JavaScript位置与大小(1)之正确理解和运用与尺寸大小相关的DOM属性_javascript技巧
在web开发中,不可避免遇到要计算元素大小以及位置的问题,解决这类问题的方法是利用DOM提供的一些API结合兼容性处理来,所有内容大概分3篇左右的文章的来说明。本文作为第一篇,介绍DOM提供的与尺寸大小相关的DOM属性,提供一些兼容性处理的方法,并结合常见的场景说明如何正确运用这些属性。
1. 正确理解offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollWidth及相应的height属性
假设某一个元素的横纵向滚动条都拖动到最末端,则offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollWidth等属性相应的范围如下图所示:
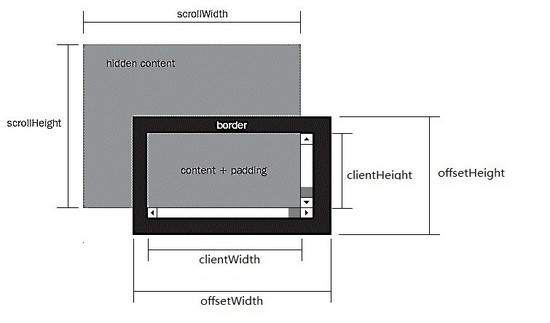
1)offsetWidth ,offsetHeight对应的是盒模型的宽度和高度,这两个值跟我们使用chrome审查元素时看到的尺寸一致:

2)scrollWidth,与scrollHeight对应的是滚动区域的宽度和高度 , 但是不包含滚动条的宽度!滚动区域由padding和content组成。
3)clientWidth,clientHeight对应的是盒模型除去边框后的那部分区域的宽度和高度,不包含滚动条的宽度。
4)任何一个DOM元素,都可以通过以下api快速得到offsetWidth,clientWidth,scrollWidh及相关的height属性:
//domE为一个DOM Html Element对象
domE.scrollWidth
domE.scrollHeight
domE.clientWidth
domE.clientHeight
domE.offsetWidth
domE.offsetHeight
//domE为一个DOM Html Element对象
domE.scrollWidth
domE.scrollHeight
domE.clientWidth
domE.clientHeight
domE.offsetWidth
domE.offsetHeight
5) 这些属性在现代浏览器包括pc和mobile上几乎没有兼容性问题,可以放心使用 。如果你想了解详细的兼容性规则,可以参考下面的2篇文章:
W3C DOM Compatibility – CSS Object Model View
cssom视图模式cssom-view-module相关整理与介绍
下面针对普通html元素,html根元素和body元素的以上相关属性一一测试,以便验证前面的结论,总结一些可在实际编码过程中直接使用的经验技巧。之所以要区分普通html元素,html根元素和body元素,是因为前面的理论,在html根元素和body元素会有一些怪异之处,需要小心处理。
注:
1、为了减少篇幅,测试贴出的代码不是完整的代码,但不影响学习参考,另外文中给出的测试结果都是在chrome(版本:45.0)下运行得出的,在测试结果有差异的情况下,还会给出IE9,IE10,IE11,firefox(版本:42.0),opera(版本:34.0)的测试结果,没有差异的会在测试结果中说明,不考虑IE8及以下。
2、safari因为设备限制暂不测试,另外它跟chrome内核相同,对标准支持的可靠性差不到哪去。
3、老版本的chrome,firefox,opera也因为设备的限制无法测试,不过从浏览器对标准的支持程度考虑,这三个浏览器在很早的版本开始对W3C的标准都是比较规矩的,加之这些浏览器更新换代的速度较快,现在市面上这些浏览器主流的版本也都是较新的。
4、由于不考虑IE8及以下,同时html现在都用html5,所以document.compatMode = ‘BackCompat' 的情况不考虑。不过尽管BackCompat模式是IE6类的浏览器引出的,但是对于chrome,firefox等也存在document.compatMode = ‘BackCompat' 的情况,比如下面的这个网页,你用chrome打开,并且在console中打印document.compatMode,你会发现它的值也是BackCompat(原因跟该页面用的是html4.0的dtd有关,如果换成html4.01的dtd就不会在chrome和firefox里出现该情况了):
http://samples.msdn.microsoft.com/workshop/samples/author/dhtml/refs/compatModeCompat.htm
更多关于compatMode的知识,你可以通过下面的几个资源学习:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Document/compatMode
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms533687(VS.85).aspx
http://www.cnblogs.com/uedt/archive/2010/09/21/1832402.html
测试一、验证普通html元素(非body及html根元素)的offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollWidth及相关height属性:
<style type="text/css">
html,
body {
margin: 0;
}
body {
padding: 100px;
}
.box {
overflow: scroll;
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
padding: 20px;
border: 10px solid #000;
margin: 0 auto;
box-sizing: content-box;
}
.box-2 {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box-2">...</div>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var boxE = document.querySelectorAll('.box')[0];
