Prinzipien und Verwendung von Javascript PJAX

pjax ist pushState + Ajax, das zur einfachen Verwendung in eine jQuery-Erweiterung gekapselt ist. pjax wird hauptsächlich verwendet, um das Problem zu lösen, dass die HTML-Seite die URL teilweise aktualisiert und nicht aktualisiert und kein Vor- und Zurückspulen unterstützt, um die Benutzererfahrung zu verbessern.
pjax-Prinzip
Die Implementierung von pjax wird durch die Kombination der neuen Funktionen von pushState() und replaceState() von HTML5 mit Ajax implementiert. pushState() und replaceState() werden zum Betreiben des State-Objekts verwendet, das historische Datensätze hinzufügen und ändern kann, wodurch die URL aktualisiert wird und Vorwärts- und Rückwärtsoperationen bereitgestellt werden. Ajax implementiert das asynchrone Laden von Daten und eine teilweise Aktualisierung.
Workflow-Diagramm
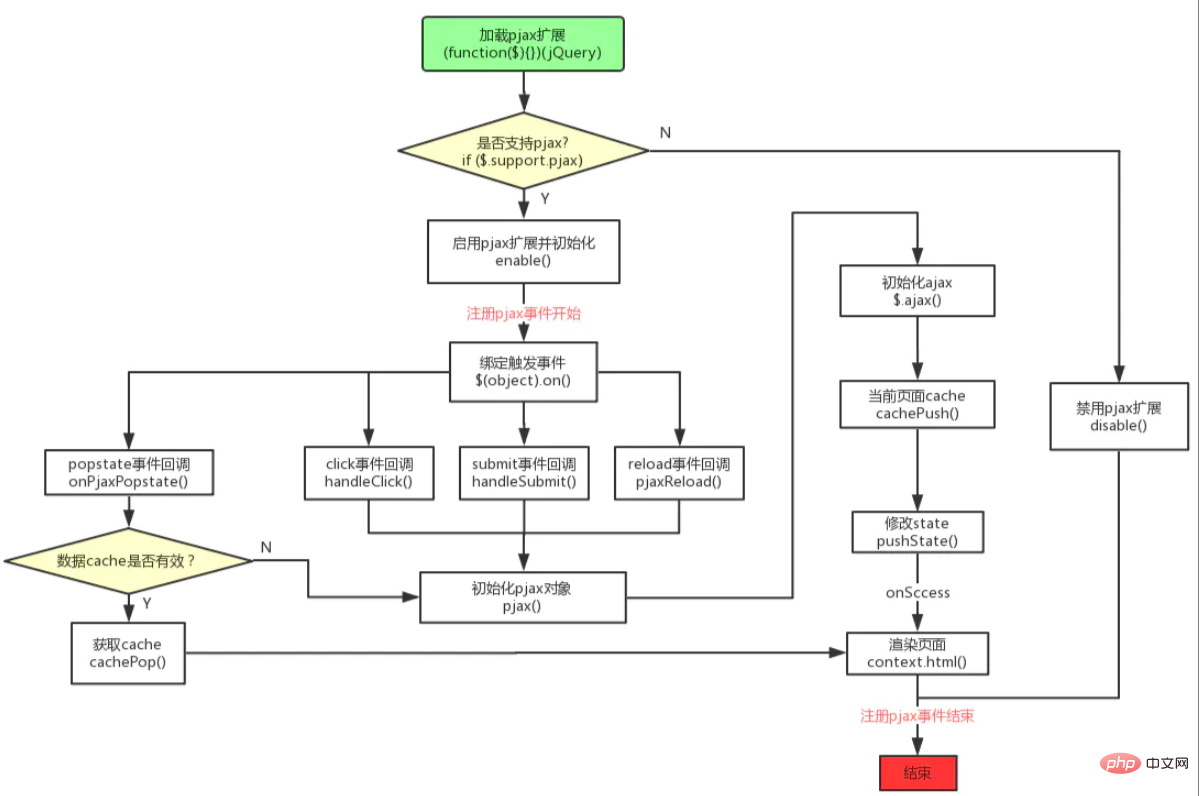
Quellcode-Analyse
- pjax-Unterstützungsbeurteilung
(function($){
$.support.pjax =
window.history && window.history.pushState && window.history.replaceState &&
// pushState isn't reliable on iOS until 5.
