
Geschichte ist interessant, nicht wahr? In früheren HTML-Versionen konnten wir den Browserverlauf nur sehr begrenzt manipulieren. Wir können hin und her gehen, welche Methoden wir verwenden können, aber das ist alles, was wir tun können.
Mit der Verlaufs-API von HTML 5 können wir jedoch den Verlauf des Browsers besser kontrollieren. Beispiel: Wir können einen Datensatz zur Liste der Verlaufseinträge hinzufügen oder die URL der Adressleiste aktualisieren, wenn keine Aktualisierung erfolgt.
Warum die History API einführen?
In diesem Artikel werden wir den Ursprung der History API in HTML 5 verstehen. Zuvor haben wir häufig Hashwerte verwendet, um Seiteninhalte zu ändern, insbesondere solche, die für die Seite besonders wichtig waren. Da keine Aktualisierung erfolgt, ist es nicht möglich, die URL einer Einzelseitenanwendung zu ändern. Wenn Sie außerdem den Hashwert einer URL ändern, hat dies keine Auswirkungen auf den Browserverlauf.
Dank der History-API von HTML 5 lassen sich diese jedoch problemlos implementieren. Da Einzelseitenanwendungen jedoch nicht unbedingt Hash-Werte verwenden, sind möglicherweise zusätzliche Entwicklungsskripte erforderlich. Es ermöglicht uns auch, neue Anwendungen auf SEO-freundliche Weise zu erstellen. Darüber hinaus wird die Bandbreite reduziert, aber wie kann man das beweisen?
In diesem Artikel werde ich die History-API verwenden, um eine einseitige Anwendung zu entwickeln, um die oben genannten Probleme zu beweisen.
Das bedeutet auch, dass ich zunächst die nötigen Ressourcen auf der Homepage laden muss. Von nun an lädt die Seite nur noch den benötigten Inhalt. Mit anderen Worten: Die Anwendung lädt zu Beginn nicht den gesamten Inhalt. Sie wird geladen, wenn der zweite Anwendungsinhalt angefordert wird.
Beachten Sie, dass Sie einige serverseitige Codierungen durchführen müssen, um nur einen Teil der Ressource und nicht den gesamten Seiteninhalt bereitzustellen.
Browser-Unterstützung
Zum Zeitpunkt des Schreibens dieses Artikels ist die Unterstützung für die History API durch die wichtigsten Browser sehr gut. Sie können hier klicken, um den Supportstatus anzuzeigen Wenn Sie einen Browser unterstützen und verwenden, empfiehlt es sich immer, die Unterstützung für bestimmte Funktionen zu erkennen.
Um festzustellen, ob der Browser diese API unterstützt, indem Sie die Methode ändern, können Sie die folgende Codezeile zur Überprüfung verwenden:
return !!(window.history && history.pushState);
Wenn Sie einen modernen Browser verwenden, können Sie Sie können den folgenden Code verwenden:
if (Modernizr.history) {
// History API Supported
}Wenn Ihr Browser die History API nicht unterstützt, können Sie stattdessen History.js verwenden.
Historie verwenden
HTML 5 bietet zwei neue Methoden:
1.history.pushState();
2.history.replaceState();
Beide Methoden ermöglichen es uns, den Verlauf hinzuzufügen und zu aktualisieren, sie funktionieren gleich und können die gleiche Anzahl von Parametern hinzufügen. Neben Methoden gibt es auch das Popstate-Ereignis. Im folgenden Artikel stellen wir vor, wie und wann das Popstate-Ereignis verwendet wird.
pushState() hat die gleichen Parameter wie replaceState(). Die Parameterbeschreibung lautet wie folgt:
state: speichert einen JSON-String und kann im Popstate-Ereignis verwendet werden.
Titel: Die meisten Browser unterstützen oder ignorieren diesen Parameter derzeit nicht.
URL: Jede gültige URL, die zum Aktualisieren der Adressleiste des Browsers verwendet wird Achten Sie darauf, ob die URL bereits in der Adressliste vorhanden ist. Darüber hinaus wird die Seite nicht neu geladen.
Der Hauptunterschied zwischen den beiden Methoden besteht darin: pushState() fügt einen neuen Eintrag zum Verlaufsstapel hinzu und replaceState() ersetzt den aktuellen Datensatzwert. Wenn Sie diesbezüglich immer noch verwirrt sind, veranschaulichen Sie den Unterschied anhand einiger Beispiele.