console.log('scrollWidth:' + boxE.scrollWidth);
console.log('scrollHeight:' + boxE.scrollHeight);
console.log('clientWidth:' + boxE.clientWidth);
console.log('clientHeight:' + boxE.clientHeight);
console.log('offsetWidth :' + boxE.offsetWidth);
console.log('offsetHeight:' + boxE.offsetHeight);
</script>
<styletype="text/css">
html,
body{
margin: 0;
}
body{
padding: 100px;
}
.box{
overflow: scroll;
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
padding: 20px;
border: 10px solid #000;
margin: 0 auto;
box-sizing: content-box;
}
.box-2{
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
<body>
<divclass="box">
<divclass="box-2">...</div>
</div>
</body>
<scripttype="text/javascript">
var boxE = document.querySelectorAll('.box')[0];
console.log('scrollWidth:' + boxE.scrollWidth);
console.log('scrollHeight:' + boxE.scrollHeight);
console.log('clientWidth:' + boxE.clientWidth);
console.log('clientHeight:' + boxE.clientHeight);
console.log('offsetWidth :' + boxE.offsetWidth);
console.log('offsetHeight:' + boxE.offsetHeight);
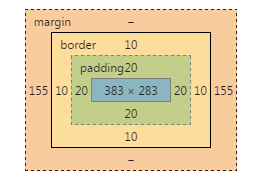
</script>在这个例子中,box元素有400*300的宽高,20px的padding和10px的border,chrome下对应的盒模型:

js执行结果:
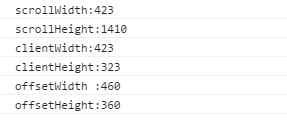
从盒模型与js执行结果可知:
1)offsetWidth与offsetHeight与chrome审查元素看到的尺寸完全一致;
2)clientWidth与clientHeight分别等于offsetWidth与offsetHeight减掉相应边框(上下共20px,左右共20px)和滚动条宽度后的值(chrome下滚动条宽度为17px);
3)对于scrollWidth由于没有发生横向的溢出,同时由于overflow: scroll的原因,scrollWidth 跟clientWidth相同,但是没有包含滚动条的宽度,这也验证了前面提出的结论;
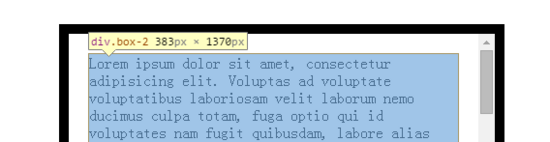
4)对于scrollHeight,在这个例子中,它其实等于上下padding(共40px) + div.box-2的offsetHeight(1370px),div.box-2:
5)以上测试还有一个css值得注意,就是box-sizing,以上代码中box-sizing设置为了content-box,如果把它改成border-box,结果也是类似的,因为offsetWidth,clientWidth还有scrollWidth对应的区域不会发生改变。
6)其它浏览器运行结果与1-5的结论一致。
测试二、验证html根元素和body元素的相关offset client scroll宽高属性:
<style type="text/css">
html,
body {
margin: 0;
}
body {
border: 10px solid #D4D2D2;
}
.box {
overflow: scroll;
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
padding: 20px;
border: 10px solid #000;
margin: 0 auto;
box-sizing: content-box;
}
.box-2 {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box-2">...</div>
</div>
<div class="box">
<div class="box-2">...</div>
</div>
<div class="box">
<div class="box-2">...</div>
</div>
<div class="box">
<div class="box-2">...</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
console.log('docE.scrollWidth:' + document.documentElement.scrollWidth);
console.log('scrollHeight:' + document.documentElement.scrollHeight);
console.log('docE.clientWidth:' + document.documentElement.clientWidth);