!navigator.userAgent.match(/((iPod|iPhone|iPad).+\bOS\s+[1-4]\D|WebApps\/.+CFNetwork)/)
if ($.support.pjax){
enable() //启用
} else {
disable() //禁用
}
})(jQuery)- enable()
function enable() {
$.fn.pjax = fnPjax //注册jQuery的pjax方法
$.pjax = pjax //注册pjax对象
$.pjax.enable = $.noop
$.pjax.disable = disable
$.pjax.click = handleClick //注册click回调
$.pjax.submit = handleSubmit //注册submit回调
$.pjax.reload = pjaxReload //注册reload回调
$.pjax.defaults = {} //设置默认值
$(window).on('popstate.pjax', onPjaxPopstate) //绑定popstate事件回调
}$.noop ist eine leere Methode, die nichts tut, das heißt function(){}. popstate.pjax ist das Namespace-Schreiben von JS-Ereignissen und popstate ist der Ereignistyp. Immer wenn sich der aktivierte Verlauf ändert (der Browser betätigt die Vorwärts- und Zurück-Schaltflächen, ruft die Methode back() oder go() auf), wird popstate angezeigt ausgelöst. Ereignis, aber der Aufruf von pushState() und replaceState() löst das Popstate-Ereignis nicht aus. .pjax ist der Namespace des Ereignisses, wodurch es einfach ist, die Ereignisantwort des angegebenen Namespace zu entbinden. Er wird häufig beim Binden anonymer Funktionen verwendet, wie zum Beispiel: this.on('click.pjax', selector, function(event){}).
- fnPjax()
Diese Methode gibt ein jQuery-Objekt zurück, das $.fn.pjax entspricht.
return this.on('click.pjax', selector, function(event) {
//获取pjax配置信息
options = optionsFor(container, options)
//自动绑定click事件响应
return this.on('click.pjax', selector, function(event) {
var opts = options
if (!opts.container) {
opts = $.extend({}, options)
//如果不配置container,则默认获取data-pjax属性值对应的
opts.container = $(this).attr('data-pjax')
}
handleClick(event, opts) //调用click回调
})
}- pjax()
// Use it just like $.ajax:
//
// var xhr = $.pjax({ url: this.href, container: '#main' })
// console.log( xhr.readyState )
//
// Returns whatever $.ajax returns.
function pjax(options) {
//获取设置
options = $.extend(true, {}, $.ajaxSettings, pjax.defaults, options)
//判断检测
if (containerType !== 'string')
/**
* ajax响应回调注册
*/
//beforeSend
options.beforeSend = function(xhr, settings) {
//设置pjax头信息,供后端做兼容处理
xhr.setRequestHeader('X-PJAX', 'true')
xhr.setRequestHeader('X-PJAX-Container', options.container)
//设置超时
}
//complete
options.complete = function(xhr, textStatus) {
//绑定pjax:complete事件
fire('pjax:complete', [xhr, textStatus, options])
//绑定pjax:end事件
fire('pjax:end', [xhr, options])
}
//error
options.error = function(xhr, textStatus, errorThrown) {
//绑定pjax:error事件
fire('pjax:error', [xhr, textStatus, errorThrown, options])
}
//success,重点
options.success = function(data, status, xhr) {
//判断检测
if (currentVersion && latestVersion && currentVersion !== latestVersion)
... ...
window.history.replaceState(pjax.state, container.title, container.url)
//绑定pjax:beforeReplace事件
fire('pjax:beforeReplace', [container.contents, options], {
state: pjax.state,
previousState: previousState
})
//渲染页面
context.html(container.contents)
//绑定pjax:success事件
fire('pjax:success', [data, status, xhr, options])
}
//初始化ajax
var xhr = pjax.xhr = $.ajax(options)
if (xhr.readyState > 0) {
//缓存页面cache
cachePush(pjax.state.id, [options.container, cloneContents(context)])
//pushState
window.history.pushState(null, "", options.requestUrl)
//绑定pjax:start事件
fire('pjax:start', [xhr, options])
//绑定pjax:send事件
fire('pjax:send', [xhr, options])
}
//返回jQuery对象
return pjax.xhr
}- Callback-Funktion
1) handleClick()
// Examples
//
// $(document).on('click', 'a', $.pjax.click)
// // is the same as
// $(document).pjax('a')
//
// Returns nothing.
function handleClick(event, container, options) {
options = optionsFor(container, options)
//环境检测
if (link.tagName.toUpperCase() !== 'A')
... ...
