Linux-Dienstverwaltung
本文目录:
11.1 服务的概念
11.2 管理独立守护进程
11.3 管理服务的开机自启动
11.4 管理xinetd及相关瞬时守护进程
11.5 CentOS 7上管理服务
CentOS 7和CentOS 6管理服务的方式完全不同。本文先说明CentOS 6上的管理方式,在最后列出CentOS 7上服务管理方式。
11.1 服务的概念
服务是向外提供服务的进程,一般来说都会放在后台,既然要持续不断的提供外界随时发来的服务请求,服务进程就需要常驻在内存中,且不应该和终端有关,否则终端退出服务程序就退出了。另外,要能够接待外界的请求为外界提供服务,那么就需要有个专属于这个服务的"服务窗口",这个服务窗口就是端口号,通过端口号就能找到服务的提供者。
提供服务的一端叫做服务端,向服务端请求服务的叫做客户端。首先,服务端启动服务进程,此时将开放对应的端口号;然后客户端指定服务端IP地址和端口号向该服务端发起请求,服务端所在主机的内核接收到请求数据包,然后分析数据包发现请求的是某某端口号,内核知道该端口号是哪个应用程序监听的端口,所以将请求报文发送给对应的应用程序,应用程序收到报文后,将和客户端建立连接,并进行数据传输。
另外需要注意的是,并非所有服务都总是提供端口号的,例如xinetd这个服务,只有在需要的时候才接管相应的端口,如rsync监听端口为222时,那么请求rsync时,xinetd在监听过程中的端口号就是222。在不被请求的时候,xinetd是没有端口号的。
在Linux中,服务分为独立守护进程和超级守护进程。独立守护进程是自行监听在后台的,基本上所有的服务都是独立守护进程类的服务。超级守护进程专指xinetd这个服务,这个服务代为管理着一些特殊的服务,这类服务在被请求的时候才会由xinetd通知它启动服务,服务提供完毕后就关闭服务,这类服务称为瞬时守护进程,即只存在于瞬时。
但要明白,超级守护进程xinetd本身是一个常驻内存的独立守护进程,因为它要监听来自外界对其管理的瞬时守护进程的请求。只不过一般不工作的时候,xinetd不占用端口号,在工作的时候它占用被请求的瞬时守护进程的端口号,并处于监听状态。
11.2 管理独立守护进程
在CentOS 6上,所有的服务脚本都在/etc/rc.d/init.d/目录下,/etc/init.d/是它的软链接。在此目录下的脚本都是LSB风格的脚本,它们基本上都能接受start/stop/restart/reload/status等参数。
[root@xuexi tmp]# ls /etc/init.d abrt-ccpp cpuspeed irqbalance messagebus psacct saslauthd abrtd crond kdump netconsole quota_nld single abrt-oops functions killall netfs rdisc smartd acpid haldaemon lvm2-lvmetad network restorecond sshd atd halt lvm2-monitor ntpd rngd svnserve auditd ip6tables mcelogd ntpdate rsyslog sysstat blk-availability iptables mdmonitor postfix sandbox udev-post
要管理独立守护进程类的服务
/etc/init.d/service_name restart|start|stop|status # 方法一 service service_name restart|start|stop|status # 方法二
要让服务能够被service命令管理,将其服务脚本放在/etc/init.d目录下即可。
11.3 管理服务的开机自启动
chkconfig命令能管理/etc/init.d/目录下存在且脚本的内容满足一定条件的服务。
要能让chkconfig管理服务的开机是否自启动行为,只需将脚本放在/etc/init.d目录下,然后在脚本的前部加上chkconfig行和description行。如:
#!/bin/bash # chkconfig: - 85 15# description: The Apache HTTP Server is an efficient and extensible
这两行必须在所有非注释行的前面,且这两行必须得被"注释"。其中chkconfig行"-"表示适用于运行级别123456上,85表示开机启动时,它的启动顺序为85,15表示关机停止服务时,它的停止顺序为15。description行随便给一点描述信息就可以,但是必须得给"description:"关键字。
然后,就可以有chkconfig来管理服务的开机自启动了。
chkconfig [--add | --del] <name> # 将/etc/init.d中可以被chkconfig管理的服务添加到chkconfig的管理列表中,或者从列表中删除 chkconfig [--list] [name] # 列出指定名称的服务的开启自启动信息。name可以使用all来表示列出所有chkconfig管理列表中的服务 chkconfig [--level <levels>] <name> <on|off|reset> # 将指定名称的服务在指定级别上打开开机自启动或关闭开机自启动功能。 # reset则表示重置为脚本中指定的级别
当然,除了chkconfig可以管理开机自启动,将启动命令放在/etc/rc.d/rc.local文件中也是可以的。
11.4 管理xinetd及相关瞬时守护进程
11.4.1 管理瞬时守护进程
该类服务不能直接使用service命令来启动。只能去/etc/xinetd.d/目录下的对应文件中进行设置(当然,也可以在/etc/xinetd.conf中配置),然后由xinetd进行管理。
首先安装xinetd程序。
[root@xuexi tmp]# yum -y install xinetd [root@xuexi tmp]# chkconfig --list ......省略 xinetd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off xinetd based services: chargen-dgram: off chargen-stream: off daytime-dgram: off daytime-stream: off discard-dgram: off discard-stream: offecho-dgram: offecho-stream: off rsync: off tcpmux-server: offtime-dgram: offtime-stream: off
首先得保证xinetd是已经工作在后台的。
service xinetd start
