 Backend-Entwicklung
Backend-Entwicklung
 Python-Tutorial
Python-Tutorial
 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Dieser Artikel vermittelt Ihnen relevantes Wissen über Python. Er stellt hauptsächlich eine Zusammenfassung der maschinellen Lern- und Deep-Learning-Bibliotheken vor, die eine große Anzahl von Beispielen enthält. Ich hoffe, dass sie für alle hilfreich sind.

Empfohlenes Lernen: Python-Video-Tutorial
Vorwort
Mit der Popularität der künstlichen Intelligenz hat sie derzeit die Aufmerksamkeit vieler Branchen auf künstliche Intelligenz gelenkt, und gleichzeitig hat sie dies getan Es gibt auch einen Aufschwung im Bereich der künstlichen Intelligenz. Obwohl wir die Prinzipien der künstlichen Intelligenz nicht im Detail in einem kurzen Artikel vorstellen können, müssen wir das Rad nicht von Grund auf neu erfinden Verwenden Sie ein umfangreiches Framework für künstliche Intelligenz, um Modelle für künstliche Intelligenz zu erstellen und mit dem Trend der künstlichen Intelligenz zu beginnen.
Künstliche Intelligenz bezieht sich auf eine Reihe von Technologien, die es Maschinen ermöglichen, Informationen wie Menschen zu verarbeiten; maschinelles Lernen ist der Prozess, bei dem mithilfe von Computerprogrammen aus historischen Daten gelernt und neue Daten basierend auf der Struktur und den Eigenschaften biologischer Gehirne vorhergesagt werden Computermodell des maschinellen Lernens; Deep Learning ist eine Teilmenge des maschinellen Lernens, die große Mengen unstrukturierter Daten wie menschliche Sprache, Text und Bilder verarbeitet. Daher sind diese Konzepte hierarchisch voneinander abhängig, wobei künstliche Intelligenz der weiteste Begriff und Deep Learning der spezifischste ist:
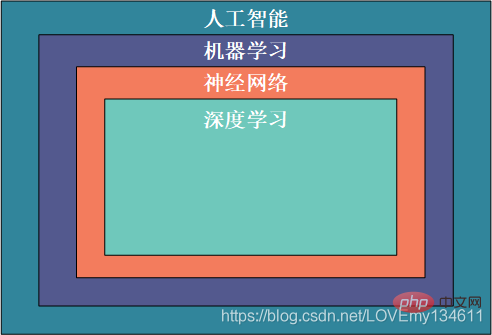
