
Der Code lautet wie folgt:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>#box{
width:200px;
height:200px;
position: absolute;
top:0;
left:200px;
background:lightblue;
}
.btn{
position:absolute;
top:200px;
left:100px;
height:50px;
}
.btn input{
display:inline-block;
margin-left:50px;
outline: none;
width:100px;
height:50px;
border:1px solid green;
cursor:pointer;
}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='box'></div>
<div class='btn'>
<input type="button" value='向左' id='btnLeft'>
<input type="button" value='向右' id='btnRight'>
</div>
<script>var oBox = document.getElementById("box");var minLeft = 0;var maxLeft = utils.win('clientWidth')-oBox.offsetWidth;var step = 5;var timer = null;function move(target){//target:告诉我要运动的目标位置 window.clearTimeout(timer);var curLeft = utils.css(oBox,"left");if(curLeft<target){//向右走if(curLeft+step>target){//边界utils.css(oBox,"left",target);return;
}
curLeft+=step;
utils.css(oBox,"left",curLeft)
}else if(curLeft>target){//向左走if(curLeft-step<target){//边界utils.css(oBox,"left",target);return;
}
curLeft-=step;
utils.css(oBox,"left",curLeft)
}else{//不需要运动return;
}// timer = window.setTimeout(move,10)//这里有一个问题,点击按钮第一次target的值是有的,但是第二次通过setTimeout执行的时候没有给target进行传值。是undefinedtimer = window.setTimeout(function(){
move(target);
},10)//这样使用匿名函数包裹一下,就解决了上面的问题,但是这样写性能不好,因为每一次到达时间的时候,都需要执行一次匿名函数(形成一个私有的作用域),在匿名函数中再执行move,但是move中需要用到的数据值在第一次执行的move方法中,需要把匿名函数形成的这个私有的作用域作为跳板找到之前的,这样就导致了匿名函数形成的这个私有的作用域不能销毁 }
document.getElementById('btnLeft').onclick = function(){
move(minLeft)
}
document.getElementById('btnRight').onclick = function(){
move(maxLeft)
} </script>
</body>
</html>Um das oben genannte Problem der schlechten Leistung zu lösen, ist das Folgende ein optimierter Code : Wird in einem Funktions-Wrapper verwendet, sodass nur ein durch die Move-Funktion erstellter privater Bereich nicht zerstört wird. Wenn _move ausgeführt wird, wird Move natürlich zerstört.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>#box{
width:200px;
height:200px;
position: absolute;
top:0;
left:200px;
background:lightblue;
}
.btn{
position:absolute;
top:200px;
left:100px;
height:50px;
}
.btn input{
display:inline-block;
margin-left:50px;
outline: none;
width:100px;
height:50px;
border:1px solid green;
cursor:pointer;
}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='box'></div>
<div class='btn'>
<input type="button" value='向左' id='btnLeft'>
<input type="button" value='向右' id='btnRight'>
</div>
<script>var oBox = document.getElementById("box");var minLeft = 0;var maxLeft = utils.win('clientWidth')-oBox.offsetWidth;var step = 5;var timer = null;function move(target){//target:告诉我要运动的目标位置 _move();function _move(){
window.clearTimeout(timer);var curLeft = utils.css(oBox,"left");if(curLeft<target){//向右走if(curLeft+step>target){//边界utils.css(oBox,"left",target);return;
}
curLeft+=step;
utils.css(oBox,"left",curLeft)
}else if(curLeft>target){//向左走if(curLeft-step<target){//边界utils.css(oBox,"left",target);return;
}
curLeft-=step;
utils.css(oBox,"left",curLeft)
}else{//不需要运动return;
}
timer = window.setTimeout(_move,10);
}
}
document.getElementById('btnLeft').onclick = function(){
move(minLeft)
}
document.getElementById('btnRight').onclick = function(){
move(maxLeft)
} </script>
</body>
</html>Hinweis: Damit das aktuelle Element nur eine Animation gleichzeitig ausführen kann (wenn die nächste Animation startet, stellen Sie zuerst den Timer ein der vorherigen Animation Clear): Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Variable, die den Timer-Rückgabewert für alle Animationen des aktuellen Elements empfängt, gemeinsam genutzt werden muss. Es gibt zwei Möglichkeiten: 1. Globaler Empfang (zum Beispiel das oben genannte). Code var timer = null) 2. Benutzerdefinierte Attribute zum Element hinzufügen (wie im Bild unten gezeigt)
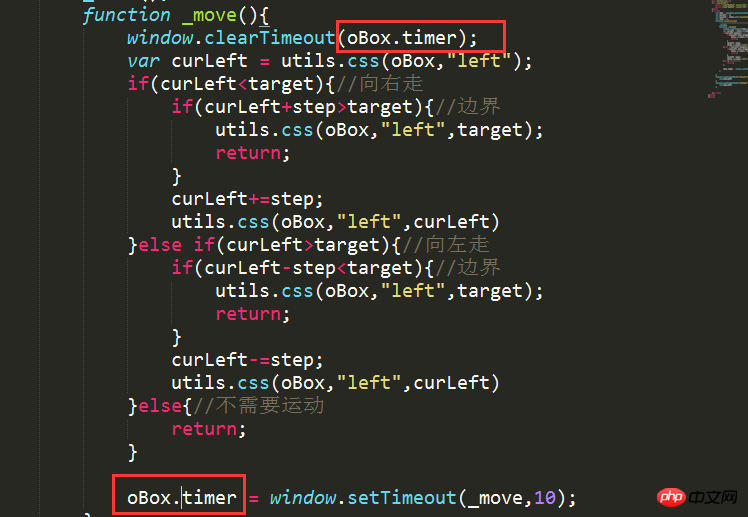
Zusammenfassung: Aus dem oben Gesagten können vier Regeln zur Optimierung abgeleitet werden:
1. Grenzbeurteilung plus Schrittgröße
2. Löschen ist nutzlos. Der Timer
3. Wenn die äußere Funktion Parameter übergeben muss, können Sie a verschachteln Funktionsschicht im Inneren, um die Anhäufung von Bereichen zu vermeiden.
4. Speichern Sie den Rückgabewert des Timers im benutzerdefinierten Attribut des Elements, um globale Variablenkonflikte und mehrere Animationsausführungen gleichzeitig zu verhindern
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonjs ---- Implementierung der Rebound-Animation. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!




