort funktioniert, indem es wiederholt durch die Liste geht, benachbarte Elemente vergleicht und sie vertauscht, wenn sie in der falschen Reihenfolge sind. Dieser Vorgang wird wiederholt, bis keine weiteren Swaps mehr erforderlich sind, was anzeigt, dass die Liste sortiert ist.
Hier ist eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Anleitung:
Lassen Sie uns diesen Prozess visualisieren:
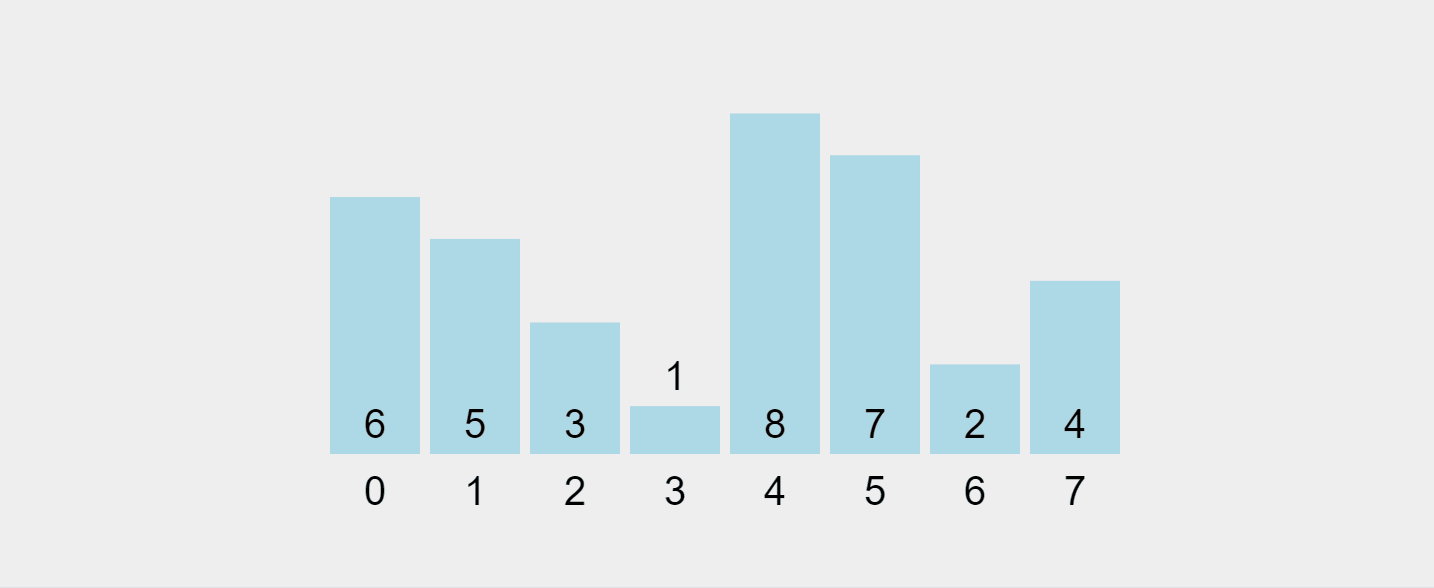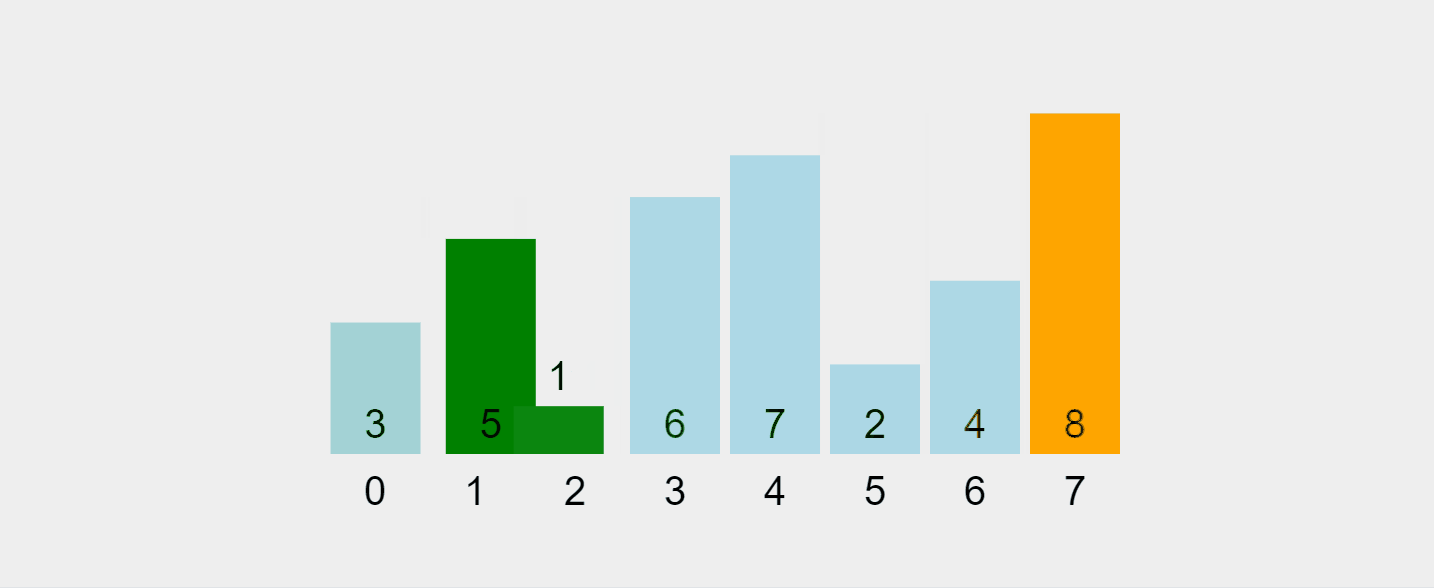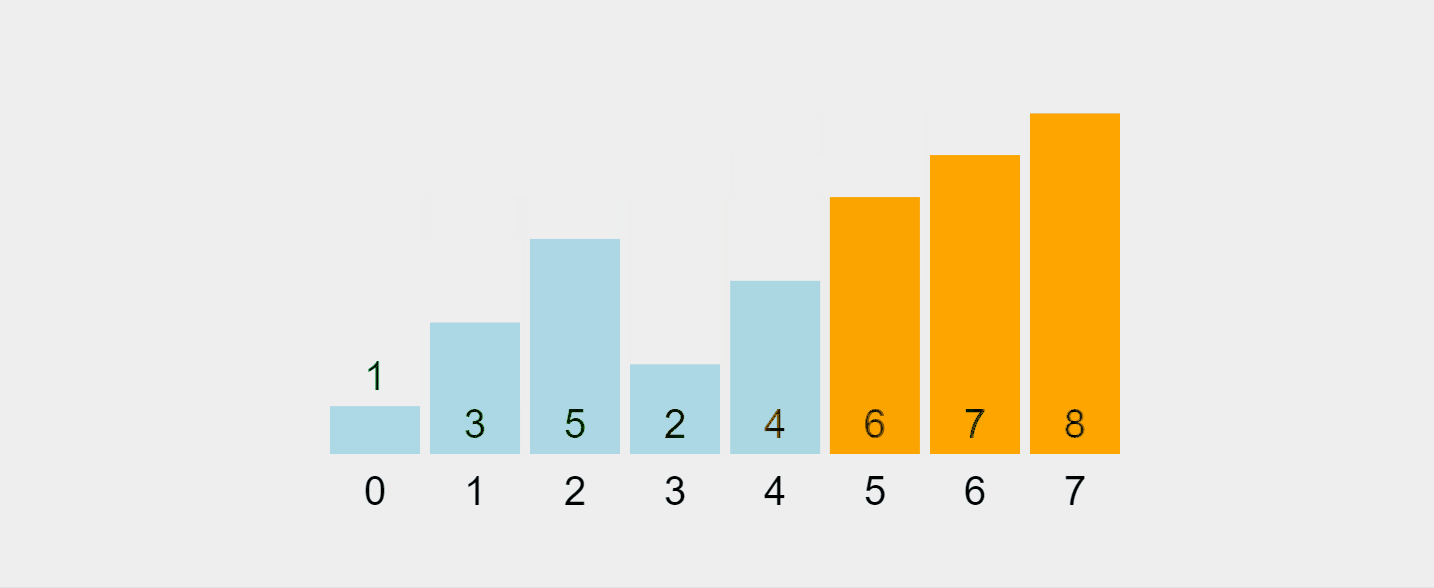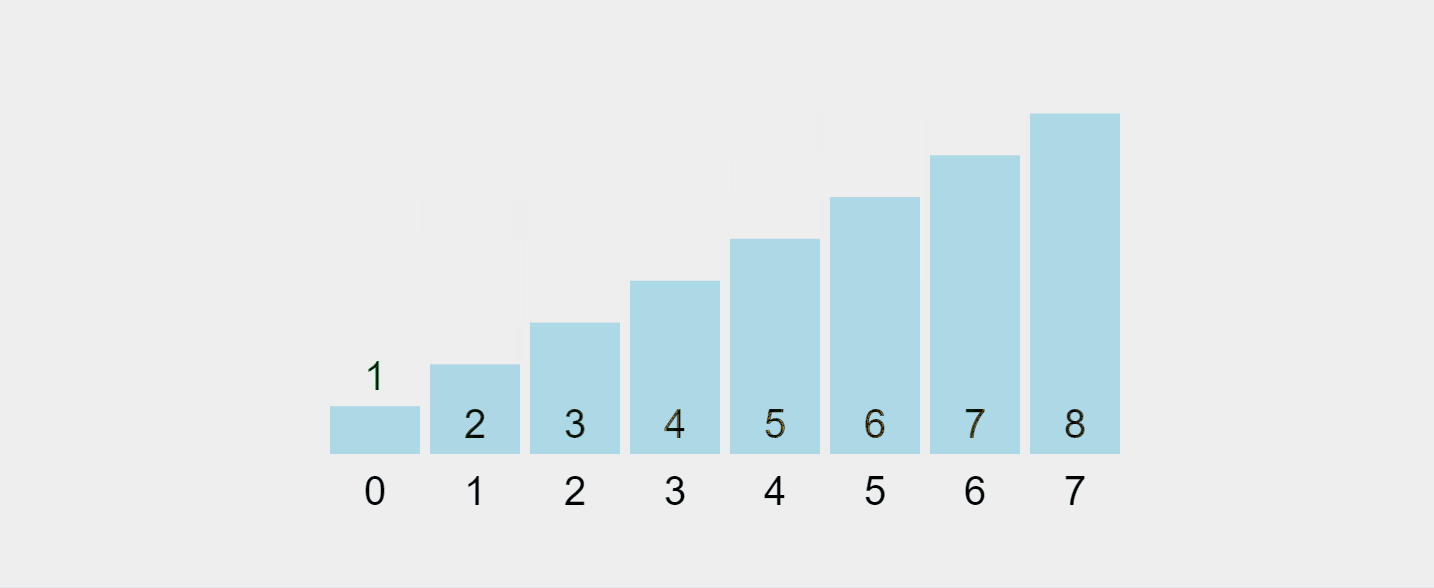
Aufgezeichnetes GIF von https://visualgo.net/en/sorting
