
1. Leinwandzeichnung
Schritte
Leinwandelement hinzufügen, ID und Bereich definieren
Leinwand in js abrufen Elemente
erhalten die 2D-Zeichenumgebung über die Methode getContext()
zeichnen Grafiken über verschiedene Funktionen
Koordinatenpositionierung
Die Zeichnungspositionierung basiert auf der oberen linken Ecke der Leinwand als (0,0)-Ursprung
Zeichne eine gerade Linie
moveTo(): gibt den Startpunkt an
lineTo(): zeichnet eine gerade Linie vom Startpunkt zu den angegebenen Koordinaten
Stroke(): implementiert die Funktion zum Zeichnen einer geraden Linie
fill(): implementiert die Füllfunktion
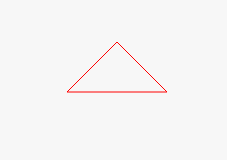
Beispiel: Zeichne ein Dreieck
HTML-Code
<body> <canvas id="canvas"></canvas> </body>
JS-Code
window.onload = function(){ var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
canvas.width = 800;
canvas.height = 800; var context = canvas.getContext('2d');
context.strokeStyle = "red";
context.moveTo(100, 100);
context.lineTo(200, 100);
context.lineTo(150,50);
context.lineTo(100,100);
context.stroke();
};
Rechteck zeichnen
fillStyle(): Legt die Füllfarbe des Rechtecks fest.
fillRect(x,y,width,height).
StrokeStyle(): Legt die Umrissfarbe des Rechtecks fest.
StrokeRect(x,y,width,height).
Zeichnen Sie einen Kreis (Bogen)
beginPath(): Beginnen Sie mit dem Zeichnen der Route
arc(x,y,radius,startAngle,endAngle,gegen den Uhrzeigersinn)
Legen Sie den Mittelpunkt, den Radius, den Startwinkel, den Endwinkel und die Zeichenrichtung des Zeichnens fest.
Bezier-Kurve
Quadratische Bezier-Kurve
quadraticCurveTo(cp1x,cp1y,x,y)
cp1x, cp1y repräsentiert die Koordinaten eines Kontrollpunkts; x, y repräsentiert die Koordinaten des Endpunkts.
Kubische Bezier-Kurve
bezierCurveTo(cp1x,cp1y,cp2x,cp2y,x,y)
cp1x,cp1y und cp2x und cp2y repräsentieren jeweils
zwei Kontrollpunkte.
Beispiel 1: Zeichne einen fünfzackigen Stern
window.onload = function() { var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas"); var context = canvas.getContext('2d');
drawStar(context, 120, 120, 80, 30, 10, "yellow", 0);
} function drawStar(context, x, y, R, r, width, color, rotation) {
context.beginPath(); for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
context.lineTo(Math.cos((18 + i * 72 - rotation) / 180 * Math.PI) * R + x, -Math.sin((18 + i * 72 - rotation) / 180 * Math.PI) * R + y);
context.lineTo(Math.cos((54 + i * 72 - rotation) / 180 * Math.PI) * r + x, -Math.sin((54 + i * 72 - rotation) / 180 * Math.PI) * r + y);
}
context.closePath();
context.lineWidth = width;
context.fillStyle = color;
context.fill();
}
Beispiel 2: Zeichne das BMW-Logo
window.onload = function() { var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
canvas.width = 800;
canvas.height = 800; var context = canvas.getContext('2d'); //圆心坐标x,y 内圆半径r 外圆半径R var x = 100; var y = 100; var r = 100; var R = r + 50; var colors = Array("#87CEFA", "#FAFAFA", "#000");
context.beginPath();
context.translate(100, 100);
context.arc(x, y, R, 0, Math.PI * 2);
line_gra = context.createLinearGradient(-10, -10,20, 50);
line_gra.addColorStop(0, "#ddd");
line_gra.addColorStop(1, "#262626");
context.lineWidth = 3;
context.strokeStyle = "#000";
context.fillStyle = line_gra;
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
context.fill();
