
In diesem Artikel wird hauptsächlich die Methode zum Abfragen der wiederholten Daten in der -Tabelle durch MySQL vorgestellt 🎜 >
Doppelte Datensätze in der Abfragetabelle in MySQL:INSERT INTO hk_test(username, passwd) VALUES ('qmf1', 'qmf1'),('qmf2', 'qmf11') delete from hk_test where username='qmf1' and passwd='qmf1'
Überprüfen Sie zunächst die doppelten Originaldaten: 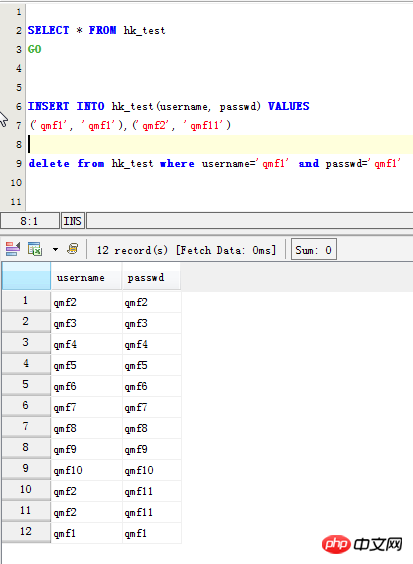
Szenario 1: Listen Sie das Feld „Benutzername“ auf Daten erneut lesen
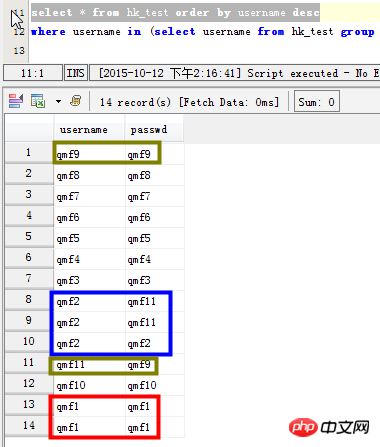
select username,count(*) as count from hk_test group by username having count>1; SELECT username,count(username) as count FROM hk_test GROUP BY username HAVING count(username) >1 ORDER BY count DESC;
Szenario 2: Listen Sie die spezifischen Datensätze mit doppelten Benutzernamenfeldern auf: 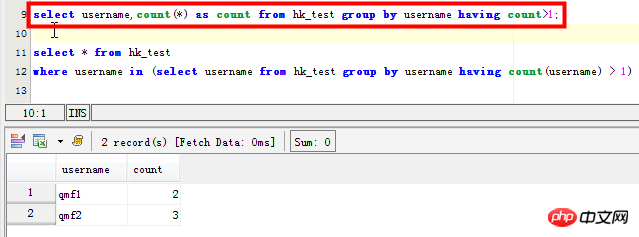
select * from hk_test where username in (select username from hk_test group by username having count(username) > 1) SELECT username,passwd FROM hk_test WHERE username in ( SELECT username FROM hk_test GROUP BY username HAVING count(username)>1) 但是这条语句在mysql中效率太差,感觉mysql并没有为子查询生成临时表。在数据量大的时候,耗时很长时间
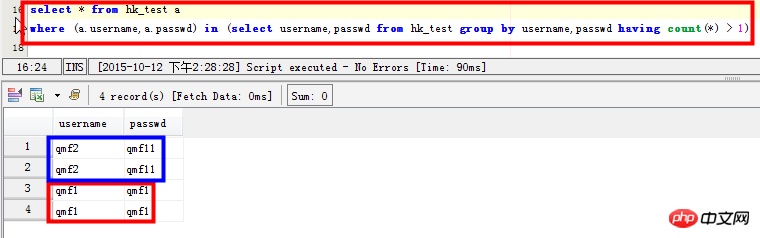
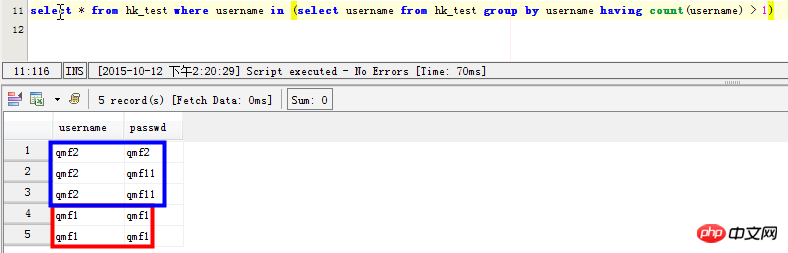 Szenario 3: Datensätze mit doppelten Feldern anzeigen: Beispielsweise weisen die Felder „Benutzername“ und „Passwort“ doppelte Datensätze auf:
Szenario 3: Datensätze mit doppelten Feldern anzeigen: Beispielsweise weisen die Felder „Benutzername“ und „Passwort“ doppelte Datensätze auf:
于是使用先建立临时表 create table `tmptable` as ( SELECT `name` FROM `table` GROUP BY `name` HAVING count(`name`) >1 ); 然后使用多表连接查询 SELECT a.`id`, a.`name` FROM `table` a, `tmptable` t WHERE a.`name` = t.`name`; 结果这次结果很快就出来了。 用 distinct去重复 SELECT distinct a.`id`, a.`name` FROM `table` a, `tmptable` t WHERE a.`name` = t.`name`;
select * from hk_test a where (a.username,a.passwd) in (select username,passwd from hk_test group by username,passwd having count(*) > 1)
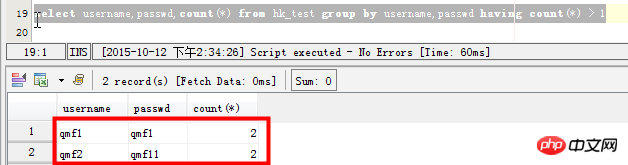
select username,passwd,count(*) from hk_test group by username,passwd having count(*) > 1