console.log('docE.clientHeight:' + document.documentElement.clientHeight);
console.log('docE.offsetWidth :' + document.documentElement.offsetWidth);
console.log('docE.offsetHeight:' + document.documentElement.offsetHeight);
console.log('');
console.log('body.scrollWidth:' + document.body.scrollWidth);
console.log('body.scrollHeight:' + document.body.scrollHeight);
console.log('body.clientWidth:' + document.body.clientWidth);
console.log('body.clientHeight:' + document.body.clientHeight);
console.log('body.offsetWidth :' + document.body.offsetWidth);
console.log('body.offsetHeight:' + document.body.offsetHeight);
</script>
<styletype="text/css">
html,
body{
margin: 0;
}
body{
border: 10px solid #D4D2D2;
}
.box{
overflow: scroll;
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
padding: 20px;
border: 10px solid #000;
margin: 0 auto;
box-sizing: content-box;
}
.box-2{
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
<body>
<divclass="box">
<divclass="box-2">...</div>
</div>
<divclass="box">
<divclass="box-2">...</div>
</div>
<divclass="box">
<divclass="box-2">...</div>
</div>
<divclass="box">
<divclass="box-2">...</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
console.log('docE.scrollWidth:' + document.documentElement.scrollWidth);
console.log('scrollHeight:' + document.documentElement.scrollHeight);
console.log('docE.clientWidth:' + document.documentElement.clientWidth);
console.log('docE.clientHeight:' + document.documentElement.clientHeight);
console.log('docE.offsetWidth :' + document.documentElement.offsetWidth);
console.log('docE.offsetHeight:' + document.documentElement.offsetHeight);
console.log('');
console.log('body.scrollWidth:' + document.body.scrollWidth);
console.log('body.scrollHeight:' + document.body.scrollHeight);
console.log('body.clientWidth:' + document.body.clientWidth);
console.log('body.clientHeight:' + document.body.clientHeight);
console.log('body.offsetWidth :' + document.body.offsetWidth);
console.log('body.offsetHeight:' + document.body.offsetHeight);
</script>在这个例子中,body下一共有4个box元素(总高度为360 * 4 = 1440px),body的宽是自适应的,body还有10px的border,运行结果如下:
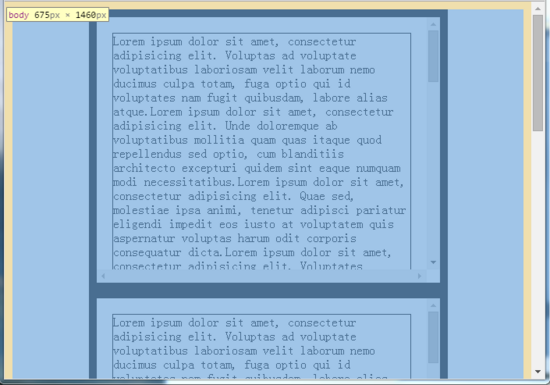

从这个结果可以看到:
1)body元素由于10px边框的原因,所以clientWidth比offsetWidth少了20px,这跟前面提到的理论是一致的,但是不可思议的是body的scrollWidth/scrollHeight竟然等于它的offsetWidth/offsetHeight,scrollWidth/scrollHeight是元素滚动区域的宽高度,按照前面给出的范围图来理解,body的scrollWidth/scrollHeight应该小于它的offsetWidth/offsetHeight才对;
2)docE的scrollWidth跟scrollHeight,应该等于body元素的offsetWidth跟offsetHeight,从运行结果来看,这一点是符合的,但是docE的clientWidth竟然等于它的offsetWidth,按照范围图,docE的clientWidth应该等于offsetWidth减去滚动条宽度才对。
其它的浏览器运行结果与chrome也有较大的差异:
IE11:

1)IE11下body元素没有出现chrome下body元素的问题
2)IE11下html根元素也有chrome类似的问题
IE10,IE9:
