 Backend-Entwicklung
Backend-Entwicklung
 C#.Net-Tutorial
C#.Net-Tutorial
 ASP.NET Core-Ausnahme- und Fehlerbehandlung (8)_Praktische Tipps
ASP.NET Core-Ausnahme- und Fehlerbehandlung (8)_Praktische Tipps
ASP.NET Core-Ausnahme- und Fehlerbehandlung (8)_Praktische Tipps
Dieser Artikel stellt hauptsächlich die relevanten Informationen zu ASP.NETKernausnahme und Fehlerbehandlung vor. Interessierte Freunde können darauf verweisen
In diesem Kapitel besprechen wir die Ausnahme- und Fehlerbehandlung. Wenn in einer ASP.NET Core-Anwendung ein Fehler auftritt, können Sie ihn auf verschiedene Arten behandeln. Schauen wir uns die Behandlung von Ausnahmen an, indem wir eineMiddleware hinzufügen, die uns bei der Fehlerbehandlung hilft.
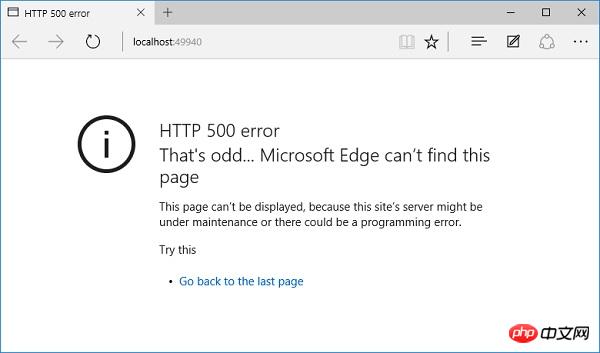
Um einen Fehler zu simulieren, gehen wir zur Anwendung, führen sie aus und sehen, wie sich das Programm verhält, wenn wir nureine Ausnahme auslösen.
using Microsoft.AspNet.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
namespace FirstAppDemo {
public class Startup {
public Startup() {
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.AddJsonFile("AppSettings.json");
Configuration = builder.Build();
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; set; }
// This method gets called by the runtime.
// Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application,
// visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
}
// This method gets called by the runtime.
// Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app) {
app.UseIISPlatformHandler();
app.UseRuntimeInfoPage();
app.Run(async (context) => {
throw new System.Exception("Throw Exception");
var msg = Configuration["message"];
await context.Response.WriteAsync(msg);
});
}
// Entry point for the application.
public static void Main(string[] args) => WebApplication.Run<Startup>(args);
}
}
// This method gets called by the runtime.
// Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app) {
app.UseIISPlatformHandler();
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseRuntimeInfoPage();
app.Run(async (context) => {
throw new System.Exception("Throw Exception");
var msg = Configuration["message"];
await context.Response.WriteAsync(msg);
});
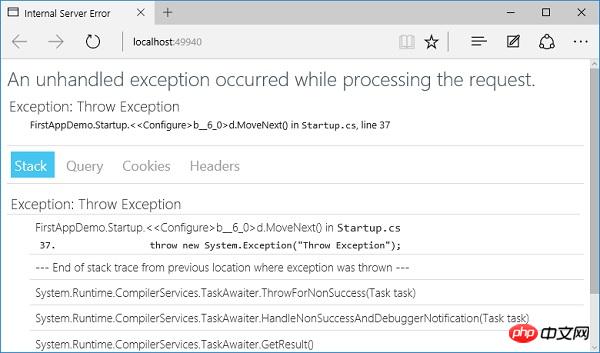
}
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonASP.NET Core-Ausnahme- und Fehlerbehandlung (8)_Praktische Tipps. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

Video Face Swap
Tauschen Sie Gesichter in jedem Video mühelos mit unserem völlig kostenlosen KI-Gesichtstausch-Tool aus!

