 Web-Frontend
Web-Frontend
 H5-Tutorial
H5-Tutorial
 So zeichnen Sie coole Energielinieneffekte auf einer HTML5-Leinwand (mit Code)
So zeichnen Sie coole Energielinieneffekte auf einer HTML5-Leinwand (mit Code)
So zeichnen Sie coole Energielinieneffekte auf einer HTML5-Leinwand (mit Code)
In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit HTML5-Canvas coole Energielinieneffekte zeichnen. Es hat einen gewissen Referenzwert. Freunde in Not können sich darauf beziehen. Ich hoffe, es wird Ihnen hilfreich sein.
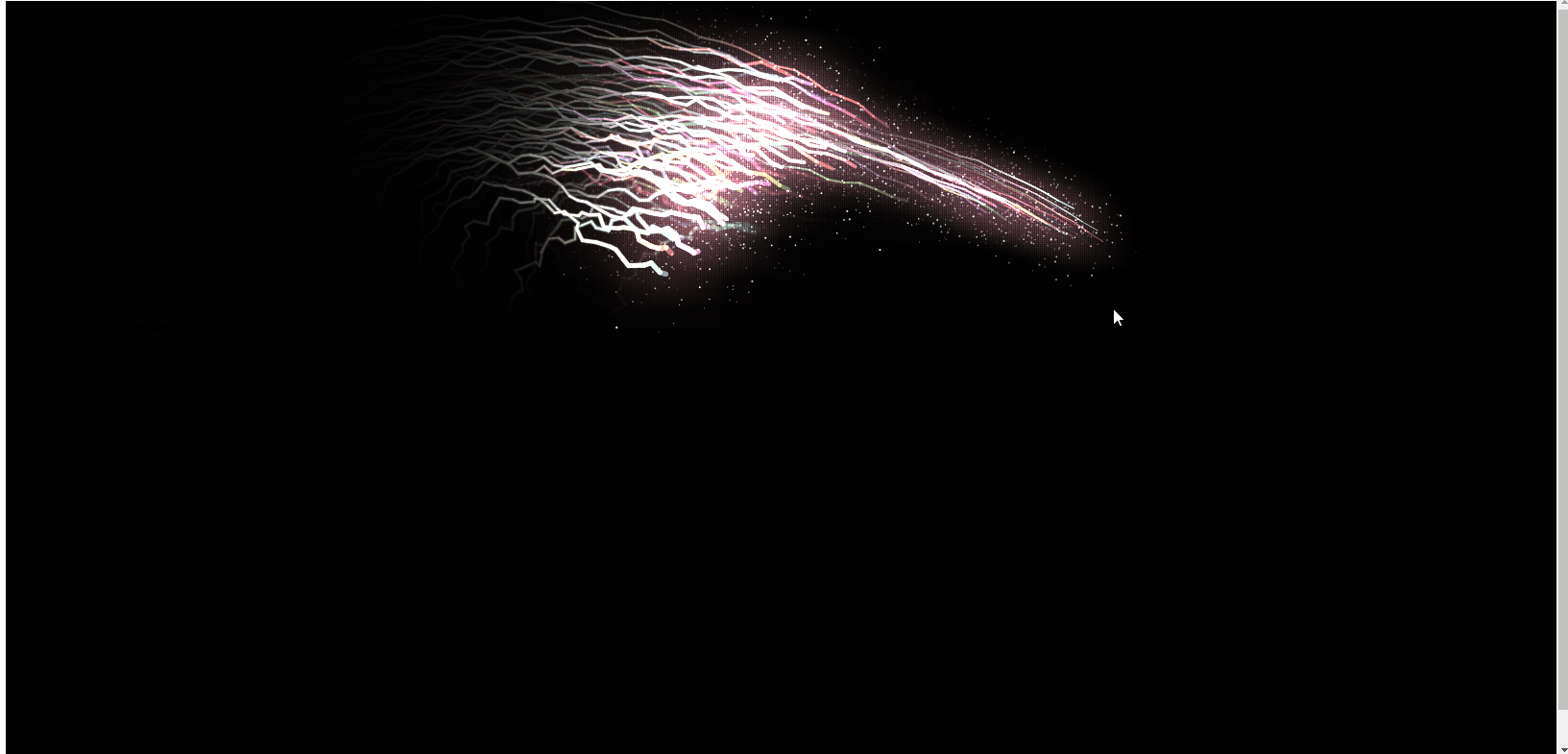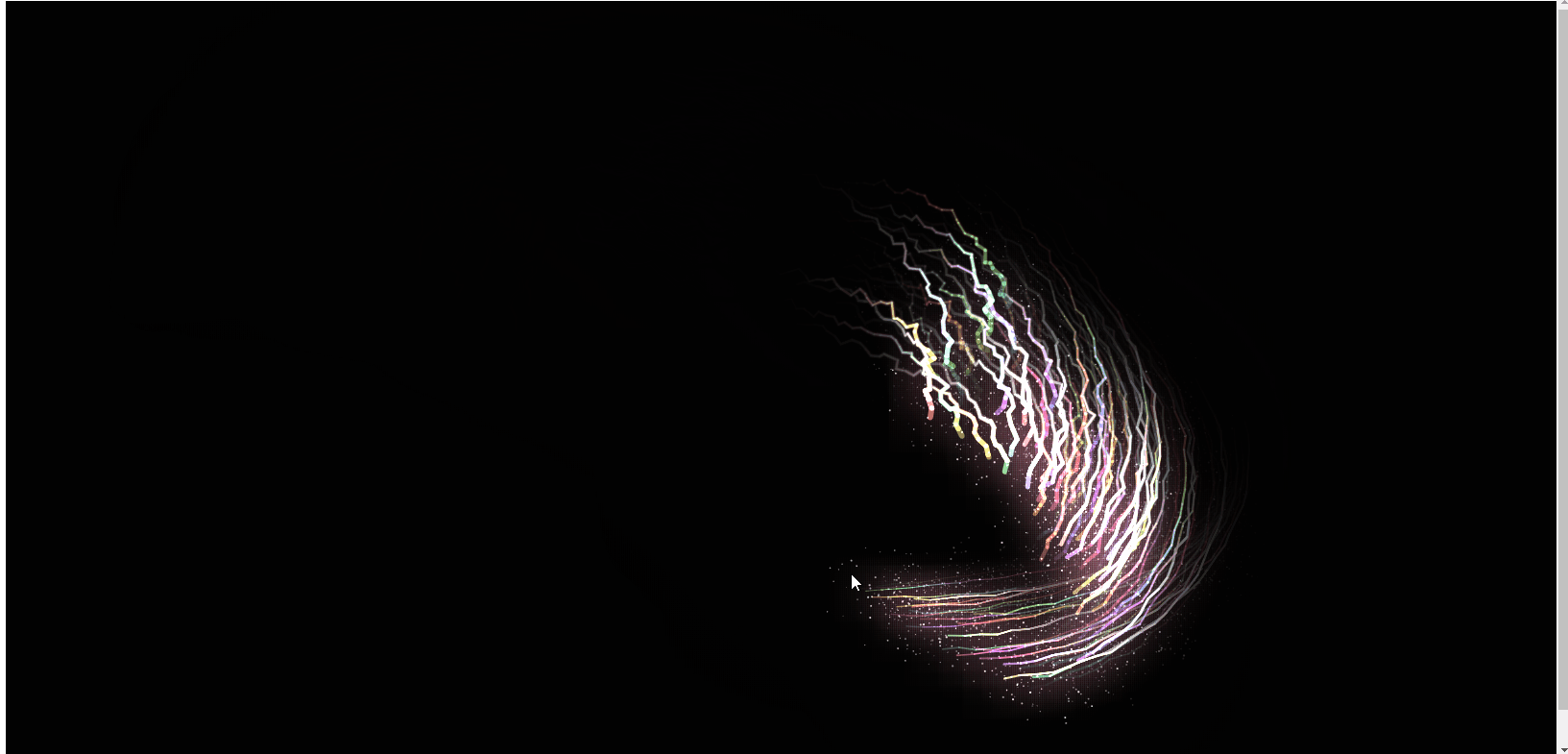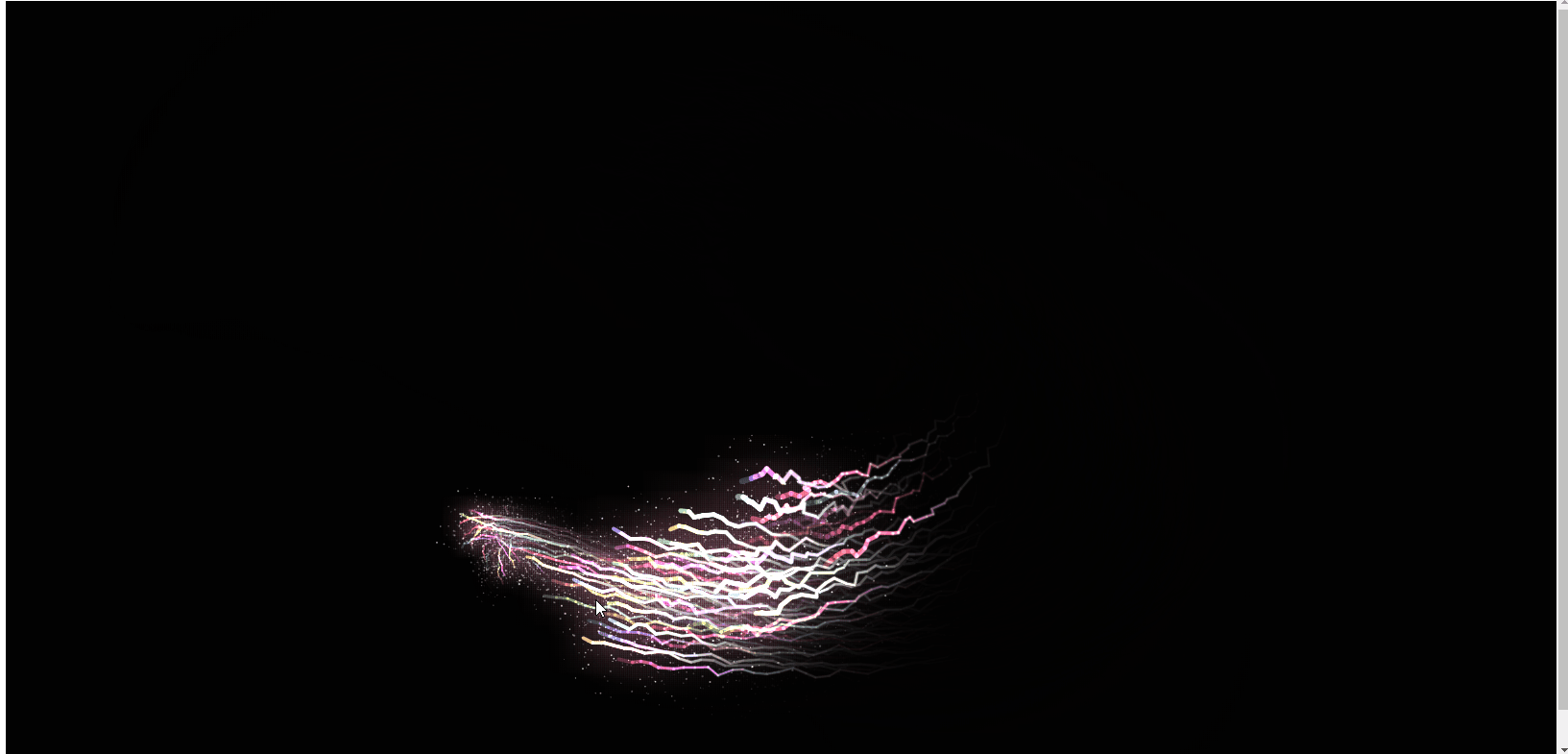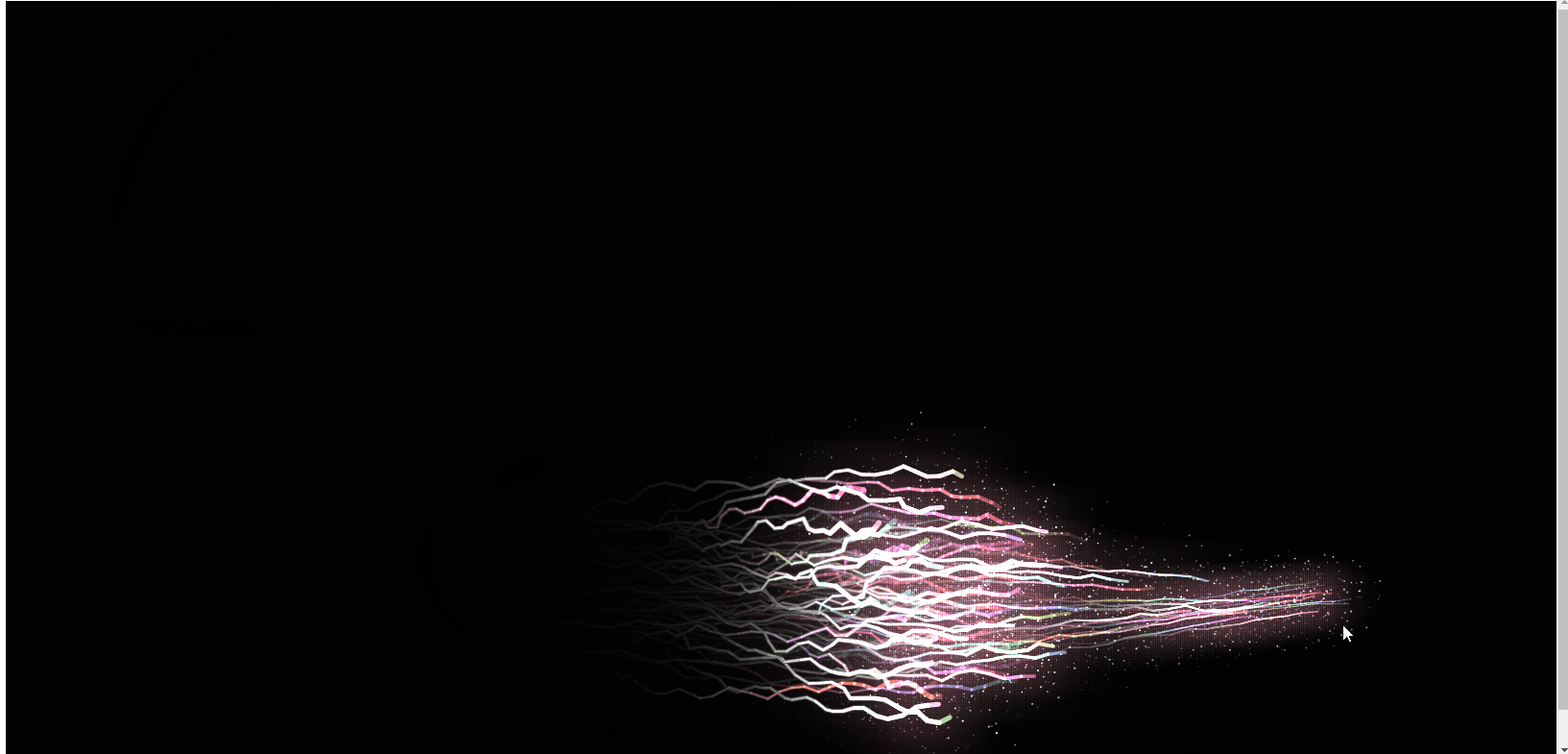
Das Obige ist das Rendering, und der js-Code ist direkt unten angehängt. Ich hoffe, er wird für alle hilfreich sein! !
// UTILconst PI = Math.PI,
TWO_PI = Math.PI * 2;const Util = {};Util.timeStamp = function() {
return window.performance.now();};Util.random = function(min, max) {
return min + Math.random() * (max - min);};Util.map = function(a, b, c, d, e) {
return (a - b) / (c - b) * (e - d) + d;};Util.lerp = function(value1, value2, amount) {
return value1 + (value2 - value1) * amount;};Util.clamp = function(value, min, max) {
return Math.max(min, Math.min(max, value));};// Vectorclass Vector {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x || 0;
this.y = y || 0;
}
set(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
reset() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
fromAngle(angle) {
let x = Math.cos(angle),
y = Math.sin(angle);
return new Vector(x, y);
}
add(vector) {
this.x += vector.x;
this.y += vector.y;
}
sub(vector) {
this.x -= vector.x;
this.y -= vector.y;
}
mult(scalar) {
this.x *= scalar;
this.y *= scalar;
}
p(scalar) {