然后管理瞬时守护进程,该类服务比较特别,其自启动状态和服务运行状态是同步的,也就是说chkconfig设置了其自启动则表示启动该服务,否则为停止该服务。另外,对其指定级别是无效的,它们的启动级别继承与xinetd的启动级别,并且xinetd会接管其触发的瞬时守护进程的端口号。
例如启动rsync这个瞬时守护进程。
chkconfig rsync on
11.4.2 瞬时守护进程的配置
瞬时守护进程受两个配置文件控制,一个是xinetd的配置文件/etc/xinetd.conf提供默认配置,一个是/etc/xinetd.d/下的配置文件针对对应的服务提供配置。
例如配置rsync,以下是/etc/xinetd.d/rsync的默认配置。
[root@xuexi tmp]# vi /etc/xinetd.d/rsync
# default: off
# description: The rsync server is a good addition to an ftp server, as it \
# allows crc checksumming etc.
service rsync # 定义rsync服务,名称要和/etc/xinetd.d/下的文件同名
{
disable = yes # yes表示不启动,no表示启动,等价于chkconfig rsync {on|off},所以这里设置后将直接在chkconfig中生效
flags = IPv6 # 不用管
socket_type = stream # 这代表的是tcp类型的套接字wait = no # 该服务是单线程还是多线程的,表现形式是超出的请求是否进行等待,no表示多线程
user = root # 以什么身份运行rsync
server = /usr/bin/rsync # 服务程序
server_args = --daemon # 服务程序启动时传递的参数
log_on_failure += USERID # 连接失败的日志记录,+表示在全局对应的条目上新增此处指定的USERID
}除此之外,还有几个选项:
【访问控制选项】以下两个控制列表中最好不要出现冲突的地址。 only_from:定义允许连接的访问控制列表,支持单IP,CIDR格式和长mask格式的网段,主机名hostname,域DOMAIN(.abc.com) no_access:定义不允许访问的列表,语法格式同only_from 【监听地址】 bind = ip_addr interface = ip_addr # 等价于bind 【资源控制】 cps=args1 args2 instances=N per_source=N
这3个选项的意义如下图。

11.5 CentOS 7上管理服务
service name start ==> systemctl start name.service
service name stop ==> systemctl stop name.service
service name restart ==> systemctl restart name.service
service name status ==> systemctl status name.service
查看服务是否激活(在运行中):systemctl is-active name.service
查看所有已经激活 :systemctl list-units --type service
查看所有服务 :systemctl list-units --type service --all
设置开机自启动:chkconfig name on ==> systemctl enable name.service
禁止开机自启动:chkconfig name off ==> systemctl disable name.service
查看服务是否开机自启动:chkconfig --list name ==> is-enabled name.service
查看所有服务的开机自启动状态:chkconfig --list ==> systemctl list-unit-files --type service
回到系列文章大纲:
转载请注明出处:
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonLinux-Dienstverwaltung. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1378
1378
 52
52
 So verwenden Sie Redis zur Implementierung einer verteilten Transaktionsverwaltung
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:07 PM
So verwenden Sie Redis zur Implementierung einer verteilten Transaktionsverwaltung
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:07 PM
So verwenden Sie Redis zur Implementierung eines verteilten Transaktionsmanagements Einführung: Mit der rasanten Entwicklung des Internets wird die Verwendung verteilter Systeme immer weiter verbreitet. In verteilten Systemen ist das Transaktionsmanagement eine wichtige Herausforderung. Herkömmliche Methoden des Transaktionsmanagements lassen sich in verteilten Systemen nur schwer implementieren und sind ineffizient. Mithilfe der Eigenschaften von Redis können wir problemlos ein verteiltes Transaktionsmanagement implementieren und die Leistung und Zuverlässigkeit des Systems verbessern. 1. Einführung in Redis Redis ist ein speicherbasiertes Datenspeichersystem mit effizienter Lese- und Schreibleistung und umfangreichen Daten.