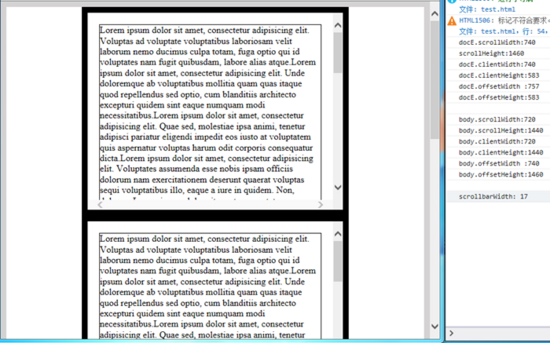
1)IE10,9下body元素没有出现chrome下body元素的问题
2)IE10,9下html根元素也没有chrome类似的问题
firefox:与IE11运行结果一致。
opera: 与chrome运行结果一致,可能是因为我这个版本的opera用的跟chrome一样的webkit内核的原因。
看起来IE9就跟IE10是最正常的,实在是有点难以理解,网上搜索很久,也没有找到相关资料来说明这些差异, 最后也只能采取大胆假设的方式,猜测出几个能解释这些问题的原因 :
1) 首先,网页整体的滚动,跟普通html元素的滚动不一样,普通html元素自身就是滚动对象, 但是对于网页来说,滚动对象不一定是html根元素或者body元素。因为当body内容为空时,body的高度是0,html根元素的高度也是0,如果这个时候给html或body加上overflow: scroll的css,会看到滚动条还是出现浏览器窗口的右边跟底边,所以对于网页整体的滚动,理论上,滚动对象应该是window,而不是html元素或者body元素!但实际情况并非如此,就测试的浏览器而言:
对于IE10,IE9,它的滚动对象是html根元素,所以它们的html根元素的offset会包含滚动条的宽度;
对于其它浏览器,滚动对象是window,所以它们的html根元素的offset不包含滚动条的宽度。
2)第二,普通元素发生滚动时,滚动内容=它的content区域+它的padding区域,当网页整体滚动时,滚动内容应该是html根元素!但实际情况也并非如此,就测试的浏览器而言:
对于IE9,IE10,IE11,firefox,它们的滚动区域是html根元素,所以它们的documentElement的scrollWidth和scrollHeight始终表示网页整体的滚动区域大小!
对于chrome和opera,它们的滚动对象是body元素,所以它们的body的scrollWidth和scrollHeight始终表示网页整体的滚动区域大小!
3)第三,浏览器始终把documentElement.clientWidth和documentElement.clientHeight描述为网页可视区域除去滚动条部分的大小,跟网页内容没有关系!
以上的这些推断也并非是毫无道理,就拿滚动对象和滚动区域来说:chrome下如果要用js滚动页面到某个位置,在不使用window.scrollTo的条件下,就必须用document.body.scrollTop = xxx 来处理,而设置document.documentElement.scrollTop无效,说明chrome的整体滚动区域是由body的滚动区域决定的;而IE11和火狐下如果要用js滚动页面到某个位置,在不使用window.scrollTo的条件下,就必须用document.documentElement.scrollTop = xxx来处理,设置document.body.scrollTop无效,说明IE11和火狐的整体滚动区域是由html根元素的滚动区域决定的。
2. 利用JS准确获取DOM对象的大小
常见的场景有:
1)获取整个网页的可视区域的大小,不包括滚动条
2)获取整个网页的大小,包括不可见的滚动区域
3)获取一个普通html元素的大小
4)判断元素或网页有无出现滚动条
5)计算滚动条的宽度
下面针对这5个场景一一说明,以下代码均 不考虑IE8及以下,不考虑html4 ,另外请注意viewport的设置,要保证在移动设备上visual viewport与layout viewport重合。
1)如何获取整个网页的可视区域的大小,不包括滚动条
document.documentElement.clientWidth; document.documentElement.clientHeight; document.documentElement.clientWidth; document.documentElement.clientHeight;
2)如何获取整个网页的大小,包括不可见的滚动区域
function pageWidth() {
var doc = document.documentElement,
body = document.body;
if (doc.clientWidth == window.innerWidth) {
return doc["clientWidth"];
}
return Math.max(
body["scrollWidth"], doc["scrollWidth"],
body["offsetWidth"], doc["clientWidth"]
);
}
function pageHeight() {
var doc = document.documentElement,
body = document.body;
if (doc.clientHeight == window.innerHeight) {
return doc["clientHeight"];
}
return Math.max(
body["scrollHeight"], doc["scrollHeight"],
body["offsetHeight"], doc["clientHeight"]
);
}
function pageWidth() {
var doc = document.documentElement,
body = document.body;
if (doc.clientWidth == window.innerWidth) {
return doc["clientWidth"];
}
return Math.max(
body["scrollWidth"], doc["scrollWidth"],
body["offsetWidth"], doc["clientWidth"]
);
}
function pageHeight() {
var doc = document.documentElement,
body = document.body;
if (doc.clientHeight == window.innerHeight) {
return doc["clientHeight"];