this.x /= scalar;
this.y /= scalar;
}
dot(vector) {
return vector.x * this.x + vector.y * this.y;
}
limit(limit_value) {
if (this.mag() > limit_value) this.setMag(limit_value);
}
mag() {
return Math.hypot(this.x, this.y);
}
setMag(new_mag) {
if (this.mag() > 0) {
this.normalize();
} else {
this.x = 1;
this.y = 0;
}
this.mult(new_mag);
}
normalize() {
let mag = this.mag();
if (mag > 0) {
this.x /= mag;
this.y /= mag;
}
}
heading() {
return Math.atan2(this.y, this.x);
}
setHeading(angle) {
let mag = this.mag();
this.x = Math.cos(angle) * mag;
this.y = Math.sin(angle) * mag;
}
dist(vector) {
return new Vector(this.x - vector.x, this.y - vector.y).mag();
}
angle(vector) {
return Math.atan2(vector.y - this.y, vector.x - this.x);
}
copy() {
return new Vector(this.x, this.y);
}}// Init canvaslet canvas = document.createElement("canvas"),
ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"),
H = (canvas.height = window.innerHeight),
W = (canvas.width = window.innerWidth);document.body.appendChild(canvas);// Mouselet mouse = {
x: W/2,
y: H/2};canvas.onmousemove = function(event) {
mouse.x = event.clientX - canvas.offsetLeft;
mouse.y = event.clientY - canvas.offsetTop;};document.body.onresize = function(event){
H = (canvas.height = window.innerHeight);
W = (canvas.width = window.innerWidth);}// Let's goclass Arrow {
constructor(x, y, target) {
this.position = new Vector(x, y);
this.velocity = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
this.acceleration = new Vector(0, 0);
this.target = target;
this.travelled_distance = 0;
this.min_size = 1;
this.max_size = 6;
this.size = Util.random(this.min_size, this.max_size);
this.zone = this.size * 4;
this.topSpeed = Util.map(this.size,this.min_size,this.max_size,40,10);
