 Backend-Entwicklung
Backend-Entwicklung
 XML/RSS-Tutorial
XML/RSS-Tutorial
 Verwenden von dom4j zum Parsen von XML in Java (Beispielcode)
Verwenden von dom4j zum Parsen von XML in Java (Beispielcode)
Verwenden von dom4j zum Parsen von XML in Java (Beispielcode)
Obwohl Java bereits über zwei Standard-Parsing-Methoden verfügt, Dom und Sax
, sind sie für einen Anfänger wie mich nicht einfach zu bedienen.
In diesem Sinne , große Entwicklungsgruppen von Drittanbietern haben Tools wie Jdom und Dom4j entwickelt
Angesichts des aktuellen Trends werden wir hier über die grundlegende Verwendung von Dom4j sprechen, ohne Rekursion und andere komplexe Operationen einzubeziehen
Dom4j hat viele Verwendungsmöglichkeiten und die Beispiele auf der offiziellen Website sind etwas unklar, daher werde ich hier nicht darauf eingehen
Zuerst müssen wir ein XML-Dokument erstellen und dann können wir es analysieren
XML-Dokument:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<books>
<book id="001">
<title>Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
</book>
<book id="002">
<title>Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
</book>
</books>Beispiel 1: Liste zum Parsen von XML verwenden
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
File file = new File("books.xml");
Document document = reader.read(file);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> childElements = root.elements();
for (Element child : childElements) {
//未知属性名情况下
/*List<Attribute> attributeList = child.attributes();
for (Attribute attr : attributeList) {
System.out.println(attr.getName() + ": " + attr.getValue());
}*/
//已知属性名情况下
System.out.println("id: " + child.attributeValue("id"));
//未知子元素名情况下
/*List<Element> elementList = child.elements();
for (Element ele : elementList) {
System.out.println(ele.getName() + ": " + ele.getText());
}
System.out.println();*/
//已知子元素名的情况下
System.out.println("title" + child.elementText("title"));
System.out.println("author" + child.elementText("author"));
//这行是为了格式化美观而存在
System.out.println();
}
}
}Beispiel 2: Verwenden Sie Iterator zum Parsen von XML
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(new File("books.xml"));
Element root = document.getRootElement();
Iterator it = root.elementIterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Element element = (Element) it.next();
//未知属性名称情况下
/*Iterator attrIt = element.attributeIterator();
while (attrIt.hasNext()) {
Attribute a = (Attribute) attrIt.next();
System.out.println(a.getValue());
}*/
//已知属性名称情况下
System.out.println("id: " + element.attributeValue("id"));
//未知元素名情况下
/*Iterator eleIt = element.elementIterator();
while (eleIt.hasNext()) {
Element e = (Element) eleIt.next();
System.out.println(e.getName() + ": " + e.getText());
}
System.out.println();*/
//已知元素名情况下
System.out.println("title: " + element.elementText("title"));
System.out.println("author: " + element.elementText("author"));
System.out.println();
}
}
}Ergebnis ausführen:
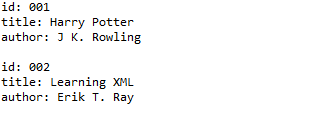
Beispiel 3: XML-Dokument erstellen und in Datei ausgeben
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Document doc = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
//增加根节点
Element books = doc.addElement("books");
//增加子元素
Element book1 = books.addElement("book");
Element title1 = book1.addElement("title");
Element author1 = book1.addElement("author");
Element book2 = books.addElement("book");
Element title2 = book2.addElement("title");
Element author2 = book2.addElement("author");
//为子节点添加属性
book1.addAttribute("id", "001");
//为元素添加内容
title1.setText("Harry Potter");
author1.setText("J K. Rowling");
book2.addAttribute("id", "002");
title2.setText("Learning XML");
author2.setText("Erik T. Ray");
//实例化输出格式对象
OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();
//设置输出编码
format.setEncoding("UTF-8");
//创建需要写入的File对象
File file = new File("D:" + File.separator + "books.xml");
//生成XMLWriter对象,构造函数中的参数为需要输出的文件流和格式
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream(file), format);
//开始写入,write方法中包含上面创建的Document对象
writer.write(doc);
}
}Ergebnis ausführen:

Weitere verwandte Artikel zur Verwendung von dom4j zum Parsen von XML (Beispielcode) in Java finden Sie auf der chinesischen PHP-Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Ist die Konversionsgeschwindigkeit beim Umwandeln von XML in PDF auf Mobiltelefon schnell?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Ist die Konversionsgeschwindigkeit beim Umwandeln von XML in PDF auf Mobiltelefon schnell?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Die Geschwindigkeit der mobilen XML zu PDF hängt von den folgenden Faktoren ab: der Komplexität der XML -Struktur. Konvertierungsmethode für mobile Hardware-Konfiguration (Bibliothek, Algorithmus) -Codierungsoptimierungsmethoden (effiziente Bibliotheken, Optimierung von Algorithmen, Cache-Daten und Nutzung von Multi-Threading). Insgesamt gibt es keine absolute Antwort und es muss gemäß der spezifischen Situation optimiert werden.