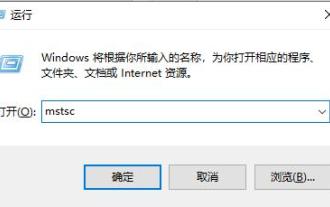 So öffnen Sie den Remotedesktopverbindungsdienst mit einem Befehl
Dec 31, 2023 am 10:38 AM
So öffnen Sie den Remotedesktopverbindungsdienst mit einem Befehl
Dec 31, 2023 am 10:38 AM
Die Remote-Desktop-Verbindung hat das tägliche Leben vieler Benutzer erleichtert. Einige Leute möchten Befehle verwenden, um eine Remote-Verbindung herzustellen, was bequemer ist. Der Remotedesktopverbindungsdienst kann Ihnen bei der Lösung dieses Problems helfen, indem er einen Befehl zum Öffnen verwendet. So richten Sie den Remote-Desktop-Verbindungsbefehl ein: Methode 1. Stellen Sie eine Remote-Verbindung her, indem Sie den Befehl ausführen. 1. Drücken Sie „Win+R“, um „Ausführen“ zu öffnen, geben Sie mstsc2 ein und klicken Sie dann auf „Optionen anzeigen“. 3. Geben Sie die IP-Adresse ein und klicken Sie "Verbinden". 4. Es wird angezeigt, dass eine Verbindung hergestellt wird. Methode 2: Remote-Verbindung über die Eingabeaufforderung 1. Drücken Sie „Win+R“, um „Ausführen“ zu öffnen, und geben Sie cmd2 ein. Geben Sie in der „Eingabeaufforderung“ mstsc/v:192.168.1.250/console ein
 Was ist der richtige Weg, einen Dienst unter Linux neu zu starten?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Was ist der richtige Weg, einen Dienst unter Linux neu zu starten?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Was ist der richtige Weg, einen Dienst unter Linux neu zu starten? Wenn wir ein Linux-System verwenden, stoßen wir häufig auf Situationen, in denen wir einen bestimmten Dienst neu starten müssen, aber manchmal können beim Neustart des Dienstes Probleme auftreten, z. B. wenn der Dienst nicht tatsächlich gestoppt oder gestartet wird. Daher ist es sehr wichtig, die richtige Methode zum Neustarten von Diensten zu beherrschen. Unter Linux können Sie normalerweise den Befehl systemctl verwenden, um Systemdienste zu verwalten. Der Befehl systemctl ist Teil des systemd-Systemmanagers
 Wie implementiert man die Leistungsmanagementfunktion für Schüler in Java?
Nov 04, 2023 pm 12:00 PM
Wie implementiert man die Leistungsmanagementfunktion für Schüler in Java?
Nov 04, 2023 pm 12:00 PM
Wie implementiert man die Leistungsmanagementfunktion für Schüler in Java? Im modernen Bildungssystem ist das Leistungsmanagement der Studierenden eine sehr wichtige Aufgabe. Durch die Verwaltung der Schülerleistungen können Schulen den Lernfortschritt der Schüler besser überwachen, ihre Schwächen und Stärken verstehen und auf der Grundlage dieser Informationen gezieltere Unterrichtspläne erstellen. In diesem Artikel besprechen wir, wie man die Programmiersprache Java verwendet, um Funktionen zur Leistungsverwaltung von Schülern zu implementieren. Zunächst müssen wir die Datenstruktur der Schülernoten bestimmen. Typischerweise können die Noten der Schüler als dargestellt werden
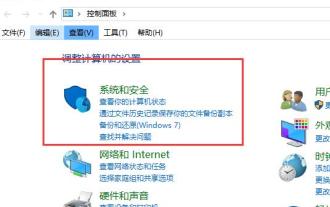 Was tun, wenn die Rechtsklick-Menüverwaltung in Windows 10 nicht geöffnet werden kann?