//绑定pjax:click事件
var clickEvent = $.Event('pjax:click')
$link.trigger(clickEvent, [opts])
//执行pjax
pjax(opts)
//成功则阻止默认行为
event.preventDefault()
//绑定pjax:clicked事件
$link.trigger('pjax:clicked', [opts])
}2 ) handleSubmit()
// Examples
//
// $(document).on('submit', 'form', function(event) {
// $.pjax.submit(event, '[data-pjax-container]')
// })
//
// Returns nothing.
function handleSubmit(event, container, options) {
options = optionsFor(container, options)
//环境检测
if (form.tagName.toUpperCase() !== 'FORM')
... ...
//默认配置
var defaults = {
type: ($form.attr('method') || 'GET').toUpperCase(),
url: $form.attr('action'),
container: $form.attr('data-pjax'),
target: form
}
if (defaults.type !== 'GET' && window.FormData !== undefined) {
//POST时data域
defaults.data = new FormData(form)
}
//执行pjax
pjax($.extend({}, defaults, options))
//成功则阻止默认行为
event.preventDefault()
}3) pjaxReload()
// Reload current page with pjax.
function pjaxReload(container, options) {
var defaults = {
//当前url
url: window.location.href,
push: false,
replace: true,
scrollTo: false
}
//执行pjax
return pjax($.extend(defaults, optionsFor(container, options)))
}4) onPjaxPopstate()
// popstate handler takes care of the back and forward buttons
function onPjaxPopstate(event) {
//环境监测
if (state && state.container)
... ...
//获取页面cache
var cache = cacheMapping[state.id] || []
//绑定pjax:popstate事件
var popstateEvent = $.Event('pjax:popstate', {
state: state,
direction: direction
})
container.trigger(popstateEvent)
if (contents) {
//有页面cache,直接渲染页面
//绑定pjax:start事件
container.trigger('pjax:start', [null, options])
//绑定pjax:beforeReplace事件
var beforeReplaceEvent = $.Event('pjax:beforeReplace', {
state: state,
previousState: previousState
})
container.trigger(beforeReplaceEvent, [contents, options])
//渲染页面
container.html(contents)
//绑定pjax:end事件
container.trigger('pjax:end', [null, options])
} else {
//无页面cache,执行pjax
pjax(options)
}
}pjax using
Nach der obigen Analyse kann es Seien Sie sehr einfach. Es ist jetzt einfach, pjax zu verwenden.
Client
pjax unterstützt die Optionskonfiguration und den Ereignismechanismus.
- Optionenkonfiguration
| 参数名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | 650 | ajax 超时时间(单位 ms),超时后会执行默认的页面跳转,所以超时时间不应过短,不过一般不需要设置 |
| push | true | 使用 window.history.pushState 改变地址栏 url(会添加新的历史记录) |
| replace | false | 使用 window.history.replaceState 改变地址栏 url(不会添加历史记录) |
| maxCacheLength | 20 | 缓存的历史页面个数(pjax 加载新页面前会把原页面的内容缓存起来,缓存加载后其中的脚本会再次执行) |
| version | 是一个函数,返回当前页面的 pjax-version,即页面中 标签内容。使用 response.setHeader(“X-PJAX-Version”, “”) 设置与当前页面不同的版本号,可强制页面跳转而不是局部刷新 | |
| scrollTo | 0 | 页面加载后垂直滚动距离(与原页面保持一致可使过度效果更平滑) |
| type | “GET” | ajax 的参数,http 请求方式 |
| dataType | “html” | ajax 的参数,响应内容的 Content-Type |
| container | 用于查找容器的 CSS 选择器,[container] 参数没有指定时使用 | |
| url | link.href | 要跳转的连接,默认 a 标签的 href 属性 |
| fragment | 使用响应内容的指定部分(css 选择器)填充页面,服务端不进行处理导致全页面请求的时候需要使用该参数,简单的说就是对请求到的页面做截取 |
- pjax事件
为了方便扩展,pjax 支持一些预定义的事件。
| 事件名 | 支持取消 | 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pjax:click | ✔ | options | 点击按钮时触发。可调用 e.preventDefault() 取消 pjaxa |
