js-Grundkenntnisse
Grundkonzepte von js
Lokale Variablen und globale Variablen von js

js Der Datentyp
var ist ein schwacher Datentyp, aber js kann seinen Datentyp erkennen
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function abc(){
var a=1;
var b="张三";
var c=true;
var d=new Date();
alert("a的数据类型:"+typeof(a));
alert("b的数据类型:"+typeof(b));
alert("c的数据类型:"+typeof(c));
alert("d的数据类型:"+typeof(d));
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" name="" id="" value="js的数据类型" onclick="abc()"/>
</body>Über js-Methoden
Schreiben von Methoden
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
console.log("不传参数");
}
function test1(a){
console.log("传1个参数"+a);
}
function test2(a,b){
console.log("传2个参数:" +a+"第二个参数:"+b);
}
function abc(a){
console.log("这是在abc的方法的值:"+a);
return a;
}
function test3(a){
var m=abc(a);
console.log("调用了别人的返回值的方法"+m)
}
</script>
<body>
<input type="button" name="" id="" value="不传参数的按钮" onclick="test()" /><br />
<input type="button" name="" id="" value="传1个参数" onclick="test1(12)" /><br />
<input type="button" name="" id="" value="传2个参数" onclick="test2(1,'张三')" /><br />
<input type="button" name="" id="" value="调用了一个有返回值的按钮" onclick="test3('张三')" /><br />
</body>Methodenabdeckung
Im Gegensatz zu Java gibt es in js Loaded kein Überschreiben von Methoden , nur Methoden decken
ab, solange die Methodennamen identisch sind. Egal wie viele Parameter vorhanden sind, js erkennt nur die letzte Methode (Methodenüberschreibung)
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function abc(a){
//var name='张三';//在方法体内部的局部变量,只能自己用
alert('这是第一个方法'+a);
}
function abc(){
alert('这是第二个方法');
}
function abc(){
alert('这是真的');
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- js中不会重载,只有方法覆盖啊 -->
<input type="button" value="方法重载和多态" onclick="abc(44)"/>
<!-- 输出:这是真的 -->
</body>JS-Datentypkonvertierung
Obwohl js nur eine Variable ist wird verwendet, um eine Variable zu beschreiben (schwacher Datentyp), aber das System kann ihren Datentyp identifizieren und auch eine Datentypkonvertierung durchführen
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
var x='12.3';
console.log("x的数据类型是:"+typeof(x));
var m=parseInt(x);
console.log("x转换后的数据类型是:"+typeof(m)+"值是:"+m);
var y='12.111';
console.log("y的数据类型是:"+typeof(x));
var m1=parseFloat(y);
console.log("y转换后的数据类型是:"+typeof(m1)+"值是:"+m1);
var z='3*4';
console.log("z的数据类型是:"+typeof(z)+"z的值是:"+z);
var m2=eval(z);
console.log("z计算后的数据类型是:"+typeof(m2)+"值是:"+m2);
var l=true;
console.log("l的数据类型是:"+typeof(l)+"l的值是:"+l);
var m3=l.toString();
console.log("l转换后的数据类型是:"+typeof(m3)+"值是:"+m3);
}
</script>
<body>
<input type="button" name="" id="" value="数据类型的转换" onclick="test()"/>
</body>Arithmetische Berechnungen in js
Die Betriebsregeln von js sind die gleichen wie bei Java (achten Sie jedoch besonders auf: x=+y)
function abc(){
var a='10';
var b='8';
console.log("b的值 "+b+" b的数据类型转换成 "+typeof(b)+" "+a)
/* =+ a先转换成number 再给a的值复制给b */
/* += 等价与 b+=a == b=b+a */
}
Auswählen Anweisungen und Schleifen Die Anweisung
wird abgekürzt: das Gleiche wie Java
js-Hauptobjekt
Fensterobjekt
Zeitintervall
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
console.log('test方法开始执行了');
/* 参数: 执行的方法, 等待的时间(毫秒单位) */
window.setTimeout("hello()",1000);
}
function hello(){
console.log('hello');
}
function test1(){
console.log('test1方法开始执行了');
window.setInterval("hello()",1000);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="等待一定时间,再执行" onclick="test()" /><br />
