
Die Speicherstruktur von HashMap ist wie in der Abbildung dargestellt: Wenn ein Bucket mehr als 8 Knoten enthält, ist die Speicherstruktur ein rot-schwarzer Baum, und wenn weniger als 8 Knoten vorhanden sind, handelt es sich um einen Ein- Art und Weise verknüpfte Liste.
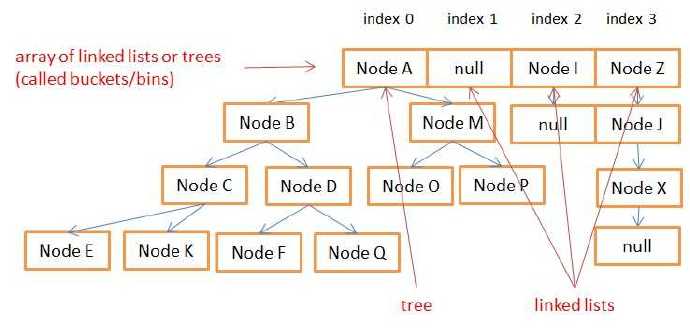
1: Einige Eigenschaften von HashMap
public class HashMap<k,v> extends AbstractMap<k,v> implements Map<k,v>, Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L;
// 默认的初始容量是16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// 最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认的填充因子(以前的版本也有叫加载因子的)
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 这是一个阈值,当桶(bucket)上的链表数大于这个值时会转成红黑树,put方法的代码里有用到
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 也是阈值同上一个相反,当桶(bucket)上的链表数小于这个值时树转链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 看源码注释里说是:树的最小的容量,至少是 4 x TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 32 然后为了避免(resizing 和 treeification thresholds) 设置成64
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
// 存储元素的数组,总是2的倍数
transient Node<k,v>[] table;
transient Set<map.entry<k,v>> entrySet;
// 存放元素的个数,注意这个不等于数组的长度。
transient int size;
// 每次扩容和更改map结构的计数器
transient int modCount;
// 临界值 当实际大小(容量*填充因子)超过临界值时,会进行扩容
int threshold;
// 填充因子
final float loadFactor;
2: Konstruktionsmethode von HashMap
// 指定初始容量和填充因子的构造方法
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 指定的初始容量非负
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(Illegal initial capacity: +
initialCapacity);
// 如果指定的初始容量大于最大容量,置为最大容量
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
// 填充比为正
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException(Illegal load factor: +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// 指定容量后,tableSizeFor方法计算出临界值,put数据的时候如果超出该值就会扩容,该值肯定也是2的倍数
// 指定的初始容量没有保存下来,只用来生成了一个临界值
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 该方法保证总是返回大于cap并且是2的倍数的值,比如传入999 返回1024
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
// 向右做无符号位移
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
// 三目运算符的嵌套
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
//构造函数2
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
//构造函数3
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
3: Bestimmen Sie die Position des Elements im Array beim Abrufen und Einfügen von
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}Um den Standort zu bestimmen
Der erste Schritt besteht darin, den Hash-Code des Schlüssels zu berechnen, bei dem es sich um eine Zahl vom Typ int handelt. Die folgenden h >>> 16 Quellcode-Kommentare besagen: Um Hash-Kollisionen (Hash-Kollisonen) zu vermeiden, werden die hohen Bits auf die niedrigen Bits verteilt. Dies erfolgt nach umfassender Berücksichtigung verschiedener Faktoren wie Geschwindigkeit und Leistung .