| pjax:beforeSend | ✔ | xhr, options | ajax 执行 beforeSend 函数时触发,可在回调函数中设置额外的请求头参数。可调用 e.preventDefault() 取消 pjax |
| pjax:start | xhr, options | pjax 开始(与服务器连接建立后触发) | |
| pjax:send | xhr, options | pjax:start之后触发 | |
| pjax:clicked | options | ajax 请求开始后触发 | |
| pjax:beforeReplace | contents, options | ajax请求成功,内容替换渲染前触发 | |
| pjax:success | data, status, xhr, options | 内容替换成功后触发 | |
| pjax:timeout | ✔ | xhr, options | ajax 请求超时后触发。可调用 e.preventDefault() 继续等待 ajax 请求结束 |
| pjax:error | ✔ | xhr, textStatus, error, options | ajax 请求失败后触发。默认失败后会跳转 url,如要阻止跳转可调用 e.preventDefault() |
| pjax:complete | xhr, textStatus, options | ajax请求结束后触发,不管成功还是失败 | |
| pjax:end | xhr, options | pjax所有事件结束后触发 | |
| pjax:popstate | forward / back(前进/后退) | ||
| pjax:start | null, options | pjax开始 | |
| pjax:beforeReplace | contents, options | 内容替换渲染前触发,如果缓存了要导航页面的内容则使用缓存,否则使用pjax加载 | |
| pjax:end | null, options | pjax结束 |
客户端通过以下 2 个步骤就可以使用 pjax :
- 引入jquery 和 jquery.pjax.js
- 注册事件
JS
<script></script>
/**
* 方式1 监听按钮父节点事件
*/
$(document).pjax(selector, [container], options);
/**
* 方式2 直接监听按钮,可以不用指定容器,默认使用按钮的data-pjax属性值查找容器
*/
$("a[data-pjax]").pjax();
/**
* 方式3 主动绑定点击事件监听
*/
$(document).on('click', 'a', $.pjax.click);
$(document).on('click', 'a', function(event) {
//获取container
var container = $(this).closest('[data-pjax-container]');
//click回调
$.pjax.click(event, container);
});
/**
* 方式4 主动绑定表单提交事件监听
*/
$(document).on('submit', 'form', function(event) {
//获取container
var container = $(this).closest('[data-pjax-container]');
//submit回调
$.pjax.submit(event, container);
});
/**
* 方式5 加载内容到指定容器
*/
$.pjax({url: this.href, container: '#main'});
/**
* 方式6 重新加载当前页面容器的内容
*/
$.pjax.reload('#container');YII
在 Yii 中,已经将 pjax 封装成了 widgets,故在渲染时如下使用即可:
//view <?php Pjax::begin(); ?> ... ... <?php Pjax::end(); ?>
pjax 封装成的 widgets 源码文件widgets/Pjax.php ,事件注册部分如下:
public function registerClientScript()
{
//a标签的click
if ($this->linkSelector !== false) {
$linkSelector = Json::htmlEncode($this->linkSelector !== null ? $this->linkSelector : '#' . $id . ' a');
$js .= "jQuery(document).pjax($linkSelector, \"#$id\", $options);";
}
//form表单的submit
if ($this->formSelector !== false) {
$formSelector = Json::htmlEncode($this->formSelector !== null ? $this->formSelector : '#' . $id . ' form[data-pjax]');
$submitEvent = Json::htmlEncode($this->submitEvent);
$js .= "\njQuery(document).on($submitEvent, $formSelector, function (event) {jQuery.pjax.submit(event, '#$id', $options);});";
}
$view->registerJs($js);
}服务端
由于只是 HTML5 支持 pjax,所以后端需要做兼容处理。通过 X-PJAX 头信息可得知客户端是否支持 pjax,如果支持,则只返回局部页面,否则 a 链接默认跳转,返回整个页面。
/**
* IndexController示例
*/
public function actionIndex() {
$dataProvider = new CActiveDataProvider('Article', array(
'criteria' => array('order' => 'create_time DESC')
));
//存在X-Pjax头,支持pjax
if (Yii::$app->getRequest()->getHeaders()->get('X-Pjax')) {
//返回局部页面
$this->renderPartial('index', array(
'dataProvider' => $dataProvider,
));
} else {
//返回整个页面
$this->render('index', array(
'dataProvider' => $dataProvider,
));
}
}pjax失效情况
在以下 9 种情况时候 pjax 会失效,源码部分如下:
//click回调
function handleClick(event, container, options) {
...