Jan 04, 2024 pm 07:07 PM
Was tun, wenn die Rechtsklick-Menüverwaltung in Windows 10 nicht geöffnet werden kann?
Jan 04, 2024 pm 07:07 PM
Wenn wir das Win10-System verwenden und mit der Maus auf den Desktop oder das Rechtsklick-Menü klicken, stellen wir fest, dass das Menü nicht geöffnet werden kann und wir den Computer nicht normal verwenden können. Zu diesem Zeitpunkt müssen wir das wiederherstellen System zur Lösung des Problems. Die Win10-Rechtsklick-Menüverwaltung kann nicht geöffnet werden: 1. Öffnen Sie zuerst unsere Systemsteuerung und klicken Sie dann auf. 2. Klicken Sie dann unter Sicherheit und Wartung auf. 3. Klicken Sie rechts, um das System wiederherzustellen. 4. Wenn die Maus immer noch nicht verwendet werden kann, prüfen Sie, ob mit der Maus selbst ein Fehler vorliegt. 5. Wenn Sie sicher sind, dass kein Problem mit der Maus vorliegt, drücken Sie + und geben Sie ein. 6. Nachdem die Ausführung abgeschlossen ist, starten Sie den Computer neu.
 Lösung dafür, dass der Ubuntu-PHP-Dienst nicht normal startet
Feb 28, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Lösung dafür, dass der Ubuntu-PHP-Dienst nicht normal startet
Feb 28, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Titel: Methoden und spezifische Codebeispiele zur Lösung des Problems, dass der PHP-Dienst unter Ubuntu nicht normal starten kann. Wenn Sie Ubuntu zum Erstellen einer Website oder Anwendung verwenden, tritt häufig das Problem auf, dass der PHP-Dienst nicht normal starten kann, was dazu führt, dass die Website nicht normal startet Es kann nicht normal darauf zugegriffen werden oder die Anwendung kann nicht normal ausgeführt werden. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie das Problem gelöst werden kann, dass der PHP-Dienst unter Ubuntu nicht normal gestartet werden kann, und es werden spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt, die den Lesern helfen, solche Fehler schnell zu beheben. 1. Überprüfen Sie die PHP-Konfigurationsdatei. Zuerst müssen wir die PHP-Konfigurationsdatei überprüfen
 So partitionieren Sie eine Festplatte
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
So partitionieren Sie eine Festplatte
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
So partitionieren Sie die Festplattenverwaltung Mit der kontinuierlichen Weiterentwicklung der Computertechnologie ist die Festplattenverwaltung zu einem unverzichtbaren Bestandteil unserer Computernutzung geworden. Als wichtiger Teil der Festplattenverwaltung kann die Festplattenpartitionierung eine Festplatte in mehrere Teile unterteilen, sodass wir Daten flexibler speichern und verwalten können. Wie kann man also die Festplattenverwaltung partitionieren? Im Folgenden werde ich Ihnen eine detaillierte Einführung geben. Zunächst müssen wir klarstellen, dass es nicht nur eine Möglichkeit gibt, Festplatten zu partitionieren. Wir können die geeignete Festplattenpartitionierungsmethode je nach Bedarf und Zweck flexibel auswählen. oft
 So verwenden Sie das Hyperf-Framework für die Cache-Verwaltung
Oct 21, 2023 am 08:36 AM
So verwenden Sie das Hyperf-Framework für die Cache-Verwaltung
Oct 21, 2023 am 08:36 AM
So verwenden Sie das Hyperf-Framework für die Cache-Verwaltung. Cache ist eines der wichtigen Mittel zur Verbesserung der Anwendungsleistung, und moderne Frameworks bieten uns bequemere Tools für die Cache-Verwaltung. In diesem Artikel wird die Verwendung des Hyperf-Frameworks für die Cache-Verwaltung vorgestellt und spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. Das Hyperf-Framework ist ein auf Swoole basierendes Hochleistungs-Framework. Es verfügt über eine Vielzahl integrierter Komponenten und Tools, einschließlich leistungsstarker Cache-Verwaltungsfunktionen. Das Hyperf-Framework unterstützt mehrere Cache-Treiber wie Redis und Memcach.




