
In diesem Artikel wird hauptsächlich die Methode zum Konvertieren des gregorianischen Kalenders (Sonnenkalenders) in den Mondkalender (Mondkalender) in Python vorgestellt, wobei die Prinzipien des Mondkalenderalgorithmus und die Betriebsfähigkeiten im Zusammenhang mit Python-Datumsoperationen berücksichtigt werden können zum Folgenden
In diesem Artikel werden die Beispiele erläutert, mit denen Python die Methode zur Konvertierung des gregorianischen Kalenders (Sonnenkalender) in den Mondkalender (Mondkalender) implementiert. Teilen Sie es als Referenz mit allen. Die Details lauten wie folgt:
Zwei wichtige Punkte:
1 Die Tabellensuchmethode wird zum Konvertieren des gregorianischen Kalenders verwendet der Mondkalender (Zeile 126)
2. Werden astronomische Methoden für Sonnenbegriffe verwendet? (Zeile 176)
Laufdiagramm (der Hintergrund ist hao123 ewiger Kalender)
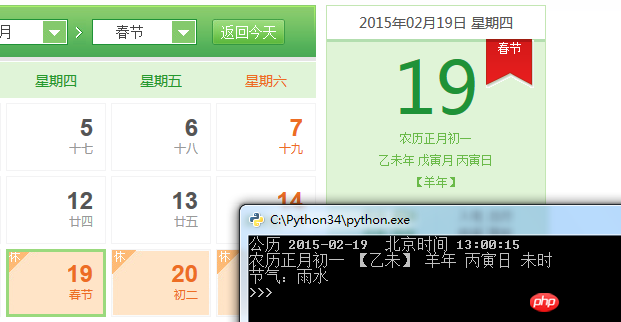

Quellcode:
# lunar.py
# 2015/02/27 罗兵
import datetime
class Lunar(object):
#******************************************************************************
# 下面为阴历计算所需的数据,为节省存储空间,所以采用下面比较变态的存储方法.
#******************************************************************************
#数组g_lunar_month_day存入阴历1901年到2050年每年中的月天数信息,
#阴历每月只能是29或30天,一年用12(或13)个二进制位表示,对应位为1表30天,否则为29天
g_lunar_month_day = [
0x4ae0, 0xa570, 0x5268, 0xd260, 0xd950, 0x6aa8, 0x56a0, 0x9ad0, 0x4ae8, 0x4ae0, #1910
0xa4d8, 0xa4d0, 0xd250, 0xd548, 0xb550, 0x56a0, 0x96d0, 0x95b0, 0x49b8, 0x49b0, #1920
0xa4b0, 0xb258, 0x6a50, 0x6d40, 0xada8, 0x2b60, 0x9570, 0x4978, 0x4970, 0x64b0, #1930
0xd4a0, 0xea50, 0x6d48, 0x5ad0, 0x2b60, 0x9370, 0x92e0, 0xc968, 0xc950, 0xd4a0, #1940
0xda50, 0xb550, 0x56a0, 0xaad8, 0x25d0, 0x92d0, 0xc958, 0xa950, 0xb4a8, 0x6ca0, #1950
0xb550, 0x55a8, 0x4da0, 0xa5b0, 0x52b8, 0x52b0, 0xa950, 0xe950, 0x6aa0, 0xad50, #1960
0xab50, 0x4b60, 0xa570, 0xa570, 0x5260, 0xe930, 0xd950, 0x5aa8, 0x56a0, 0x96d0, #1970
0x4ae8, 0x4ad0, 0xa4d0, 0xd268, 0xd250, 0xd528, 0xb540, 0xb6a0, 0x96d0, 0x95b0, #1980
0x49b0, 0xa4b8, 0xa4b0, 0xb258, 0x6a50, 0x6d40, 0xada0, 0xab60, 0x9370, 0x4978, #1990
0x4970, 0x64b0, 0x6a50, 0xea50, 0x6b28, 0x5ac0, 0xab60, 0x9368, 0x92e0, 0xc960, #2000
0xd4a8, 0xd4a0, 0xda50, 0x5aa8, 0x56a0, 0xaad8, 0x25d0, 0x92d0, 0xc958, 0xa950, #2010
0xb4a0, 0xb550, 0xb550, 0x55a8, 0x4ba0, 0xa5b0, 0x52b8, 0x52b0, 0xa930, 0x74a8, #2020
0x6aa0, 0xad50, 0x4da8, 0x4b60, 0x9570, 0xa4e0, 0xd260, 0xe930, 0xd530, 0x5aa0, #2030
