 Backend-Entwicklung
Backend-Entwicklung
 PHP-Tutorial
PHP-Tutorial
 Detaillierte Erläuterung der Beispiele für Auth-Module in Laravel
Detaillierte Erläuterung der Beispiele für Auth-Module in Laravel
Detaillierte Erläuterung der Beispiele für Auth-Module in Laravel
Dieser Artikel basiert auf der Analyse und dem Schreiben des Lokalisierungsmodulcodes der Laravel 5.4-Version. Ich hoffe, er kann jedem helfen, das Auth-Modul besser zu erlernen.
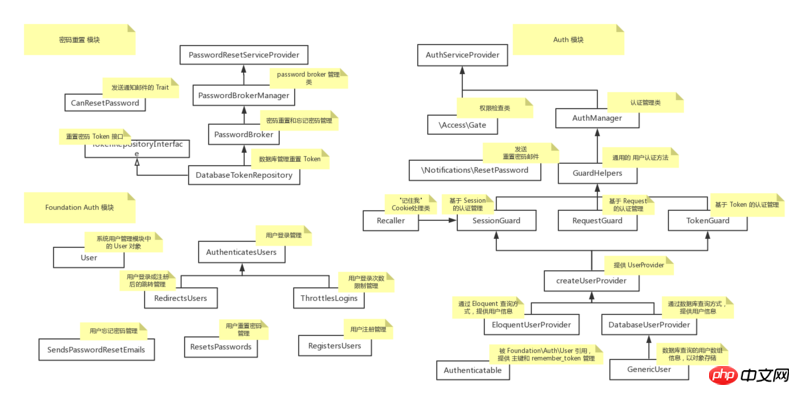
Modulzusammensetzung
Das Auth-Modul ist funktional in zwei Teile unterteilt: Benutzerauthentifizierung und Berechtigungsverwaltung. In Bezug auf die Dateizusammensetzung dient das IlluminateAuthPasswords-Verzeichnis zum Zurücksetzen von Passwörtern oder zur Verarbeitung vergessener Passwörter IlluminateAuth ist ein kleines Modul, das für die Benutzerauthentifizierung und Berechtigungsverwaltung verantwortlich ist und eine Reihe spezifischer Logikimplementierungen wie Anmeldung, Kennwortänderung, Kennwortzurücksetzung usw. bereitstellt Die verschiedenen Dateien des Auth-Moduls. Und geben Sie eine kurze Erklärung Token-Identifizierung während der Systeminteraktion.
Interpretation der Konfigurationsdatei
Anbieter stellen Benutzerdatenschnittstellen bereit, das Treiberobjekt und das Zielobjekt müssen hier markiert werden, der Schlüsselname Benutzer ist der Name einer Reihe von Anbietern, gesteuert durch eloquent, und modal ist AppUser::class; 🎜>
Guards-Teil dient zum Konfigurieren des Authentifizierungsverwaltungsteils. Es gibt zwei Authentifizierungsmethoden, eine heißt Web und die andere basiert auf der Sitzungsinteraktion und der Benutzer-ID Die Sitzungs-ID und der Benutzer werden im Benutzer-API-Authentifizierungstool abgefragt. Die Wertinteraktion basiert ebenfalls auf Benutzern als Anbieter.