let tailLength = Math.floor(Util.map(this.size, this.min_size, this.max_size, 4, 16));
this.tail = [];
for (let i = 0; i < tailLength; i++) {
this.tail.push({
x: this.position.x,
y: this.position.y });
}
this.wiggle_speed = Util.map(this.size, this.min_size, this.max_size, 2 , 1.2);
this.blink_offset = Util.random(0, 100);
this.alpha = Util.random(0.1,1)
}
render() {
this.update();
this.draw();
}
update() {
let old_position = this.position.copy();
// Focus on target
let t = new Vector(this.target.x, this.target.y),
angle = this.position.angle(t);
let d_f_target = t.dist(this.position);
let f = new Vector().fromAngle(angle);
f.setMag(Util.map(Util.clamp(d_f_target,0,400), 0, 400, 0, this.topSpeed * 0.1));
this.addForce(f);
// Update position and velocity
this.velocity.add(this.acceleration);
if(d_f_target < 800){
this.velocity.limit(Util.map(Util.clamp(d_f_target,0,800), 0, 800, this.topSpeed*0.4, this.topSpeed));
}else{
this.velocity.limit(this.topSpeed);
}
this.position.add(this.velocity);
// Reset acceleration for the next loop
this.acceleration.mult(0);
this.travelled_distance += old_position.dist(this.position);
let wiggle =
Math.sin(frame * this.wiggle_speed) *
Util.map(this.velocity.mag(), 0, this.topSpeed, 0, this.size);
let w_a = this.velocity.heading() + Math.PI / 2;
let w_x = this.position.x + Math.cos(w_a) * wiggle,
w_y = this.position.y + Math.sin(w_a) * wiggle;
this.travelled_distance = 0;
let from = this.tail.length - 1,
to = 0;
let n = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
n.setMag(Math.random()*this.size);
var tail = { x: w_x+ n.x, y: w_y + n.y};
this.tail.splice(from, 1);
this.tail.splice(to, 0, tail);
}
draw() {
let energy = Util.map(this.velocity.mag(),0,this.topSpeed,0.1,1);
let color =