Angenommen, wir haben zwei Stapelblöcke, einen mit der Bezeichnung 1 und den anderen mit der Bezeichnung 2, und Sie haben einen dritten Stapelblock mit der Bezeichnung 3. Wenn pushState() ausgeführt wird, wird Stapelblock 3 zum vorhandenen Stapel hinzugefügt, sodass der Stapel über 3 Blockstapel verfügt.
Im gleichen hypothetischen Szenario wird Block 3 bei Ausführung von replaceState() auf dem Stapel von Block 2 platziert. Daher bleibt die Anzahl der Verlaufsdatensätze unverändert, d. h. pushState() erhöht die Anzahl der Verlaufsdatensätze um 1.
Das Vergleichsergebnis lautet wie folgt:
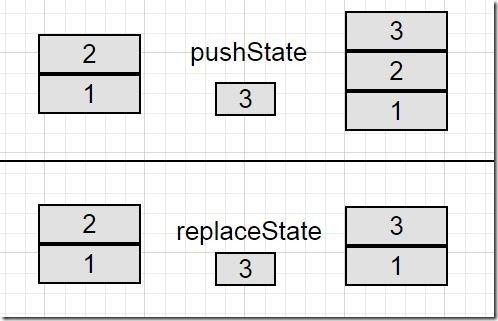
Um den Verlauf des Browsers zu steuern, haben wir an dieser Stelle die Ereignisse pushState() und replaceState() ignoriert. Aber vorausgesetzt, der Browser zählt viele fehlerhafte Datensätze, wird der Benutzer möglicherweise auf diese Seiten umgeleitet oder auch nicht. In diesem Fall treten unerwartete Probleme auf, wenn Benutzer die Vorwärts- und Zurück-Navigationsschaltflächen des Browsers verwenden.
Wenn wir jedoch pushState() und replaceState() für die Verarbeitung verwenden, können wir damit rechnen, dass das Popstate-Ereignis ausgelöst wird. Aber in Wirklichkeit ist dies nicht der Fall. Wenn Sie stattdessen den Sitzungsverlauf durchsuchen, unabhängig davon, ob Sie auf die Schaltflächen „Vorwärts“ oder „Zurück“ klicken oder die Methoden „history.go“ und „history.back“ verwenden, wird „popstate“ ausgelöst.
注意:在WebKit浏览器中,popstate事件在document的onload事件后触发,Firefox和IE没有这种行为。
Demo示例
HTML:
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li><a href="home.html" class="historyAPI">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="about.html" class="historyAPI">About</a></li>
<li><a href="contact.html" class="historyAPI">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="well">
Click on Links above to see history API usage using <code>pushState</code> method.
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="jumbotron" id="contentHolder">
<h1>Home!</h1>
<p>Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>JavaScript:
<script type="text/javascript">
jQuery('document').ready(function(){
jQuery('.historyAPI').on('click', function(e){
e.preventDefault();
var href = $(this).attr('href');
// Getting Content
getContent(href, true);
jQuery('.historyAPI').removeClass('active');
$(this).addClass('active');
});
});
// Adding popstate event listener to handle browser back button
window.addEventListener("popstate", function(e) {
// Get State value using e.state
getContent(location.pathname, false);
});
function getContent(url, addEntry) {
$.get(url)
.done(function( data ) {
// Updating Content on Page
$('#contentHolder').html(data);
if(addEntry == true) {
// Add History Entry using pushState
history.pushState(null, null, url);
}
});
}
</script>HTML 5中的History API 对Web应用有着很大的影响。为了更容易的创建有效率的、对SEO友好的单页面应用,它移除了对散列值的依赖。
 Was sind die Produktionsmethoden der HTML5-Animationsproduktion?
Was sind die Produktionsmethoden der HTML5-Animationsproduktion?
 Der Unterschied zwischen HTML und HTML5
Der Unterschied zwischen HTML und HTML5
 mintui
mintui
 Der Computer meldet, dass msvcr110.dll fehlt und wie man das Problem beheben kann
Der Computer meldet, dass msvcr110.dll fehlt und wie man das Problem beheben kann
 So lesen Sie Makrosteuerdaten in Javascript
So lesen Sie Makrosteuerdaten in Javascript
 Top 10 Währungsbörsen
Top 10 Währungsbörsen
 Soundkartentreiber für HP Notebooks
Soundkartentreiber für HP Notebooks
 Was bedeutet ICO?
Was bedeutet ICO?