0x6b50, 0x96d0, 0x4ae8, 0x4ad0, 0xa4d0, 0xd258, 0xd250, 0xd520, 0xdaa0, 0xb5a0, #2040
0x56d0, 0x4ad8, 0x49b0, 0xa4b8, 0xa4b0, 0xaa50, 0xb528, 0x6d20, 0xada0, 0x55b0, #2050
]
#数组gLanarMonth存放阴历1901年到2050年闰月的月份,如没有则为0,每字节存两年
g_lunar_month = [
0x00, 0x50, 0x04, 0x00, 0x20, #1910
0x60, 0x05, 0x00, 0x20, 0x70, #1920
0x05, 0x00, 0x40, 0x02, 0x06, #1930
0x00, 0x50, 0x03, 0x07, 0x00, #1940
0x60, 0x04, 0x00, 0x20, 0x70, #1950
0x05, 0x00, 0x30, 0x80, 0x06, #1960
0x00, 0x40, 0x03, 0x07, 0x00, #1970
0x50, 0x04, 0x08, 0x00, 0x60, #1980
0x04, 0x0a, 0x00, 0x60, 0x05, #1990
0x00, 0x30, 0x80, 0x05, 0x00, #2000
0x40, 0x02, 0x07, 0x00, 0x50, #2010
0x04, 0x09, 0x00, 0x60, 0x04, #2020
0x00, 0x20, 0x60, 0x05, 0x00, #2030
0x30, 0xb0, 0x06, 0x00, 0x50, #2040
0x02, 0x07, 0x00, 0x50, 0x03 #2050
]
START_YEAR = 1901
# 天干
gan = '甲乙丙丁戊己庚辛壬癸'
# 地支
zhi = '子丑寅卯辰巳午未申酉戌亥'
# 生肖
xiao = '鼠牛虎兔龙蛇马羊猴鸡狗猪'
# 月份
lm = '正二三四五六七八九十冬腊'
# 日份
ld = '初一初二初三初四初五初六初七初八初九初十十一十二十三十四十五十六十七十八十九二十廿一廿二廿三廿四廿五廿六廿七廿八廿九三十'
# 节气
jie = '小寒大寒立春雨水惊蛰春分清明谷雨立夏小满芒种夏至小暑大暑立秋处暑白露秋分寒露霜降立冬小雪大雪冬至'
def __init__(self, dt = None):
'''初始化:参数为datetime.datetime类实例,默认当前时间'''
self.localtime = dt if dt else datetime.datetime.today()
def sx_year(self): # 返回生肖年
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = self.ln_year() - 3 - 1 # 农历年份减3 (说明:补减1)
year = year % 12 # 模12,得到地支数
return self.xiao[year]
def gz_year(self): # 返回干支纪年
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = self.ln_year() - 3 - 1 # 农历年份减3 (说明:补减1)
G = year % 10 # 模10,得到天干数
Z = year % 12 # 模12,得到地支数
return self.gan[G] + self.zhi[Z]
def gz_month(self): # 返回干支纪月(未实现)
pass
def gz_day(self): # 返回干支纪日
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
C = ct.year // 100 #取世纪数,减一
y = ct.year % 100 #取年份后两位(若为1月、2月则当前年份减一)
y = y - 1 if ct.month == 1 or ct.month == 2 else y
M = ct.month #取月份(若为1月、2月则分别按13、14来计算)
M = M + 12 if ct.month == 1 or ct.month == 2 else M
d = ct.day #取日数
i = 0 if ct.month % 2 == 1 else 6 #取i (奇数月i=0,偶数月i=6)
#下面两个是网上的公式
# http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=MbTKmhrTHTOAz735gi37tEtwd29zqE9GJ92cZQZd0X8uFO5XgmyMKQru6aetzcGadqekzKd3nZHVS99rewya6q
# 计算干(说明:补减1)
G = 4 * C + C // 4 + 5 * y + y // 4 + 3 * (M + 1) // 5 + d - 3 - 1
G = G % 10
# 计算支(说明:补减1)
Z = 8 * C + C // 4 + 5 * y + y // 4 + 3 * (M + 1) // 5 + d + 7 + i - 1
Z = Z % 12
#返回 干支纪日
return self.gan[G] + self.zhi[Z]
def gz_hour(self): # 返回干支纪时(时辰)
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
#计算支
Z = round((ct.hour/2) + 0.1) % 12 # 之所以加0.1是因为round的bug!!