Schritt 2: h ist der Hash-Code, Länge ist die Länge des Node[]-Arrays oben, führen Sie die UND-Operation h & (Länge-1) aus. Da die Länge ein Vielfaches von 2 -1 ist, ist ihr Binärcode alle 1, und das Ergebnis von 1 und anderen oben genannten Zahlen kann 0 oder 1 sein, wodurch die Einheitlichkeit nach der Operation gewährleistet wird. Das heißt, die Hash-Methode stellt die Einheitlichkeit der Ergebnisse sicher, was sehr wichtig ist und einen großen Einfluss auf die Put- und Get-Leistung von HashMap hat. Schauen Sie sich den Vergleich unten an:
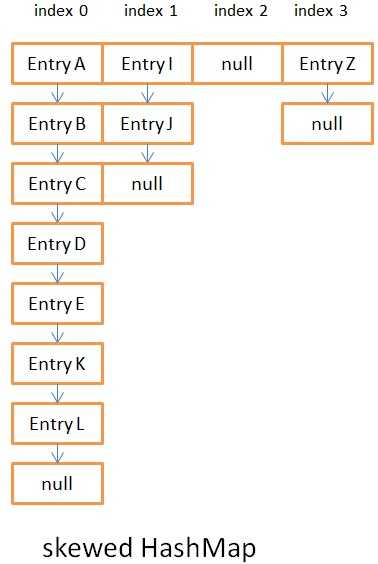
Abbildung 3.1 ist das asymmetrische Hash-Ergebnis
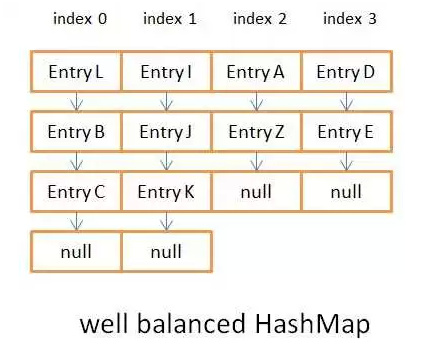
Abbildung 3.2 ist das ausgeglichene Hash-Ergebnis
Diese beiden Bilder enthalten nicht viele Daten. Wenn die Länge der verknüpften Liste 8 überschreitet, wird sie in einen rot-schwarzen Baum umgewandelt. Zu diesem Zeitpunkt wird es offensichtlicher sein, dass es sich immer um eine verknüpfte Liste handelt. Die Komplexität der Abfrage einer verknüpften Liste beträgt O (n), während die Abfragekomplexität des Rot-Schwarz-Baums O (log (n)) beträgt zu seinen eigenen Eigenschaften. Wenn die Hash-Ergebnisse ungleichmäßig sind, wirkt sich dies stark auf die Komplexität des Vorgangs aus. Verwandtes Wissen finden Sie hierRed-Black Tree Basic Knowledge BlogEs gibt auch ein Beispiel im Internet Zur Überprüfung: Passen Sie ein Objekt als Schlüssel an, passen Sie die Methode hashCode() an, um zu sehen, wie lange es dauert,
public class MutableKeyTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
class MyKey {
Integer i;
public void setI(Integer i) {
this.i = i;
}
public MyKey(Integer i) {
this.i = i;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// 如果返回1
// return 1
return i;
}
// object作为key存map里,必须实现equals方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof MyKey) {
return i.equals(((MyKey)obj).i);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
// 我机器配置不高,25000的话正常情况27毫秒,可以用2500万试试,如果hashCode()方法返回1的话,250万就卡死
Map<MyKey,String> map = new HashMap<>(25000,1);
Date begin = new Date();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++){
map.put(new MyKey(i), "test " + i);
}
Date end = new Date();
System.out.println("时间(ms) " + (end.getTime() - begin.getTime()));
4: get method < einzufügen 🎜>
public V get(Object key) {
Node<k,v> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<k,v> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<k,v>[] tab; Node<k,v> first, e; int n; K k;
// hash & (length-1)得到红黑树的树根位置或者是链表的表头
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 如果是树,遍历红黑树复杂度是O(log(n)),得到节点值
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<k,v>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// else是链表结构
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<k,v>[] tab; Node<k,v> p; int n, i;
// 如果tab为空或长度为0,则分配内存resize()
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// (n - 1) & hash找到put位置,如果为空,则直接put
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<k,v> e; K k;
// 第一节节点hash值同,且key值与插入key相同
if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树的put方法比较复杂,putVal之后还要遍历整个树,必要的时候修改值来保证红黑树的特点
e = ((TreeNode<k,v>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// e为空,表示已到表尾也没有找到key值相同节点,则新建节点
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 新增节点后如果节点个数到达阈值,则将链表转换为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 容许空key空value
if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 更新hash值和key值均相同的节点Value值
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 这一句比较重要,可以看出每次扩容是2倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}