}
return Math.max(
body["scrollHeight"], doc["scrollHeight"],
body["offsetHeight"], doc["clientHeight"]
);
}以上出现的window.innerWidth和window.innerHeight分别用来获取网页包括滚动条的可视区域的宽高,这也是一个兼容性不错的方法,不过从实际开发情况来看,我们需要不包括滚动条的可视区域更多一些,所以在前面没有单独介绍。另外在之前给出的PPK的博客中也有关于这两个属性的兼容性测试,可以去了解。
3)如何获取一个普通html元素的大小
简单方法:
docE.offsetWidth; docE.offsetHeight; docE.offsetWidth; docE.offsetHeight;
利用getBoundingClientRect:
var obj = docE.getBoundingClientRect(),
elemWidth,
elemHeight;
if(obj) {
if(obj.width) {
elemWidth = obj.width;
elemHeight = obj.height;
} else {
elemWidth = obj.right - obj.left;
elemHeight = obj.bottom - obj.top;
}
} else {
elemWidth = docE.offsetWidth;
elemHeight = docE.offsetHeight;
}
var obj = docE.getBoundingClientRect(),
elemWidth,
elemHeight;
if(obj) {
if(obj.width) {
elemWidth = obj.width;
elemHeight = obj.height;
} else {
elemWidth = obj.right - obj.left;
elemHeight = obj.bottom - obj.top;
}
} else {
elemWidth = docE.offsetWidth;
elemHeight = docE.offsetHeight;
}getBoundingClientRect将在下篇文章中跟其它与位置有关的DOM属性一起再详细介绍。
4 )判断元素或网页有无出现滚动条
function scrollbarState(elem) {
var docE = document.documentElement,
body = document.body;
if (!elem || elem === document || elem === docE || elem === body) {
return {
scrollbarX: docE.clientHeight window.innerHeight,
scrollbarY: docE.clientWidth window.innerWidth
}
}
if (typeof(Element) == 'function' & !(elem instanceof(Element) || !body.contains(elem))) {
return {
scrollbarX: false,
scrollbarY: false
};
}
var elemStyle = elem.style,
overflowStyle = {
hidden: elemStyle.overflow == 'hidden',
hiddenX: elemStyle.overflowX == 'hidden',
hiddenY: elemStyle.overflowY == 'hidden',
scroll: elemStyle.overflow == 'scroll',
scrollX: elemStyle.overflowX == 'scroll',
scrollY: elemStyle.overflowY == 'scroll'
};
return {
scrollbarX: overflowStyle.scroll || overflowStyle.scrollX || (!overflowStyle.hidden & !overflowStyle.hiddenX && elem.clientWidth elem.scrollWidth),
scrollbarY: overflowStyle.scroll || overflowStyle.scrollY || (!overflowStyle.hidden && !overflowStyle.hiddenY && elem.clientHeight elem.scrollHeight)
};
}
function scrollbarState(elem) {
var docE = document.documentElement,
body = document.body;
if (!elem || elem === document || elem === docE || elem === body) {
return {
scrollbarX: docE.clientHeight window.innerHeight,
scrollbarY: docE.clientWidth window.innerWidth
}
}
if (typeof(Element) == 'function' & !(eleminstanceof(Element) || !body.contains(elem))) {
return {
scrollbarX: false,
scrollbarY: false
};
}
var elemStyle = elem.style,
overflowStyle = {
hidden: elemStyle.overflow == 'hidden',
hiddenX: elemStyle.overflowX == 'hidden',
hiddenY: elemStyle.overflowY == 'hidden',
scroll: elemStyle.overflow == 'scroll',