"hsl("+Math.sin((frame + this.blink_offset) * 0.1) * 360+",50%,"+
Util.map(this.velocity.mag(),0,this.topSpeed,40,100) * this.alpha
+"%)";
ctx.globalAlpha = this.alpha;
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
for (let i = 0; i < this.tail.length - 1; i++) {
let t = this.tail[i],
next_t = this.tail[i + 1];
ctx.lineWidth = Util.map(i, 0, this.tail.length - 1, this.size, 1);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(t.x, t.y);
ctx.lineTo(next_t.x, next_t.y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.stroke();
}
let gradient_size = 140 * energy;var grd = ctx.createRadialGradient(
this.position.x,this.position.y , 5,
this.position.x,this.position.y, gradient_size);grd.addColorStop(0, "rgba(255,255,255,0.01)");grd.addColorStop(0.1, "rgba(255,120,200,0.02)");grd.addColorStop(0.9, "rgba(255,255,120,0)");grd.addColorStop(1, "rgba(0,0,0,0)");// Fill with gradientctx.fillStyle = grd;ctx.fillRect(this.position.x - gradient_size / 2 ,this.position.y - gradient_size / 2 , gradient_size, gradient_size);
ctx.globalAlpha = energy+0.2;
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
for(let i = 0; i < 4; i++){
let n = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
n.setMag(Math.random()*energy*100);
n.add(this.position);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(n.x,n.y,Math.random(),0,TWO_PI)
ctx.fill();
}
}
addForce(vector) {
this.acceleration.add(vector);
}
avoid(others) {
others.forEach(other => {
if (other !== this) {
let dist = this.position.dist(other.position),
max_dist = this.zone + other.size;
if (max_dist - dist >= 0) {
let angle = other.position.angle(this.position);
let force = new Vector().fromAngle(angle);
force.setMag(Util.map(dist, 0, max_dist, 2, 0));