#返回 干支纪时(时辰)
return self.zhi[Z]
def ln_year(self): # 返回农历年
year, _, _ = self.ln_date()
return year
def ln_month(self): # 返回农历月
_, month, _ = self.ln_date()
return month
def ln_day(self): # 返回农历日
_, _, day = self.ln_date()
return day
def ln_date(self): # 返回农历日期整数元组(年、月、日)(查表法)
delta_days = self._date_diff()
#阳历1901年2月19日为阴历1901年正月初一
#阳历1901年1月1日到2月19日共有49天
if (delta_days < 49):
year = self.START_YEAR - 1
if (delta_days <19):
month = 11;
day = 11 + delta_days
else:
month = 12;
day = delta_days - 18
return (year, month, day)
#下面从阴历1901年正月初一算起
delta_days -= 49
year, month, day = self.START_YEAR, 1, 1
#计算年
tmp = self._lunar_year_days(year)
while delta_days >= tmp:
delta_days -= tmp
year += 1
tmp = self._lunar_year_days(year)
#计算月
(foo, tmp) = self._lunar_month_days(year, month)
while delta_days >= tmp:
delta_days -= tmp
if (month == self._get_leap_month(year)):
(tmp, foo) = self._lunar_month_days(year, month)
if (delta_days < tmp):
return (0, 0, 0)
return (year, month, delta_days+1)
delta_days -= tmp
month += 1
(foo, tmp) = self._lunar_month_days(year, month)
#计算日
day += delta_days
return (year, month, day)
def ln_date_str(self):# 返回农历日期字符串,形如:农历正月初九
_, month, day = self.ln_date()
return '农历{}月{}'.format(self.lm[month-1], self.ld[(day-1)*2:day*2])
def ln_jie(self): # 返回农历节气
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = ct.year
for i in range(24):
#因为两个都是浮点数,不能用相等表示
delta = self._julian_day() - self._julian_day_of_ln_jie(year, i)
if -.5 <= delta <= .5:
return self.jie[i*2:(i+1)*2]
return ''
#显示日历
def calendar(self):
pass
#######################################################
# 下面皆为私有函数
#######################################################
def _date_diff(self):
'''返回基于1901/01/01日差数'''
return (self.localtime - datetime.datetime(1901, 1, 1)).days
def _get_leap_month(self, lunar_year):
flag = self.g_lunar_month[(lunar_year - self.START_YEAR) // 2]
if (lunar_year - self.START_YEAR) % 2:
return flag & 0x0f
else:
return flag >> 4
def _lunar_month_days(self, lunar_year, lunar_month):
if (lunar_year < self.START_YEAR):
return 30
high, low = 0, 29
iBit = 16 - lunar_month;
if (lunar_month > self._get_leap_month(lunar_year) and self._get_leap_month(lunar_year)):
iBit -= 1
if (self.g_lunar_month_day[lunar_year - self.START_YEAR] & (1 << iBit)):
low += 1
if (lunar_month == self._get_leap_month(lunar_year)):
if (self.g_lunar_month_day[lunar_year - self.START_YEAR] & (1 << (iBit -1))):
high = 30
else:
high = 29
return (high, low)
def _lunar_year_days(self, year):
days = 0
for i in range(1, 13):
(high, low) = self._lunar_month_days(year, i)
days += high
days += low
return days
# 返回指定公历日期的儒略日
def _julian_day(self):
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = ct.year
month = ct.month
day = ct.day
if month <= 2:
month += 12
year -= 1
B = year / 100
B = 2 - B + year / 400
dd = day + 0.5000115740 #本日12:00后才是儒略日的开始(过一秒钟)*/
return int(365.25 * (year + 4716) + 0.01) + int(30.60001 * (month + 1)) + dd + B - 1524.5
# 返回指定年份的节气的儒略日数
def _julian_day_of_ln_jie(self, year, st):
s_stAccInfo =[
0.00, 1272494.40, 2548020.60, 3830143.80, 5120226.60, 6420865.80,
7732018.80, 9055272.60, 10388958.00, 11733065.40, 13084292.40, 14441592.00,
15800560.80, 17159347.20, 18513766.20, 19862002.20, 21201005.40, 22529659.80,
23846845.20, 25152606.00, 26447687.40, 27733451.40, 29011921.20, 30285477.60]
#已知1900年小寒时刻为1月6日02:05:00
base1900_SlightColdJD = 2415025.5868055555
if (st < 0) or (st > 24):
return 0.0
stJd = 365.24219878 * (year - 1900) + s_stAccInfo[st] / 86400.0
return base1900_SlightColdJD + stJd
# 测试
def test(ct=None):
ln = Lunar(ct)
print('公历 {} 北京时间 {}'.format(ln.localtime.date(), ln.localtime.time()))
print('{} 【{}】 {}年 {}日 {}时'.format(ln.ln_date_str(), ln.gz_year(), ln.sx_year(), ln.gz_day(), ln.gz_hour()))
print('节气:{}'.format(ln.ln_jie()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
ct = datetime.datetime(2015,2,19,13,0,15)
test(ct)Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo teilen Sie die Methode zum Konvertieren des Sonnenkalenders in den Mondkalender in Python. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!