drawBigRound(context, x, y, r, 53, "#ADD8E6", 7);
drawBm(context, x, y, r, colors);
drawBigRound(context, x, y, r, 3, "#9FB6CD", 5);
context.beginPath();
context.fillStyle = "#fff";
context.font = "bold 40px verdana";
context.fillText("M", 80, -10);
context.rotate(Math.PI / 6);
context.fillText("W", 125, -75);
context.rotate(-(Math.PI / 2));
context.fillText("B", 0, 35);
context.restore();
} function drawBm(context, x, y, r, colors) { var color; for (var i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(x, y);
context.arc(x, y, r, Math.PI * i / 2, Math.PI * (i + 1) / 2); if (i == 0 || i == 2) {
color = colors[0];
} else {
color = colors[1];
}
context.fillStyle = color;
context.lineWidth = 2;
context.strokeStyle = colors[2];
context.closePath();
context.fill();
context.stroke();
}
} function drawBigRound(context, x, y, r, addr, color, lineWidth) {
context.beginPath();
context.arc(x, y, r + addr, 0, Math.PI * 2);
context.lineWidth = lineWidth;
context.strokeStyle = color;
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
}
2.CSS3 Shadow Box-Shadow
Box-Shadow: H-Shadow V-Shadow Blur Farbeinsatz verteilen ;
H-Schatten erforderlich. Die Position des horizontalen Schattens. Negative Werte sind erlaubt.
V-Shadow erforderlich. Die Position des vertikalen Schattens. Negative Werte sind erlaubt.
unschärfe Optional. Unscharfe Distanz.
Spread Optional. Die Größe des Schattens.
Farbe optional. Die Farbe des Schattens. Siehe CSS-Farbwerte.
Einsatz optional. Ändern Sie den äußeren Schatten (Anfang) in den inneren Schatten.
3.CSS3-Transformationsattribut
transform: none|transform-functions;
transform :rotate(): Drehung, Grad bedeutet Grad
transform: rotate(-10deg);
transform:skew(): Neigung
transform:skew(20deg);
transform:scale(): Skalierung, 2-fach in x-Richtung, 1,5-fach in y-Richtung
transform: scale(2, 1.5);
transformation :translate(): Übersetzung, 120 Pixel in x-Richtung, 10 Pixel in y-Richtung
transform:translate(120px,10px);
4. CSS3-Übersetzungseigenschaft
Übergang: Zeitdauer der Eigenschaft Funktionsverzögerung ;
transition-property gibt den Namen der CSS-Eigenschaft an, die den Übergangseffekt festlegt.
transition-duration gibt an, wie viele Sekunden oder Millisekunden es dauert, bis der Übergangseffekt abgeschlossen ist.
transition-timing-function 规定速度效果的速度曲线。
transition-delay 定义过渡效果何时开始。
div { width:100px; transition: width 2s; -moz-transition: width 2s; /* Firefox 4 */ -webkit-transition: width 2s; /* Safari 和 Chrome */ -o-transition: width 2s; /* Opera */ } Was sind die Produktionsmethoden der HTML5-Animationsproduktion?
Was sind die Produktionsmethoden der HTML5-Animationsproduktion?
 Der Unterschied zwischen HTML und HTML5
Der Unterschied zwischen HTML und HTML5
 So verwenden Sie insertBefore in Javascript
So verwenden Sie insertBefore in Javascript
 Die zehn besten Börsen für digitale Währungen
Die zehn besten Börsen für digitale Währungen
 So beheben Sie Zugriffsverletzungen
So beheben Sie Zugriffsverletzungen
 Welche Datentypen gibt es?
Welche Datentypen gibt es?
 Linux-Befehl „Datei suchen'.
Linux-Befehl „Datei suchen'.
 Welche Methoden gibt es, um eine Operatorüberladung in der Go-Sprache zu implementieren?
Welche Methoden gibt es, um eine Operatorüberladung in der Go-Sprache zu implementieren?