MySQL查询表内重复记录 查询及删除重复记录的方法 (一) 1、查找表中多余的重复记录,重复记录是根据单个字段(peopleId)来判断 select * from people where peopleId in (select peopleId from people group by peopleId having count(peopleId)>1) 2、删除表中多余的重复记录,重复记录是根据单个字段(peopleId)来判断,只留有一个记录 delete from people where peopleId in (select peopleId from people group by peopleId having count(peopleId)>1) and min(id) not in (select id from people group by peopleId having count(peopleId)>1) 3、查找表中多余的重复记录(多个字段) select * from vitae a where (a.peopleId,a.seq) in (select peopleId,seq from vitae group by peopleId,seq having count(*)>1) 4、删除表中多余的重复记录(多个字段),只留有rowid最小的记录 delete from vitae a where (a.peopleId,a.seq) in (select peopleId,seq from vitae group by peopleId,seq having count(*) > 1) and rowid not in (select min(rowid) from vitae group by peopleId,seq having count(*)>1) 5、查找表中多余的重复记录(多个字段),不包含rowid最小的记录 select * from vitae a where (a.peopleId,a.seq) in (select peopleId,seq from vitae group by peopleId,seq having count(*) > 1) and rowid not in (select min(rowid) from vitae group by peopleId,seq having count(*)>1) (二) 比方说 在A表中存在一个字段“name”,而且不同记录之间的“name”值有可能会相同,现在就是需要查询出在该表中的各记录之间,“name”值存在重复的项; Select Name,Count(*) From A Group By Name Having Count(*) > 1 如果还查性别也相同大则如下: Select Name,sex,Count(*) From A Group By Name,sex Having Count(*) > 1 (三) 方法一 declare @max integer,@id integer declare cur_rows cursor local for select 主字段,count(*) from 表名 group by 主字段 having count(*) >; 1 open cur_rows fetch cur_rows into @id,@max while @@fetch_status=0 begin select @max = @max -1 set rowcount @max delete from 表名 where 主字段 = @id fetch cur_rows into @id,@max end close cur_rows set rowcount 0
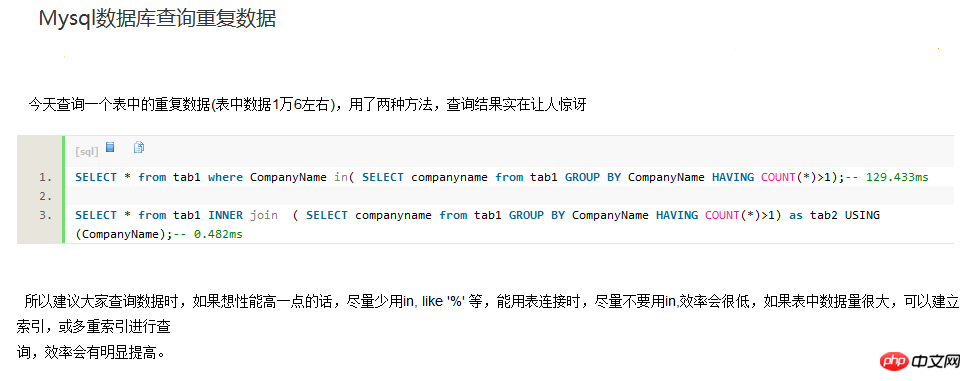
Duplikate Datensätze in der MySQL-Datentabelle finden
SELECT * from tab1 where CompanyName in( SELECT companyname from tab1 GROUP BY CompanyName HAVING COUNT(*)>1); -- 129.433ms SELECT * from tab1 INNER join ( SELECT companyname from tab1 GROUP BY CompanyName HAVING COUNT(*)>1) as tab2 USING(CompanyName); -- 0.482ms 方法二 有两个意义上的重复记录,一是完全重复的记录,也即所有字段均重复的记录,二是部分关键字段重复的记录,比如Name字段重复,而其他字段不一定重复或都重复可以忽略。 1、对于第一种重复,比较容易解决,使用 select distinct * from tableName 就可以得到无重复记录的结果集。 如果该表需要删除重复的记录(重复记录保留1条),可以按以下方法删除 select distinct * into #Tmp from tableName drop table tableName select * into tableName from #Tmp drop table #Tmp 发生这种重复的原因是表设计不周产生的,增加唯一索引列即可解决。 