 Wie konvertiere ich XML -Dateien in PDF auf Ihrem Telefon?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
Wie konvertiere ich XML -Dateien in PDF auf Ihrem Telefon?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
Mit einer einzigen Anwendung ist es unmöglich, XML -zu -PDF -Konvertierung direkt auf Ihrem Telefon zu vervollständigen. Es ist erforderlich, Cloud -Dienste zu verwenden, die in zwei Schritten erreicht werden können: 1. XML in PDF in der Cloud, 2. Zugriff auf die konvertierte PDF -Datei auf dem Mobiltelefon konvertieren oder herunterladen.
 Wie konvertieren Sie XML in Ihr Telefon in PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Wie konvertieren Sie XML in Ihr Telefon in PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Es ist nicht einfach, XML direkt auf Ihr Telefon in PDF umzuwandeln, kann jedoch mit Hilfe von Cloud -Diensten erreicht werden. Es wird empfohlen, eine leichte mobile App zu verwenden, um XML -Dateien hochzuladen und generierte PDFs zu empfangen und sie mit Cloud -APIs zu konvertieren. Cloud -APIs verwenden serverlose Computerdienste, und die Auswahl der richtigen Plattform ist entscheidend. Bei der Behandlung von XML -Parsen und PDF -Generation müssen Komplexität, Fehlerbehebung, Sicherheit und Optimierungsstrategien berücksichtigt werden. Der gesamte Prozess erfordert, dass die Front-End-App und die Back-End-API zusammenarbeiten, und es erfordert ein gewisses Verständnis einer Vielzahl von Technologien.
 So öffnen Sie Web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
So öffnen Sie Web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
Um eine Web.xml -Datei zu öffnen, können Sie die folgenden Methoden verwenden: Verwenden Sie einen Texteditor (z.
 Empfohlenes XML -Formatierungswerkzeug
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Empfohlenes XML -Formatierungswerkzeug
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML -Formatierungs -Tools können Code nach Regeln eingeben, um die Lesbarkeit und das Verständnis zu verbessern. Achten Sie bei der Auswahl eines Tools auf die Anpassungsfunktionen, den Umgang mit besonderen Umständen, die Leistung und die Benutzerfreundlichkeit. Zu den häufig verwendeten Werkzeugtypen gehören Online-Tools, IDE-Plug-Ins und Befehlszeilen-Tools.
 Gibt es eine mobile App, die XML in PDF umwandeln kann?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Gibt es eine mobile App, die XML in PDF umwandeln kann?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Eine Anwendung, die XML direkt in PDF konvertiert, kann nicht gefunden werden, da es sich um zwei grundlegend unterschiedliche Formate handelt. XML wird zum Speichern von Daten verwendet, während PDF zur Anzeige von Dokumenten verwendet wird. Um die Transformation abzuschließen, können Sie Programmiersprachen und Bibliotheken wie Python und ReportLab verwenden, um XML -Daten zu analysieren und PDF -Dokumente zu generieren.
 So öffnen Sie das XML -Format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
So öffnen Sie das XML -Format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Verwenden Sie die meisten Texteditoren, um XML -Dateien zu öffnen. Wenn Sie eine intuitivere Baumanzeige benötigen, können Sie einen XML -Editor verwenden, z. B. Sauerstoff XML -Editor oder XMLSPY. Wenn Sie XML -Daten in einem Programm verarbeiten, müssen Sie eine Programmiersprache (wie Python) und XML -Bibliotheken (z. B. XML.etree.elementtree) verwenden, um zu analysieren.
 XML Online -Formatierung
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
XML Online -Formatierung
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
XML Online-Format-Tools organisieren automatisch den chaotischen XML-Code in einfach zu lesenden und verwalteten Formaten. Durch die Parsen des Syntaxbaums von XML und die Anwendung von Formatierungsregeln optimieren diese Tools die Struktur des Codes und verbessern die Wartbarkeit und die Effizienz der Teamarbeit.