<input type="button" name="" id="" value="每间隔一定时间,反复执行" onclick="test1()"/>
</body>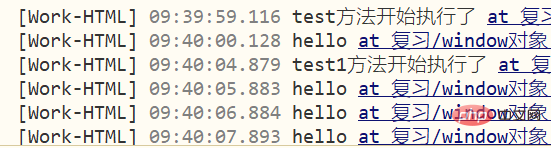
Verwendung eines Arrays
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
/* 第一种声明方式 */
var a=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
for (var i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
console.log("当前数组的角标:"+i+"当前的值:"+a[i]);
}
}
function test1(){
/* 第二种声明方式 */
var a=new Array();
a[0]=[1,2,3];
a[1]=['张三','李四','王五'];
a[2]=[2,5,1,3,6];
for (var i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
console.log("当前数组的角标:"+i+", "+j+"当前位置的值:"+a[i][j]);
}
}
}
function test2(){
/* join(分隔符) 将数组元素中加分割符号后串接并返回一个字符串 */
var a=[1,3,2,9,7,8,5];
console.log(a.join("*"));
/* reverse() 将数组元素按照原先相反位置存放 */
console.log("数组的取反:"+a.reverse());
/* slice(始[,终) 返回一个子数组 (前包后不包)*/
console.log(a.slice(1,4));
/* sort() 按照字母排序 */
console.log(a.sort());
}
</script>
<body>
<input type="button" value="一维数组的遍历" onclick="test()"/>
<input type="button" value="二维数组的遍历" onclick="test1()"/>
<input type="button" value="数组的操作" onclick="test2()"/>
</body>
Grundlegende String-Operationen
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
var a="hello world";
var index_a=a.indexOf("o");//第一个字母的位置
var index_b=a.indexOf("p");//没有就返回-1
console.log("o的角标位置:"+index_a);
/* 字符截取(前包后不包) */
var new_a=a.substring(1,3);
console.log(new_a);
/* 根据特定字符,格式化字符串 */
var ip='192.168.0.1';
var ip_array=ip.split(".");
for (var i = 0; i < ip_array.length; i++) {
console.log(ip_array[i]);
}
/* 大小写转换 */
var b='abc';
console.log(b.toUpperCase());
var c='ABC';
console.log(c.toLowerCase());
}
</script>
<body>
<input type="button" value="字符串处理" onclick="test()"/>
</body>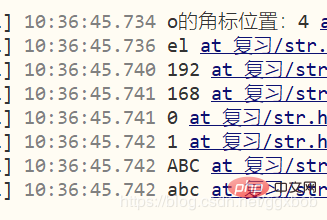
JS-Zeitformatierung
<script src="../js/dateFormat.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
var date=new Date();
console.log(date);
//方法1:引入控件
var sdate=date.format('yyyy-MM-dd');
var stime=date.format('yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')
console.log(sdate);
console.log(stime);
//方法2:
var y=date.getFullYear();//年
var mon=date.getMonth()+1;//月
var d=date.getDate();//日
var h=date.getHours();//时
var m=date.getMinutes();//分
var s=date.getSeconds();//秒
var weeks=date.getDay();
var weekday=["星期日","星期一","星期二","星期三","星期四","星期五","星期六"];
console.log(y+"年 "+mon+"月 "+d+"日 "+h+":"+m+":"+s+" "+weekday[weeks])
}
</script>
<body>
<input type="button" value="日期处理" onclick="test()" />
</body>
Empfohlenes Tutorial: „JS-Tutorial“
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonjs-Grundkenntnisse. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1384
1384
 52
52
 So implementieren Sie ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
So implementieren Sie ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
So implementieren Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem. Einführung: Mit der kontinuierlichen Weiterentwicklung der Technologie ist die Spracherkennungstechnologie zu einem wichtigen Bestandteil des Bereichs der künstlichen Intelligenz geworden. Das auf WebSocket und JavaScript basierende Online-Spracherkennungssystem zeichnet sich durch geringe Latenz, Echtzeit und plattformübergreifende Eigenschaften aus und hat sich zu einer weit verbreiteten Lösung entwickelt. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem implementieren.
 WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Implementierung von Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Implementierung von Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Realisierung von Echtzeit-Überwachungssystemen Einführung: Mit der rasanten Entwicklung der Internet-Technologie wurden Echtzeit-Überwachungssysteme in verschiedenen Bereichen weit verbreitet eingesetzt. Eine der Schlüsseltechnologien zur Erzielung einer Echtzeitüberwachung ist die Kombination von WebSocket und JavaScript. In diesem Artikel wird die Anwendung von WebSocket und JavaScript in Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen vorgestellt, Codebeispiele gegeben und deren Implementierungsprinzipien ausführlich erläutert. 1. WebSocket-Technologie
 Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Einführung in die Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Online-Bestellsystems in Echtzeit: Mit der Popularität des Internets und dem Fortschritt der Technologie haben immer mehr Restaurants damit begonnen, Online-Bestelldienste anzubieten. Um ein Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystem zu implementieren, können wir JavaScript und WebSocket-Technologie verwenden. WebSocket ist ein Vollduplex-Kommunikationsprotokoll, das auf dem TCP-Protokoll basiert und eine bidirektionale Kommunikation zwischen Client und Server in Echtzeit realisieren kann. Im Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystem, wenn der Benutzer Gerichte auswählt und eine Bestellung aufgibt
 So implementieren Sie ein Online-Reservierungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
So implementieren Sie ein Online-Reservierungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
So implementieren Sie ein Online-Reservierungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript. Im heutigen digitalen Zeitalter müssen immer mehr Unternehmen und Dienste Online-Reservierungsfunktionen bereitstellen. Es ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, ein effizientes Online-Reservierungssystem in Echtzeit zu implementieren. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Reservierungssystem implementieren, und es werden spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. 1. Was ist WebSocket? WebSocket ist eine Vollduplex-Methode für eine einzelne TCP-Verbindung.
 JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems Einführung: Heutzutage ist die Genauigkeit von Wettervorhersagen für das tägliche Leben und die Entscheidungsfindung von großer Bedeutung. Mit der Weiterentwicklung der Technologie können wir genauere und zuverlässigere Wettervorhersagen liefern, indem wir Wetterdaten in Echtzeit erhalten. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit JavaScript und WebSocket-Technologie ein effizientes Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystem aufbauen. In diesem Artikel wird der Implementierungsprozess anhand spezifischer Codebeispiele demonstriert. Wir
 Einfaches JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie den HTTP-Statuscode
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Einfaches JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie den HTTP-Statuscode
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie HTTP-Statuscode. Es sind spezifische Codebeispiele erforderlich. Vorwort: Bei der Webentwicklung ist häufig die Dateninteraktion mit dem Server erforderlich. Bei der Kommunikation mit dem Server müssen wir häufig den zurückgegebenen HTTP-Statuscode abrufen, um festzustellen, ob der Vorgang erfolgreich ist, und die entsprechende Verarbeitung basierend auf verschiedenen Statuscodes durchführen. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit JavaScript HTTP-Statuscodes abrufen und einige praktische Codebeispiele bereitstellen. Verwenden von XMLHttpRequest
 So verwenden Sie insertBefore in Javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
So verwenden Sie insertBefore in Javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Verwendung: In JavaScript wird die Methode insertBefore() verwendet, um einen neuen Knoten in den DOM-Baum einzufügen. Diese Methode erfordert zwei Parameter: den neuen Knoten, der eingefügt werden soll, und den Referenzknoten (d. h. den Knoten, an dem der neue Knoten eingefügt wird).
 JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Bildverarbeitungssystems
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Bildverarbeitungssystems
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript ist eine in der Webentwicklung weit verbreitete Programmiersprache, während WebSocket ein Netzwerkprotokoll für die Echtzeitkommunikation ist. Durch die Kombination der leistungsstarken Funktionen beider können wir ein effizientes Echtzeit-Bildverarbeitungssystem erstellen. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie dieses System mithilfe von JavaScript und WebSocket implementiert wird, und es werden spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. Zunächst müssen wir die Anforderungen und Ziele des Echtzeit-Bildverarbeitungssystems klären. Angenommen, wir haben ein Kameragerät, das Bilddaten in Echtzeit sammeln kann