this.addForce(force);
}
}
});
}}let arrows = [];for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
arrows.push(new Arrow(W / 2, H / 2, mouse));}let frame = 0;ctx.strokeStyle = "white";function loop() {
ctx.fillStyle="black";
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "source-over";
ctx.globalAlpha = 0.2;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, W, H);
ctx.globalAlpha = 1;
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "lighter";
arrows.forEach(a => {
a.avoid(arrows);
});
arrows.forEach(a => {
a.render();
});
frame += 1;
requestAnimationFrame(loop);}ctx.lineCap = "round";ctx.lineJoin = "round";loop();Empfohlenes Lernen: Html5-Video-Tutorial
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo zeichnen Sie coole Energielinieneffekte auf einer HTML5-Leinwand (mit Code). Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Tabellenrahmen in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Tabellenrahmen in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Anleitung zum Tabellenrahmen in HTML. Hier besprechen wir verschiedene Möglichkeiten zum Definieren von Tabellenrändern anhand von Beispielen für den Tabellenrand in HTML.
 Verschachtelte Tabelle in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Verschachtelte Tabelle in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Dies ist eine Anleitung für verschachtelte Tabellen in HTML. Hier diskutieren wir anhand der entsprechenden Beispiele, wie man eine Tabelle innerhalb der Tabelle erstellt.
 HTML-Rand links
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML-Rand links
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Anleitung zum HTML-Rand links. Hier besprechen wir einen kurzen Überblick über HTML margin-left und seine Beispiele sowie seine Code-Implementierung.