2、这类重复问题通常要求保留重复记录中的第一条记录,操作方法如下 假设有重复的字段为Name,Address,要求得到这两个字段唯一的结果集 select identity(int,1,1) as autoID, * into #Tmp from tableName select min(autoID) as autoID into #Tmp2 from #Tmp group by Name,autoID select * from #Tmp where autoID in(select autoID from #tmp2) 最后一个select即得到了Name,Address不重复的结果集(但多了一个autoID字段,实际写时可以写在select子句中省去此列) (四)查询重复 select * from tablename where id in ( select id from tablename group by id having count(id) > 1) 常用的语句 1、查找表中多余的重复记录,重复记录是根据单个字段(mail_id)来判断 代码如下 复制代码 SELECT * FROM table WHERE mail_id IN (SELECT mail_id FROM table GROUP BY mail_id HAVING COUNT(mail_id) > 1); 2、删除表中多余的重复记录,重复记录是根据单个字段(mail_id)来判断,只留有rowid最小的记录 代码如下 复制代码 DELETE FROM table WHERE mail_id IN (SELECT mail_id FROM table GROUP BY mail_id HAVING COUNT(mail_id) > 1) AND rowid NOT IN (SELECT MIN(rowid) FROM table GROUP BY mail_id HAVING COUNT(mail_id )>1); 3、查找表中多余的重复记录(多个字段) 代码如下 复制代码 SELECT * FROM table WHERE (mail_id,phone) IN (SELECT mail_id,phone FROM table GROUP BY mail_id,phone HAVING COUNT(*) > 1); 4、删除表中多余的重复记录(多个字段),只留有rowid最小的记录 代码如下 复制代码 DELETE FROM table WHERE (mail_id,phone) IN (SELECT mail_id,phone FROM table GROUP BY mail_id,phone HAVING COU(www.jb51.net)NT(*) > 1) AND rowid NOT IN (SELECT MIN(rowid) FROM table GROUP BY mail_id,phone HAVING COUNT(*)>1); 5、查找表中多余的重复记录(多个字段),不包含rowid最小的记录 代码如下 复制代码 SELECT * FROM table WHERE (a.mail_id,a.phone) IN (SELECT mail_id,phone FROM table GROUP BY mail_id,phone HAVING COUNT(*) > 1) AND rowid NOT IN (SELECT MIN(rowid) FROM table GROUP BY mail_id,phone HAVING COUNT(*)>1); 存储过程 declare @max integer,@id integer declare cur_rows cursor local for select 主字段,count(*) from 表名 group by 主字段 having count(*) >; 1 open cur_rows fetch cur_rows into @id,@max while @@fetch_status=0 begin select @max = @max -1 set rowcount @max delete from 表名 where 主字段 = @id fetch cur_rows into @id,@max end close cur_rows set rowcount 0 (一)单个字段 1、查找表中多余的重复记录,根据(question_title)字段来判断 代码如下 复制代码 select * from questions where question_title in (select question_title from people group by question_title having count(question_title) > 1) 2、删除表中多余的重复记录,根据(question_title)字段来判断,只留有一个记录 代码如下 复制代码 delete from questions where peopleId in (select peopleId from people group by peopleId having count(question_title) > 1) and min(id) not in (select question_id from questions group by question_title having count(question_title)>1) (二)多个字段 删除表中多余的重复记录(多个字段),只留有rowid最小的记录 代码如下 复制代码 DELETE FROM questions WHERE (questions_title,questions_scope) IN (SELECT questions_title,questions_scope FROM que(www.jb51.net)stions GROUP BY questions_title,questions_scope HAVING COUNT(*) > 1) AND question_id NOT IN (SELECT MIN(question_id) FROM questions GROUP BY questions_scope,questions_title HAVING COUNT(*)>1) 用上述语句无法删除,创建了临时表才删的,求各位达人解释一下。 