// 1. 点击的事件源不是a标签。a标签可以对旧版本浏览器的兼容,因此不建议使用其他标签注册事件
if (link.tagName.toUpperCase() !== 'A')
throw "$.fn.pjax or $.pjax.click requires an anchor element"
// 2. 使用鼠标滚轮点击、点击超链接的同时按下Shift、Ctrl、Alt和Meta
if (event.which > 1 || event.metaKey || event.ctrlKey || event.shiftKey || event.altKey)
return
// 3. 跨域
if (location.protocol !== link.protocol || location.hostname !== link.hostname)
return
// 4. 当前页面的锚点定位
if (link.href.indexOf('#') > -1 && stripHash(link) == stripHash(location))
return
// 5. 已经阻止元素发生默认的行为
if (event.isDefaultPrevented())
return
...
var clickEvent = $.Event('pjax:click')
$(link).trigger(clickEvent, [opts])
// 6. pjax:click事件回调中已经阻止元素发生默认的行为
if (!clickEvent.isDefaultPrevented()) {
pjax(opts)
}
}
//pjax
function pjax(options) {
options.beforeSend = function(xhr, settings) {
//7. ajx超时
timeoutTimer = setTimeout(function() {
if (fire('pjax:timeout', [xhr, options]))
xhr.abort('timeout')
}, settings.timeout)
}
options.success = function(data, status, xhr) {
//8. 当前页面和请求的新页面版本不一致
if (currentVersion && latestVersion && currentVersion !== latestVersion) {
return
}
//9. ajax失败
context.html(container.contents)
}其他方案
除了使用 pjax 解决局部刷新并支持前进和后退问题外,也可以使用 browserstate/history.js + ajax 方案来实现
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonPrinzipien und Verwendung von Javascript PJAX. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1376
1376
 52
52
 So implementieren Sie ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
So implementieren Sie ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
So implementieren Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem. Einführung: Mit der kontinuierlichen Weiterentwicklung der Technologie ist die Spracherkennungstechnologie zu einem wichtigen Bestandteil des Bereichs der künstlichen Intelligenz geworden. Das auf WebSocket und JavaScript basierende Online-Spracherkennungssystem zeichnet sich durch geringe Latenz, Echtzeit und plattformübergreifende Eigenschaften aus und hat sich zu einer weit verbreiteten Lösung entwickelt. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem implementieren.
 Wesentliche Tools für die Aktienanalyse: Lernen Sie die Schritte zum Zeichnen von Kerzendiagrammen mit PHP und JS
Dec 17, 2023 pm 06:55 PM
Wesentliche Tools für die Aktienanalyse: Lernen Sie die Schritte zum Zeichnen von Kerzendiagrammen mit PHP und JS
Dec 17, 2023 pm 06:55 PM
Wesentliche Tools für die Aktienanalyse: Lernen Sie die Schritte zum Zeichnen von Kerzendiagrammen in PHP und JS. Mit der rasanten Entwicklung des Internets und der Technologie ist der Aktienhandel für viele Anleger zu einer wichtigen Möglichkeit geworden. Die Aktienanalyse ist ein wichtiger Teil der Anlegerentscheidung, und Kerzendiagramme werden häufig in der technischen Analyse verwendet. Wenn Sie lernen, wie man Kerzendiagramme mit PHP und JS zeichnet, erhalten Anleger intuitivere Informationen, die ihnen helfen, bessere Entscheidungen zu treffen. Ein Candlestick-Chart ist ein technischer Chart, der Aktienkurse in Form von Candlesticks anzeigt. Es zeigt den Aktienkurs
 Empfohlen: Ausgezeichnetes JS-Open-Source-Projekt zur Gesichtserkennung und -erkennung
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Empfohlen: Ausgezeichnetes JS-Open-Source-Projekt zur Gesichtserkennung und -erkennung
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Die Technologie zur Gesichtserkennung und -erkennung ist bereits eine relativ ausgereifte und weit verbreitete Technologie. Derzeit ist JS die am weitesten verbreitete Internetanwendungssprache. Die Implementierung der Gesichtserkennung und -erkennung im Web-Frontend hat im Vergleich zur Back-End-Gesichtserkennung Vor- und Nachteile. Zu den Vorteilen gehören die Reduzierung der Netzwerkinteraktion und die Echtzeiterkennung, was die Wartezeit des Benutzers erheblich verkürzt und das Benutzererlebnis verbessert. Die Nachteile sind: Es ist durch die Größe des Modells begrenzt und auch die Genauigkeit ist begrenzt. Wie implementiert man mit js die Gesichtserkennung im Web? Um die Gesichtserkennung im Web zu implementieren, müssen Sie mit verwandten Programmiersprachen und -technologien wie JavaScript, HTML, CSS, WebRTC usw. vertraut sein. Gleichzeitig müssen Sie auch relevante Technologien für Computer Vision und künstliche Intelligenz beherrschen. Dies ist aufgrund des Designs der Webseite erwähnenswert
 WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Implementierung von Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Implementierung von Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Realisierung von Echtzeit-Überwachungssystemen Einführung: Mit der rasanten Entwicklung der Internet-Technologie wurden Echtzeit-Überwachungssysteme in verschiedenen Bereichen weit verbreitet eingesetzt. Eine der Schlüsseltechnologien zur Erzielung einer Echtzeitüberwachung ist die Kombination von WebSocket und JavaScript. In diesem Artikel wird die Anwendung von WebSocket und JavaScript in Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen vorgestellt, Codebeispiele gegeben und deren Implementierungsprinzipien ausführlich erläutert. 1. WebSocket-Technologie
 So implementieren Sie ein Online-Reservierungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
So implementieren Sie ein Online-Reservierungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
So implementieren Sie ein Online-Reservierungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript. Im heutigen digitalen Zeitalter müssen immer mehr Unternehmen und Dienste Online-Reservierungsfunktionen bereitstellen. Es ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, ein effizientes Online-Reservierungssystem in Echtzeit zu implementieren. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Reservierungssystem implementieren, und es werden spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. 1. Was ist WebSocket? WebSocket ist eine Vollduplex-Methode für eine einzelne TCP-Verbindung.
 Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Einführung in die Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Online-Bestellsystems in Echtzeit: Mit der Popularität des Internets und dem Fortschritt der Technologie haben immer mehr Restaurants damit begonnen, Online-Bestelldienste anzubieten. Um ein Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystem zu implementieren, können wir JavaScript und WebSocket-Technologie verwenden. WebSocket ist ein Vollduplex-Kommunikationsprotokoll, das auf dem TCP-Protokoll basiert und eine bidirektionale Kommunikation zwischen Client und Server in Echtzeit realisieren kann. Im Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystem, wenn der Benutzer Gerichte auswählt und eine Bestellung aufgibt
 PHP- und JS-Entwicklungstipps: Beherrschen Sie die Methode zum Zeichnen von Aktienkerzendiagrammen
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
PHP- und JS-Entwicklungstipps: Beherrschen Sie die Methode zum Zeichnen von Aktienkerzendiagrammen
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
Mit der rasanten Entwicklung der Internetfinanzierung sind Aktieninvestitionen für immer mehr Menschen zur Wahl geworden. Im Aktienhandel sind Kerzendiagramme eine häufig verwendete Methode der technischen Analyse. Sie können den sich ändernden Trend der Aktienkurse anzeigen und Anlegern helfen, genauere Entscheidungen zu treffen. In diesem Artikel werden die Entwicklungskompetenzen von PHP und JS vorgestellt, der Leser wird zum Verständnis des Zeichnens von Aktienkerzendiagrammen geführt und es werden spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. 1. Aktien-Kerzendiagramme verstehen Bevor wir uns mit dem Zeichnen von Aktien-Kerzendiagrammen befassen, müssen wir zunächst verstehen, was ein Kerzendiagramm ist. Candlestick-Charts wurden von den Japanern entwickelt
 JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems Einführung: Heutzutage ist die Genauigkeit von Wettervorhersagen für das tägliche Leben und die Entscheidungsfindung von großer Bedeutung. Mit der Weiterentwicklung der Technologie können wir genauere und zuverlässigere Wettervorhersagen liefern, indem wir Wetterdaten in Echtzeit erhalten. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit JavaScript und WebSocket-Technologie ein effizientes Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystem aufbauen. In diesem Artikel wird der Implementierungsprozess anhand spezifischer Codebeispiele demonstriert. Wir