 HTML-Tabellenlayout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML-Tabellenlayout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Leitfaden zum HTML-Tabellenlayout. Hier besprechen wir die Werte des HTML-Tabellenlayouts zusammen mit den Beispielen und Ausgaben im Detail.
 HTML-geordnete Liste
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML-geordnete Liste
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Leitfaden zur HTML-geordneten Liste. Hier besprechen wir auch die Einführung von HTML-geordneten Listen und Typen sowie deren Beispiele
 Text in HTML verschieben
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Text in HTML verschieben
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Anleitung zum Verschieben von Text in HTML. Hier besprechen wir eine Einführung, wie Marquee-Tags funktionieren, mit Syntax und Beispielen für die Implementierung.
 HTML-Eingabeplatzhalter
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML-Eingabeplatzhalter
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Leitfaden für HTML-Eingabeplatzhalter. Hier besprechen wir die Beispiele für HTML-Eingabeplatzhalter zusammen mit den Codes und Ausgaben.
 Wie analysiert und verarbeitet man HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Wie analysiert und verarbeitet man HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Dieses Tutorial zeigt, wie XML -Dokumente mit PHP effizient verarbeitet werden. XML (Extensible Markup-Sprache) ist eine vielseitige textbasierte Markup-Sprache, die sowohl für die Lesbarkeit des Menschen als auch für die Analyse von Maschinen entwickelt wurde. Es wird üblicherweise für die Datenspeicherung ein verwendet und wird häufig verwendet