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 Der Betriebsprozess des WIN10-Diensthosts belegt zu viel CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
Der Betriebsprozess des WIN10-Diensthosts belegt zu viel CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
1. Zuerst klicken wir mit der rechten Maustaste auf die leere Stelle der Taskleiste und wählen die Option [Task-Manager] oder klicken mit der rechten Maustaste auf das Startlogo und wählen dann die Option [Task-Manager]. 2. In der geöffneten Task-Manager-Oberfläche klicken wir ganz rechts auf die Registerkarte [Dienste]. 3. Klicken Sie in der geöffneten Registerkarte [Dienst] unten auf die Option [Dienst öffnen]. 4. Klicken Sie im sich öffnenden Fenster [Dienste] mit der rechten Maustaste auf den Dienst [InternetConnectionSharing(ICS)] und wählen Sie dann die Option [Eigenschaften]. 5. Ändern Sie im sich öffnenden Eigenschaftenfenster die Option „Öffnen mit“ in „Deaktiviert“, klicken Sie auf „Übernehmen“ und dann auf „OK“. 6. Klicken Sie auf das Startlogo, dann auf die Schaltfläche zum Herunterfahren, wählen Sie [Neustart] und schließen Sie den Neustart des Computers ab.
 Zusammenfassung häufig gestellter Fragen zum Importieren von Excel-Daten in MySQL: Wie gehe ich mit Fehlerprotokollproblemen um, die beim Importieren von Daten auftreten?
Sep 10, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Zusammenfassung häufig gestellter Fragen zum Importieren von Excel-Daten in MySQL: Wie gehe ich mit Fehlerprotokollproblemen um, die beim Importieren von Daten auftreten?
Sep 10, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Zusammenfassung häufig gestellter Fragen zum Importieren von Excel-Daten in MySQL: Wie gehe ich mit Fehlerprotokollproblemen um, die beim Importieren von Daten auftreten? Das Importieren von Excel-Daten in eine MySQL-Datenbank ist eine häufige Aufgabe. Allerdings stoßen wir bei diesem Prozess häufig auf verschiedene Fehler und Probleme. Eines davon ist das Problem mit dem Fehlerprotokoll. Wenn wir versuchen, Daten zu importieren, generiert das System möglicherweise ein Fehlerprotokoll, das die spezifischen Informationen über den aufgetretenen Fehler auflistet. Wie sollen wir also mit dem Fehlerprotokoll umgehen, wenn wir auf diese Situation stoßen? Zuerst müssen wir wissen, wie
 Eine Kurzanleitung zur CSV-Dateibearbeitung
Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:23 PM
Eine Kurzanleitung zur CSV-Dateibearbeitung
Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:23 PM
Lernen Sie schnell, wie Sie Dateien im CSV-Format öffnen und verarbeiten. Mit der kontinuierlichen Weiterentwicklung der Datenanalyse und -verarbeitung ist das CSV-Format zu einem der am weitesten verbreiteten Dateiformate geworden. Eine CSV-Datei ist eine einfache und leicht lesbare Textdatei mit verschiedenen, durch Kommas getrennten Datenfeldern. Ob in der akademischen Forschung, in der Geschäftsanalyse oder in der Datenverarbeitung – wir stoßen häufig auf Situationen, in denen wir CSV-Dateien öffnen und verarbeiten müssen. Die folgende Anleitung zeigt Ihnen, wie Sie schnell lernen, Dateien im CSV-Format zu öffnen und zu verarbeiten. Schritt 1: Verstehen Sie zunächst das CSV-Dateiformat.
 Erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit Sonderzeichen umgehen und einfache Anführungszeichen in PHP konvertieren
Mar 27, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit Sonderzeichen umgehen und einfache Anführungszeichen in PHP konvertieren
Mar 27, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Im PHP-Entwicklungsprozess ist der Umgang mit Sonderzeichen ein häufiges Problem, insbesondere bei der Zeichenfolgenverarbeitung werden Sonderzeichen häufig mit Escapezeichen versehen. Unter diesen ist die Umwandlung von Sonderzeichen in einfache Anführungszeichen eine relativ häufige Anforderung, da einfache Anführungszeichen in PHP eine gängige Methode zum Umschließen von Zeichenfolgen sind. In diesem Artikel erklären wir, wie man in PHP mit einfachen Anführungszeichen bei der Konvertierung von Sonderzeichen umgeht, und stellen spezifische Codebeispiele bereit. Zu den Sonderzeichen in PHP gehören unter anderem einfache Anführungszeichen ('), doppelte Anführungszeichen ("), Backslash () usw. In Zeichenfolgen
 Wie gehe ich mit dem Fehler java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError in Java um?
Aug 24, 2023 am 11:01 AM
Wie gehe ich mit dem Fehler java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError in Java um?