Damit jeder mit der Python-Bibliothek vertraut ist, die üblicherweise für künstliche Intelligenz verwendet wird Intelligenz Verschaffen Sie sich ein vorläufiges Verständnis für die Auswahl einer Bibliothek, die Ihren Lernbedürfnissen gerecht wird, und geben Sie eine kurze und umfassende Einführung in die derzeit gängigeren Bibliotheken für künstliche Intelligenz. Python 库有一个初步的了解,以选择能够满足自己需求的库进行学习,对目前较为常见的Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)库进行简要全面的介绍。
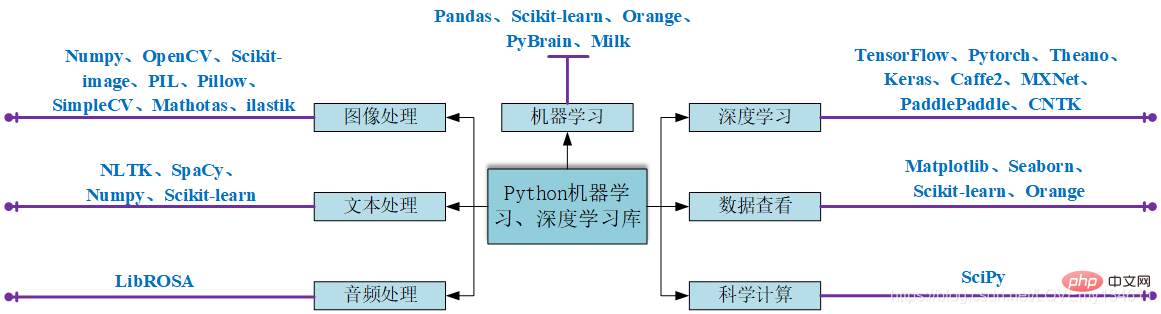
python常用机器学习及深度学习库介绍
1、 Numpy
NumPy(Numerical Python)是 Python的一个扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库,Numpy底层使用C语言编写,数组中直接存储对象,而不是存储对象指针,所以其运算效率远高于纯Python代码。
我们可以在示例中对比下纯Python与使用Numpy库在计算列表sin值的速度对比:
import numpy as npimport mathimport randomimport time
start = time.time()for i in range(10):
list_1 = list(range(1,10000))
for j in range(len(list_1)):
list_1[j] = math.sin(list_1[j])print("使用纯Python用时{}s".format(time.time()-start))start = time.time()for i in range(10):
list_1 = np.array(np.arange(1,10000))
list_1 = np.sin(list_1)print("使用Numpy用时{}s".format(time.time()-start))从如下运行结果,可以看到使用 Numpy 库的速度快于纯 Python 编写的代码:
使用纯Python用时0.017444372177124023s 使用Numpy用时0.001619577407836914s
2、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 是一个的跨平台计算机视觉库,可以运行在 Linux、Windows 和 Mac OS 操作系统上。它轻量级而且高效——由一系列 C 函数和少量 C++ 类构成,同时也提供了 Python 接口,实现了图像处理和计算机视觉方面的很多通用算法。
下面代码尝试使用一些简单的滤镜,包括图片的平滑处理、高斯模糊等:
import numpy as npimport cv2 as cvfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv.imread('h89817032p0.png')kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.float32)/25dst = cv.filter2D(img,-1,kernel)blur_1 = cv.