代码如下 复制代码 CREATE TABLE tmp AS SELECT question_id FROM questions WHERE (questions_title,questions_scope) IN (SELECT questions_title,questions_scope FROM questions GROUP BY questions_title,questions_scope HAVING COUNT(*) > 1) AND question_id NOT IN (SELECT MIN(question_id) FROM questions GROUP BY questions_scope,questions_title HAVING COUNT(*)>1); DELETE FROM questions WHERE question_id IN (SELECT question_id FROM tmp); DROP TABLE tmp;
Natürlich können doppelte Daten nicht ausgeschlossen werden. Bei der Pflege der Daten kam mir plötzlich der Gedanke, die redundanten Daten zu löschen und wertvolle Daten zu belassen. Die folgende SQL-Anweisung kann alle doppelten Datensätze in einer Tabelle finden.
wählen Sie user_name,count(*) als Anzahl aus der Gruppe user_table aus, indem Sie user_name count>1 haben; Parameterbeschreibung:
user_name ist das zu findende doppelte Feld.
Gruppieren verwendet
Haben wird zum Filtern verwendet.Der Effekt ist wie folgt:Nachteile: Der Nachteil dieser Methode besteht darin, dass die Effizienz sinkt, wenn die Datenmenge in Ihrer Datenbank groß ist Sehr gering. Die Datenmenge ist nicht groß und die Effizienz ist sehr hoch. Natürlich gibt es auch
andere SQL-Anweisungen, die Daten wiederholt abfragen Bitte studieren Sie sorgfältig und finden Sie eine Abfrageanweisung, die zu Ihrer Website passt. 
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonDetaillierte Einführung in die Abfragemethode für doppelte Daten in der MySQL-Tabelle (Bild). Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
 MySQL ändert den Namen der Datentabelle
MySQL ändert den Namen der Datentabelle
 MySQL erstellt eine gespeicherte Prozedur
MySQL erstellt eine gespeicherte Prozedur
 Der Unterschied zwischen Mongodb und MySQL
Der Unterschied zwischen Mongodb und MySQL
 So überprüfen Sie, ob das MySQL-Passwort vergessen wurde
So überprüfen Sie, ob das MySQL-Passwort vergessen wurde
 MySQL-Datenbank erstellen
MySQL-Datenbank erstellen
 MySQL-Standard-Transaktionsisolationsstufe
MySQL-Standard-Transaktionsisolationsstufe
 Der Unterschied zwischen SQL Server und MySQL
Der Unterschied zwischen SQL Server und MySQL
 mysqlPasswort vergessen
mysqlPasswort vergessen