Untersuchen wir drei Implementierungen von Bubble Sort in JavaScript, jeweils mit zunehmendem Optimierungsgrad.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
}
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Diese grundlegende Implementierung verwendet verschachtelte Schleifen, um benachbarte Elemente zu vergleichen und auszutauschen. Die äußere Schleife stellt sicher, dass wir genügend Durchläufe durch das Array machen, während die innere Schleife die Vergleiche und Swaps durchführt.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Diese Version führt ein Swap-Flag ein, um zu überprüfen, ob in einem Durchgang Swaps vorgenommen wurden. Wenn keine Vertauschungen stattfinden, ist die Liste bereits sortiert und wir können die Schleife frühzeitig verlassen.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
// Note: We reduce the upper bound by i in each pass
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1 - i; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Diese letzte Optimierung reduziert den Bereich der inneren Schleife in jedem Durchgang um i. Dies liegt daran, dass nach jedem Durchgang das größte unsortierte Element an seine korrekte Position am Ende des Arrays „aufsteigt“.
Die Leistungsmerkmale von Bubble Sort sind wie folgt:
Zeitkomplexität:
Raumkomplexität: O(1) – Bubble Sort ist ein In-Place-Sortieralgorithmus, der nur eine konstante Menge an zusätzlichem Speicher benötigt.