scrollX: elemStyle.overflowX == 'scroll',
scrollY: elemStyle.overflowY == 'scroll'
};
return {
scrollbarX: overflowStyle.scroll || overflowStyle.scrollX || (!overflowStyle.hidden & !overflowStyle.hiddenX && elem.clientWidth elem.scrollWidth),
scrollbarY: overflowStyle.scroll || overflowStyle.scrollY || (!overflowStyle.hidden && !overflowStyle.hiddenY && elem.clientHeight elem.scrollHeight)
};
}当x或y方向的overflow为scroll的时候,该方向的scrollbarX为true,表示出现滚动条。
5)计算滚动条的宽度
function scrollbarWidth() {
var docE = document.documentElement,
body = document.body,
e = document.createElement('div');
e.style.cssText = 'position: absolute; top: -9999px; width: 50px; height: 50px; overflow: scroll;';
body.appendChild(e);
var _scrollbarWidth = e.offsetWidth - e.clientWidth
body.removeChild(e);
return _scrollbarWidth;
}
function scrollbarWidth() {
var docE = document.documentElement,
body = document.body,
e = document.createElement('div');
e.style.cssText = 'position: absolute; top: -9999px; width: 50px; height: 50px; overflow: scroll;';
body.appendChild(e);
var _scrollbarWidth = e.offsetWidth - e.clientWidth
body.removeChild(e);
return _scrollbarWidth;
}以上就是本文的全部内容,希望能对您有所帮助:)另外本文第二部分提供的代码,是根据个人思考和经验总结出的一些方法,在兼容性方面可能还有未考虑到的地方, 如果您有遇到其它不兼容的情况或者有更好的代码,还请不吝赐教 ,欢迎您的指导。

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

Video Face Swap
Tauschen Sie Gesichter in jedem Video mühelos mit unserem völlig kostenlosen KI-Gesichtstausch-Tool aus!

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Was soll ich tun, wenn ich auf den Codendruck auf Kleidungsstücke für Front-End-Thermalpapier-Quittungen stoße?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Was soll ich tun, wenn ich auf den Codendruck auf Kleidungsstücke für Front-End-Thermalpapier-Quittungen stoße?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Häufig gestellte Fragen und Lösungen für das Ticket-Ticket-Ticket-Ticket in Front-End im Front-End-Entwicklungsdruck ist der Ticketdruck eine häufige Voraussetzung. Viele Entwickler implementieren jedoch ...
 Wer bekommt mehr Python oder JavaScript bezahlt?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Wer bekommt mehr Python oder JavaScript bezahlt?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Es gibt kein absolutes Gehalt für Python- und JavaScript -Entwickler, je nach Fähigkeiten und Branchenbedürfnissen. 1. Python kann mehr in Datenwissenschaft und maschinellem Lernen bezahlt werden. 2. JavaScript hat eine große Nachfrage in der Entwicklung von Front-End- und Full-Stack-Entwicklung, und sein Gehalt ist auch beträchtlich. 3. Einflussfaktoren umfassen Erfahrung, geografische Standort, Unternehmensgröße und spezifische Fähigkeiten.