return [ 'defaults' => [ 'guard' => 'web', ... ], 'guards' => [ 'web' => [ 'driver' => 'session', 'provider' => 'users', ], 'api' => [ 'driver' => 'token', 'provider' => 'users', ], ], 'providers' => [ 'users' => [ 'driver' => 'eloquent', 'model' => App\User::class, ], ], ], ];
Authentifizierung
- Sitzungsbindende Authentifizierungsinformationen:
- HTTP-Basisauthentifizierung, die Authentifizierungsinformationen werden in der platziert Anforderungsheader; auf nachfolgende Anforderungen wird über die Sitzungs-ID zugegriffen;
- Nur in der aktuellen Sitzung authentifizieren, und es werden keine Authentifizierungsinformationen in der Sitzung aufgezeichnet:
还有一些其他的认证方法:
检查是否存在认证用户:Auth::check()
获取当前认证用户:Auth::user()
退出系统:Auth::logout()
密码处理
配置解读
return [ 'defaults' => [ 'passwords' => 'users', ... ], 'passwords' => [ 'users' => [ 'provider' => 'users', 'table' => 'password_resets', 'expire' => 60, ], ], ]
从下往上,看配置;
passwords数组是重置密码的配置;users是配置方案的别名,包含三个元素:provider(提供用户的方案,是上面providers数组)、table(存放重置密码token的表)、expire(token过期时间)
default 项会设置默认的 passwords 重置方案;
重置密码的调用与实现
先看看Laravel的重置密码功能是怎么实现的:
public function reset(array $credentials, Closure $callback) {
// 验证用户名、密码和 token 是否有效
$user = $this->validateReset($credentials);
if (! $user instanceof CanResetPasswordContract) {
return $user;
}
$password = $credentials['password'];
// 回调函数执行修改密码,及持久化存储
$callback($user, $password);
// 删除重置密码时持久化存储保存的 token
$this->tokens->delete($user);
return static::PASSWORD_RESET;
}再看看Foundation\Auth模块封装的重置密码模块是怎么调用的:
// 暴露的重置密码 API
public function reset(Request $request) {
// 验证请求参数 token、email、password、password_confirmation
$this->validate($request, $this->rules(), $this->validationErrorMessages());
// 调用重置密码的方法,第二个参数是回调,做一些持久化存储工作
$response = $this->broker()->reset(
$this->credentials($request), function ($user, $password) {
$this->resetPassword($user, $password);
}
);
// 封装 Response
return $response == Password::PASSWORD_RESET
? $this->sendResetResponse($response)
: $this->sendResetFailedResponse($request, $response);
}
// 获取重置密码时的请求参数
protected function credentials(Request $request) {
return $request->only(
'email', 'password', 'password_confirmation', 'token'
);
}
// 重置密码的真实性验证后,进行的持久化工作
protected function resetPassword($user, $password) {
// 修改后的密码、重新生成 remember_token
$user->forceFill([
'password' => bcrypt($password),
'remember_token' => Str::random(60),
])->save();
// session 中的用户信息也进行重新赋值
$this->guard()->login($user);
}“忘记密码 => 发邮件 => 重置密码” 的大体流程如下:
点击“忘记密码”,通过路由配置,跳到“忘记密码”页面,页面上有“要发送的邮箱”这个字段要填写;
验证“要发送的邮箱”是否是数据库中存在的,如果存在,即向该邮箱发送重置密码邮件;
重置密码邮件中有一个链接(点击后会携带 token 到修改密码页面),同时数据库会保存这个 token 的哈希加密后的值;
填写“邮箱”,“密码”,“确认密码”三个字段后,携带 token 访问重置密码API,首页判断邮箱、密码、确认密码这三个字段,然后验证 token是否有效;如果是,则重置成功;
权限管理
权限管理是依靠内存空间维护的一个数组变量abilities来维护,结构如下:
$abilities = array(
'定义的动作名,比如以路由的 as 名(common.dashboard.list)' => function($user) {
// 方法的参数,第一位是 $user, 当前 user, 后面的参数可以自行决定
return true; // 返回 true 意味有权限, false 意味没有权限
},
......
);但只用 $abilities,会使用定义的那部分代码集中在一起太烦索,所以有policy策略类的出现;
policy策略类定义一组实体及实体权限类的对应关系,比如以文章举例:
有一个 Modal实体类叫 Post,可以为这个实体类定义一个PostPolicy权限类,在这个权限类定义一些动作为方法名;
class PostPolicy {
// update 权限,文章作者才可以修改
public function update(User $user, Post $post) {
return $user->id === $post->user_id;
}
}然后在ServiceProvider中注册,这样系统就知道,如果你要检查的类是Post对象,加上你给的动作名,系统会找到PostPolicy类的对应方法;
protected $policies = [ Post::class => PostPolicy::class, ];
怎么调用呢?