Im Vergleich zu fortgeschritteneren Algorithmen wie Quick Sort (durchschnittliches O(n log n)) oder Merge Sort (O(n log n)) ist Bubble Sort aufgrund seiner quadratischen Zeitkomplexität für große Datensätze ineffizient.
Vorteile:
Nachteile:
Cocktail Sort, auch bekannt als Cocktail Shake Sort oder Bidirektionale Bubble Sort, ist eine verbesserte Version von Bubble Sort. Es durchläuft die Liste in beide Richtungen und trägt so dazu bei, Elemente effizienter an ihre richtigen Positionen zu verschieben.
Cocktail Sort is particularly useful in cases where the array has elements that are initially large at the beginning and small at the end, as it can reduce the total number of passes needed compared to traditional Bubble Sort.
Here's a visualization of Cocktail Sort:
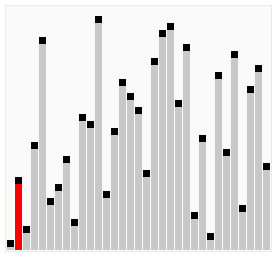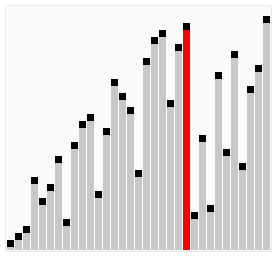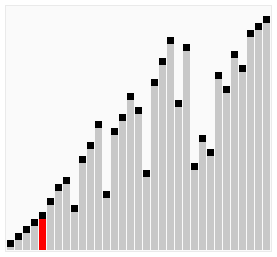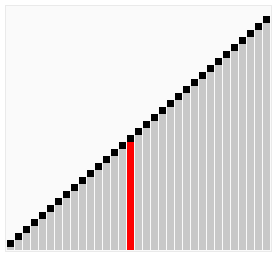
Visual from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cocktail_shaker_sort
function cocktailSort(list) {
let swapped;
// The do...while loop ensures the sorting continues until no swaps are needed
do {
// Reset the swapped flag at the beginning of each complete iteration
swapped = false;
// First pass: left to right (like standard bubble sort)
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in the first pass, the array is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the do...while loop early
}
// Reset the swapped flag for the second pass
swapped = false;
// Second pass: right to left (this is what makes it "cocktail" sort)
for (let i = list.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// The loop will continue if any swaps occurred in either pass
} while (swapped);
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
This implementation alternates between forward and backward passes through the list, potentially reducing the number of iterations needed to sort the array.
While Bubble Sort isn't typically used in production environments for large-scale applications, it can still find use in certain scenarios:
Bubble Sort, despite its inefficiencies with large datasets, offers valuable insights into the world of sorting algorithms and algorithm analysis. Its straightforward approach makes it an excellent teaching tool for beginners in computer science.
Key takeaways are:
While you're unlikely to use Bubble Sort in production code for large-scale applications, the principles behind it are fundamental to many algorithms. The process of optimizing Bubble Sort teaches valuable lessons about algorithm improvement, serving as a stepping stone to more advanced computational problem-solving.
When it comes to algorithms, there's rarely a one-size-fits-all solution. The best algorithm for a given task depends on the specific requirements, constraints, and characteristics of your data. Bubble Sort, with all its limitations, still has its place in this diverse algorithmic ecosystem.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonEine Reise durch Algorithmen mit Javascript – Bubble Sort. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
 Welche Zeichensoftware gibt es?
Welche Zeichensoftware gibt es?
 Funktionsfunktionsverwendung
Funktionsfunktionsverwendung
 Anrufwarnung des Nationalen Zentrums für Betrugsbekämpfung
Anrufwarnung des Nationalen Zentrums für Betrugsbekämpfung
 So kaufen und verkaufen Sie Bitcoin auf Okex
So kaufen und verkaufen Sie Bitcoin auf Okex
 Warum verschwinden die Wörter nach der Worteingabe?
Warum verschwinden die Wörter nach der Worteingabe?
 In der Sprache C gibt es mehrere Ausgabe- und Eingabefunktionen
In der Sprache C gibt es mehrere Ausgabe- und Eingabefunktionen
 Was ist der Unterschied zwischen USB-C und TYPE-C?
Was ist der Unterschied zwischen USB-C und TYPE-C?
 So zentrieren Sie ein Div in CSS
So zentrieren Sie ein Div in CSS