 Entmystifizieren JavaScript: Was es tut und warum es wichtig ist
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Entmystifizieren JavaScript: Was es tut und warum es wichtig ist
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript ist der Eckpfeiler der modernen Webentwicklung. Zu den Hauptfunktionen gehören eine ereignisorientierte Programmierung, die Erzeugung der dynamischen Inhalte und die asynchrone Programmierung. 1) Ereignisgesteuerte Programmierung ermöglicht es Webseiten, sich dynamisch entsprechend den Benutzeroperationen zu ändern. 2) Die dynamische Inhaltsgenerierung ermöglicht die Anpassung der Seiteninhalte gemäß den Bedingungen. 3) Asynchrone Programmierung stellt sicher, dass die Benutzeroberfläche nicht blockiert ist. JavaScript wird häufig in der Webinteraktion, der einseitigen Anwendung und der serverseitigen Entwicklung verwendet, wodurch die Flexibilität der Benutzererfahrung und die plattformübergreifende Entwicklung erheblich verbessert wird.
 Wie fusioniere ich Arrayelemente mit derselben ID mit JavaScript in ein Objekt?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Wie fusioniere ich Arrayelemente mit derselben ID mit JavaScript in ein Objekt?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Wie fusioniere ich Array -Elemente mit derselben ID in ein Objekt in JavaScript? Bei der Verarbeitung von Daten begegnen wir häufig die Notwendigkeit, dieselbe ID zu haben ...
 Wie kann man Parallax -Scrolling- und Element -Animationseffekte wie die offizielle Website von Shiseido erzielen?
oder:
Wie können wir den Animationseffekt erzielen, der von der Seite mit der Seite mit der offiziellen Website von Shiseido begleitet wird?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Wie kann man Parallax -Scrolling- und Element -Animationseffekte wie die offizielle Website von Shiseido erzielen?
oder:
Wie können wir den Animationseffekt erzielen, der von der Seite mit der Seite mit der offiziellen Website von Shiseido begleitet wird?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Diskussion über die Realisierung von Parallaxe -Scrolling- und Elementanimationseffekten in diesem Artikel wird untersuchen, wie die offizielle Website der Shiseeido -Website (https://www.shiseeido.co.jp/sb/wonderland/) ähnlich ist ...
 Der Unterschied in der Konsole.log -Ausgabeergebnis: Warum unterscheiden sich die beiden Anrufe?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
Der Unterschied in der Konsole.log -Ausgabeergebnis: Warum unterscheiden sich die beiden Anrufe?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
Eingehende Diskussion der Ursachen des Unterschieds in der Konsole.log-Ausgabe. In diesem Artikel wird die Unterschiede in den Ausgabeergebnissen der Konsolenfunktion in einem Code analysiert und die Gründe dafür erläutert. � ...
 Ist JavaScript schwer zu lernen?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Ist JavaScript schwer zu lernen?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
JavaScript zu lernen ist nicht schwierig, aber es ist schwierig. 1) Verstehen Sie grundlegende Konzepte wie Variablen, Datentypen, Funktionen usw. 2) Beherrschen Sie die asynchrone Programmierung und implementieren Sie sie durch Ereignisschleifen. 3) Verwenden Sie DOM -Operationen und versprechen Sie, asynchrone Anfragen zu bearbeiten. 4) Vermeiden Sie häufige Fehler und verwenden Sie Debugging -Techniken. 5) Die Leistung optimieren und Best Practices befolgen.
 Kann PowerPoint JavaScript ausführen?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
Kann PowerPoint JavaScript ausführen?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
JavaScript kann in PowerPoint ausgeführt werden und durch Aufrufen externer JavaScript -Dateien oder der Einbettung von HTML -Dateien über VBA implementiert werden. 1. Um VBA zu verwenden, um JavaScript -Dateien aufzurufen, müssen Sie Makros aktivieren und VBA -Programmierkenntnisse haben. 2. Einbetten Sie HTML -Dateien ein, die JavaScript enthalten, die einfach und einfach zu bedienen sind, aber Sicherheitsbeschränkungen unterliegen. Zu den Vorteilen zählen erweiterte Funktionen und Flexibilität, während Nachteile Sicherheit, Kompatibilität und Komplexität beinhalten. In der Praxis sollte die Aufmerksamkeit auf Sicherheit, Kompatibilität, Leistung und Benutzererfahrung geschenkt werden.