Aug 24, 2023 am 11:01 AM
Die Java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError-Ausnahme tritt zur Laufzeit auf, wenn ein Versuch, auf eine native Methode oder Bibliothek zuzugreifen oder diese zu laden, aufgrund einer Nichtübereinstimmung zwischen Architektur, Betriebssystem oder Bibliothekspfadkonfiguration und der referenzierten Methode fehlschlägt. Dies weist normalerweise darauf hin, dass eine Inkompatibilität mit der Architektur, der Betriebssystemkonfiguration oder der Pfadkonfiguration vorliegt, die den Erfolg verhindert. Normalerweise stimmt die lokale Bibliothek, auf die verwiesen wird, nicht mit der auf dem System installierten Bibliothek überein und ist zur Laufzeit nicht verfügbar Der Schlüssel liegt darin, dass die Bibliothek nativ mit Ihrem System kompatibel ist und über die Einstellung des Bibliothekspfads darauf zugegriffen werden kann. Sie sollten überprüfen, ob Bibliotheksdateien an den angegebenen Speicherorten vorhanden sind und die Systemanforderungen erfüllen. java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkErrorjava.lang
 Umgang mit XML- und JSON-Datenformaten in der C#-Entwicklung
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
Umgang mit XML- und JSON-Datenformaten in der C#-Entwicklung
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
Für den Umgang mit XML- und JSON-Datenformaten in der C#-Entwicklung sind spezifische Codebeispiele erforderlich. In der modernen Softwareentwicklung sind XML und JSON zwei weit verbreitete Datenformate. XML (Extensible Markup Language) ist eine Auszeichnungssprache zum Speichern und Übertragen von Daten, während JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) ein leichtes Datenaustauschformat ist. Bei der C#-Entwicklung müssen wir häufig XML- und JSON-Daten verarbeiten und verarbeiten. Dieser Artikel konzentriert sich auf die Verwendung von C# zum Verarbeiten und Anhängen dieser beiden Datenformate
 Wie kann ich Daten durch Aufrufen der API-Schnittstelle in einem PHP-Projekt crawlen und verarbeiten?
Sep 05, 2023 am 08:41 AM
Wie kann ich Daten durch Aufrufen der API-Schnittstelle in einem PHP-Projekt crawlen und verarbeiten?
Sep 05, 2023 am 08:41 AM
Wie kann ich Daten durch Aufrufen der API-Schnittstelle in einem PHP-Projekt crawlen und verarbeiten? 1. Einführung In PHP-Projekten müssen wir häufig Daten von anderen Websites crawlen und diese Daten verarbeiten. Viele Websites bieten API-Schnittstellen, und wir können Daten durch Aufrufen dieser Schnittstellen abrufen. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie Sie mit PHP die API-Schnittstelle zum Crawlen und Verarbeiten von Daten aufrufen. 2. Ermitteln Sie die URL und die Parameter der API-Schnittstelle. Bevor Sie beginnen, müssen Sie die URL der Ziel-API-Schnittstelle und die erforderlichen Parameter ermitteln.
 Wie kann das Problem gelöst werden, nachdem das Upgrade von Win7 auf Win10 fehlgeschlagen ist?
Dec 26, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Wie kann das Problem gelöst werden, nachdem das Upgrade von Win7 auf Win10 fehlgeschlagen ist?
Dec 26, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Wenn das von uns verwendete Betriebssystem Win7 ist, können einige Freunde beim Upgrade möglicherweise kein Upgrade von Win7 auf Win10 durchführen. Der Herausgeber meint, wir könnten es noch einmal mit einem Upgrade versuchen, um zu sehen, ob das Problem dadurch gelöst werden kann. Schauen wir uns an, was der Editor getan hat, um Einzelheiten zu erfahren. Was zu tun ist, wenn das Upgrade von Win7 auf Win10 fehlschlägt: 1. Es wird empfohlen, zuerst einen Treiber herunterzuladen, um zu prüfen, ob Ihr Computer auf Win10 aktualisiert werden kann Verwenden Sie nach dem Upgrade den Treibertest. Überprüfen Sie, ob Treiberanomalien vorliegen, und beheben Sie diese dann mit einem Klick. Methode 2: 1. Löschen Sie alle Dateien unter C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download. 2.win+R führen Sie „wuauclt.e“ aus