对于定义在abilities数组的权限:
当前用户是否具备common.dashboard.list权限:Gate::allows('common.dashboard.list')
当前用户是否具备common.dashboard.list权限:! Gate::denies('common.dashboard.list')
当前用户是否具备common.dashboard.list权限:$request->user()->can('common.dashboard.list')
当前用户是否具备common.dashboard.list权限:! $request->user()->cannot('common.dashboard.list')
指定用户是否具备common.dashboard.list权限:Gate::forUser($user)->allows('common.dashboard.list')
对于policy策略类调用的权限:
当前用户是否可以修改文章(Gate 调用):Gate::allows('update', $post)
当前用户是否可以修改文章(user 调用):$user->can('update', $post)
当前用户是否可以修改文章(用帮助函数):policy($post)->update($user, $post)
当前用户是否可以修改文章(Controller 类方法中调用):$this->authorize('update', $post);
当前用户是否可以修改文章(Controller 类同名方法中调用):$this->authorize($post);
指定用户是否可以修改文章(Controller 类方法中调用):$this->authorizeForUser($user, 'update', $post);
有用的技巧
获取当前系统注册的权限,包括两部分abilities和policies数组内容,代码如下:
$gate = app(\Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Access\Gate::class);
$reflection_gate = new ReflectionClass($gate);
$policies = $reflection_gate->getProperty('policies');
$policies->setAccessible(true);
// 获取当前注册的 policies 数组
dump($policies->getValue($gate));
$abilities = $reflection_gate->getProperty('abilities');
$abilities->setAccessible(true);
// 获取当前注册的 abilities 数组
dump($abilities->getValue($gate));相关推荐:
Laravel5.3如何通过公共的auth模块验证不同表中的用户
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonDetaillierte Erläuterung der Beispiele für Auth-Module in Laravel. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Vergleich der neuesten Versionen von Laravel und CodeIgniter
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Vergleich der neuesten Versionen von Laravel und CodeIgniter
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Die neuesten Versionen von Laravel 9 und CodeIgniter 4 bieten aktualisierte Funktionen und Verbesserungen. Laravel9 übernimmt die MVC-Architektur und bietet Funktionen wie Datenbankmigration, Authentifizierung und Template-Engine. CodeIgniter4 nutzt die HMVC-Architektur, um Routing, ORM und Caching bereitzustellen. In Bezug auf die Leistung sorgen das auf Dienstanbietern basierende Designmuster von Laravel9 und das leichte Framework von CodeIgniter4 für eine hervorragende Leistung. In praktischen Anwendungen eignet sich Laravel9 für komplexe Projekte, die Flexibilität und leistungsstarke Funktionen erfordern, während CodeIgniter4 für schnelle Entwicklung und kleine Anwendungen geeignet ist.
 Wie vergleichen sich die Datenverarbeitungsfunktionen in Laravel und CodeIgniter?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 01:34 PM
Wie vergleichen sich die Datenverarbeitungsfunktionen in Laravel und CodeIgniter?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 01:34 PM
Vergleichen Sie die Datenverarbeitungsfunktionen von Laravel und CodeIgniter: ORM: Laravel verwendet EloquentORM, das eine relationale Klassen-Objekt-Zuordnung bereitstellt, während CodeIgniter ActiveRecord verwendet, um das Datenbankmodell als Unterklasse von PHP-Klassen darzustellen. Abfrage-Builder: Laravel verfügt über eine flexible verkettete Abfrage-API, während der Abfrage-Builder von CodeIgniter einfacher und Array-basiert ist. Datenvalidierung: Laravel bietet eine Validator-Klasse, die benutzerdefinierte Validierungsregeln unterstützt, während CodeIgniter über weniger integrierte Validierungsfunktionen verfügt und eine manuelle Codierung benutzerdefinierter Regeln erfordert. Praxisfall: Beispiel einer Benutzerregistrierung zeigt Lar
 Was ist einsteigerfreundlicher: Laravel oder CodeIgniter?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:50 PM
Was ist einsteigerfreundlicher: Laravel oder CodeIgniter?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:50 PM
Für Anfänger bietet CodeIgniter eine sanftere Lernkurve und weniger Funktionen, deckt aber die Grundbedürfnisse ab. Laravel bietet einen größeren Funktionsumfang, weist jedoch eine etwas steilere Lernkurve auf. In Bezug auf die Leistung schneiden sowohl Laravel als auch CodeIgniter gut ab. Laravel verfügt über eine umfangreichere Dokumentation und aktive Community-Unterstützung, während CodeIgniter einfacher und leichtgewichtiger ist und über starke Sicherheitsfunktionen verfügt. Im praktischen Fall der Erstellung einer Blogging-Anwendung vereinfacht EloquentORM von Laravel die Datenmanipulation, während CodeIgniter mehr manuelle Konfiguration erfordert.
 Laravel – Handwerkerbefehle
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel – Handwerkerbefehle
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel – Artisan Commands – Laravel 5.7 bietet eine neue Möglichkeit, neue Befehle zu behandeln und zu testen. Es enthält eine neue Funktion zum Testen von Handwerkerbefehlen und die Demonstration wird unten erwähnt?
 Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Welches Framework ist besser für große Projekte?
Jun 04, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Welches Framework ist besser für große Projekte?
Jun 04, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Bei der Auswahl eines Frameworks für große Projekte haben Laravel und CodeIgniter jeweils ihre eigenen Vorteile. Laravel ist für Anwendungen auf Unternehmensebene konzipiert und bietet modularen Aufbau, Abhängigkeitsinjektion und einen leistungsstarken Funktionsumfang. CodeIgniter ist ein leichtes Framework, das sich eher für kleine bis mittelgroße Projekte eignet und Wert auf Geschwindigkeit und Benutzerfreundlichkeit legt. Für große Projekte mit komplexen Anforderungen und einer großen Anzahl von Benutzern sind die Leistung und Skalierbarkeit von Laravel besser geeignet. Für einfache Projekte oder Situationen mit begrenzten Ressourcen sind die leichten und schnellen Entwicklungsfunktionen von CodeIgniter idealer.
 Fragen und Antworten zum Design der PHP-Microservice-Architektur für Unternehmensanwendungen
May 07, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Fragen und Antworten zum Design der PHP-Microservice-Architektur für Unternehmensanwendungen
May 07, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Die Microservice-Architektur nutzt PHP-Frameworks (wie Symfony und Laravel) zur Implementierung von Microservices und folgt RESTful-Prinzipien und Standarddatenformaten zum Entwerfen von APIs. Microservices kommunizieren über Nachrichtenwarteschlangen, HTTP-Anfragen oder gRPC und nutzen Tools wie Prometheus und ELKStack zur Überwachung und Fehlerbehebung.
 Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Welches Framework ist besser für kleine Projekte?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Welches Framework ist besser für kleine Projekte?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Für kleine Projekte eignet sich Laravel, für größere Projekte, die starke Funktionalität und Sicherheit erfordern. CodeIgniter eignet sich für sehr kleine Projekte, die geringes Gewicht und Benutzerfreundlichkeit erfordern.
 Welche ist die bessere Template-Engine, Laravel oder CodeIgniter?
Jun 03, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Welche ist die bessere Template-Engine, Laravel oder CodeIgniter?
Jun 03, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Vergleichen Sie Laravel's Blade und die Twig-Vorlagen-Engine von CodeIgniter und wählen Sie je nach Projektanforderungen und persönlichen Vorlieben: Blade basiert auf der MVC-Syntax, die eine gute Codeorganisation und Vorlagenvererbung fördert. Twig ist eine Bibliothek eines Drittanbieters, die flexible Syntax, leistungsstarke Filter, erweiterten Support und eine Sicherheits-Sandbox bietet.