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5),0)blur_2 = cv.bilateralFilter(img,9,75,75)plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(img[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Original')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(dst[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Averaging')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(blur_1[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Gaussian')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(blur_1[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Bilateral')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.show()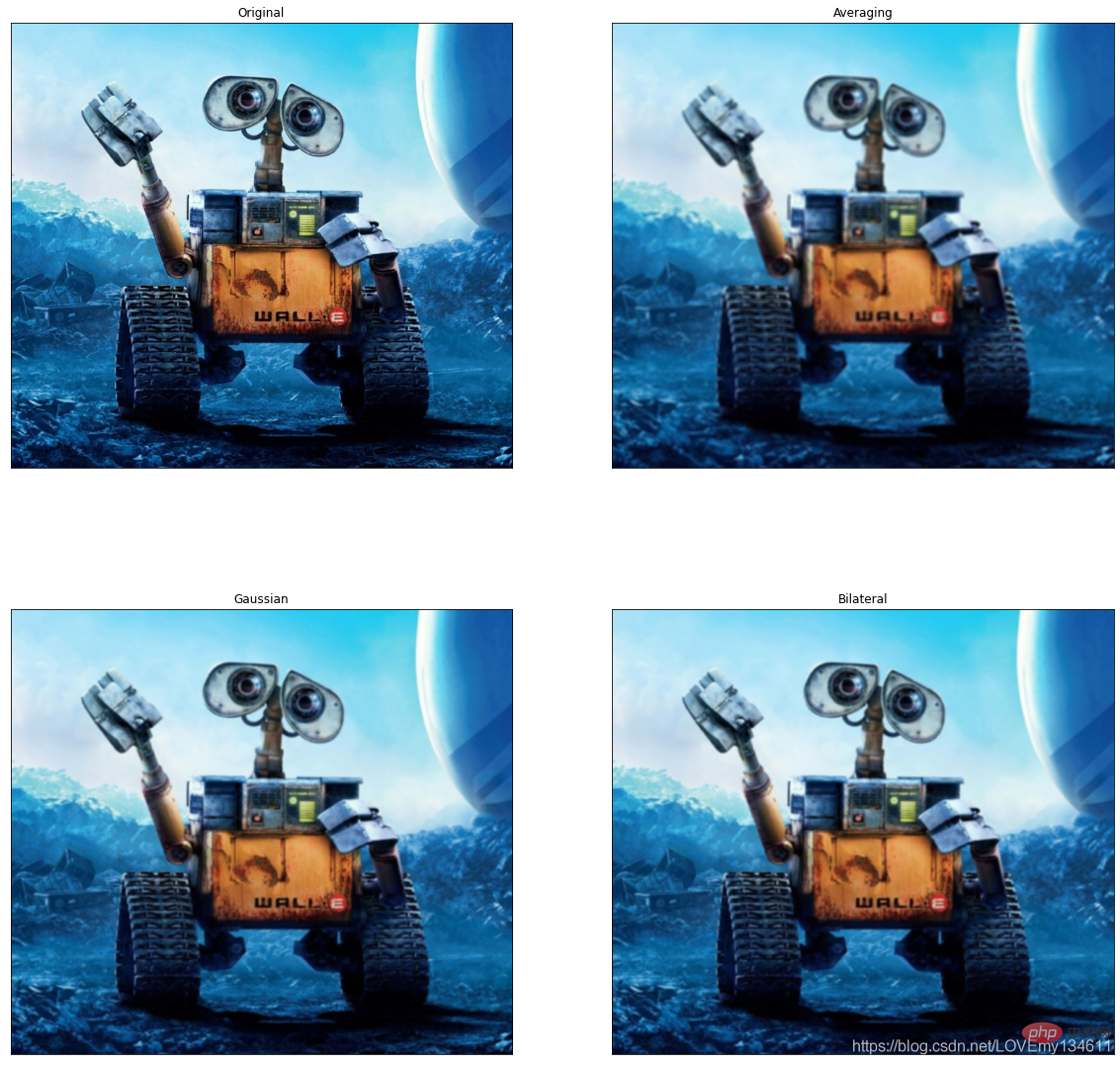
可以参考Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)图像处理基础(变换和去噪),了解更多 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 图像处理操作。
3、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
scikit-image是基于scipy的图像处理库,它将图片作为numpy数组进行处理。
例如,可以利用scikit-image改变图片比例,scikit-image提供了rescale、resize以及downscale_local_mean等函数。
from skimage import data, color, iofrom skimage.transform import rescale, resize, downscale_local_mean
image = color.rgb2gray(io.imread('h89817032p0.png'))image_rescaled = rescale(image, 0.25, anti_aliasing=False)image_resized = resize(image, (image.shape[0] // 4, image.shape[1] // 4),
anti_aliasing=True)image_downscaled = downscale_local_mean(image, (4, 3))plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Original')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(image_rescaled, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Rescaled')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(image_resized, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Resized')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(image_downscaled, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Downscaled')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.show()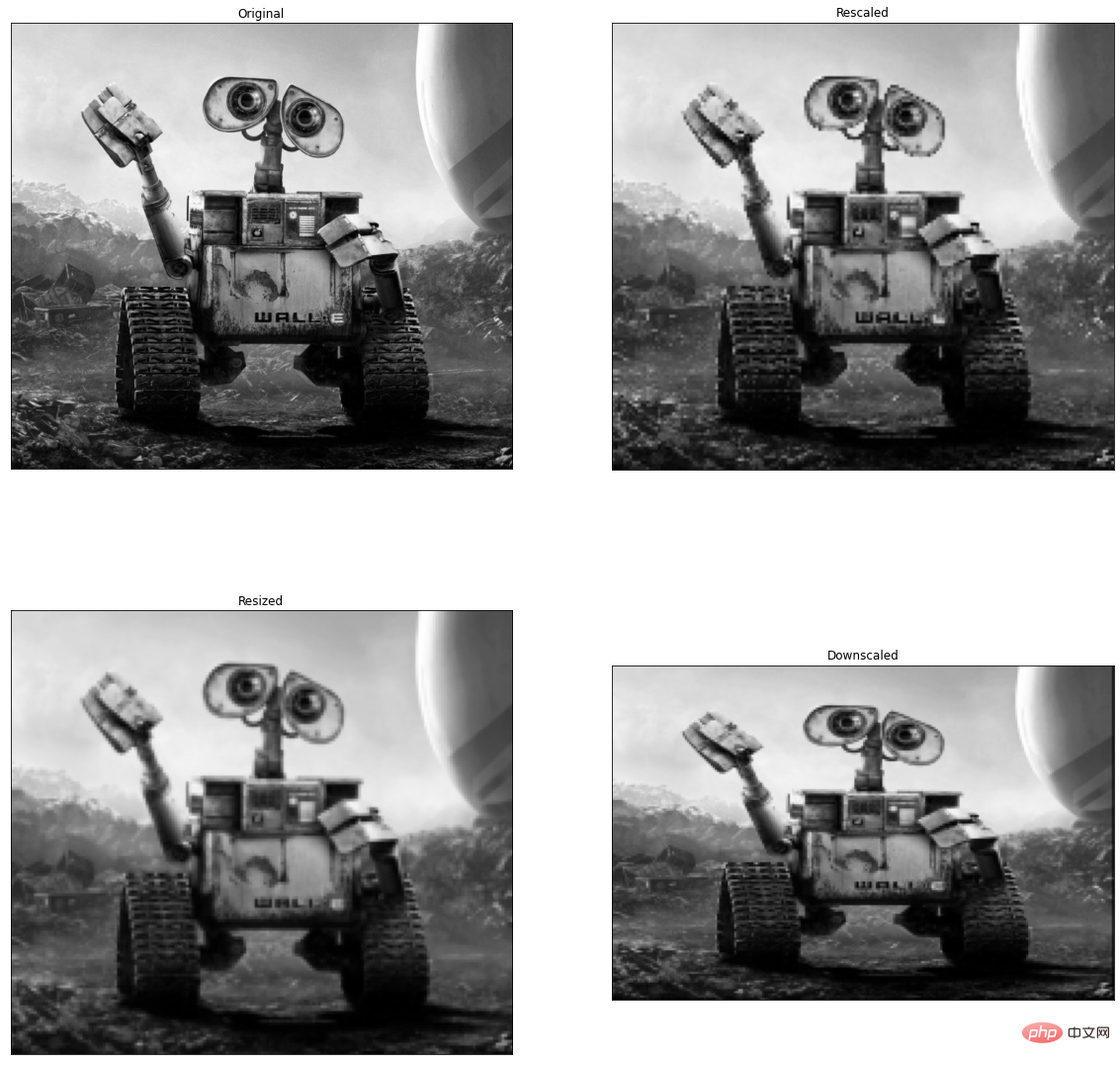
4、 Python Imaging Library(PIL)
Python Imaging Library(PIL) 已经成为 Python 事实上的图像处理标准库了,这是由于,PIL 功能非常强大,但API却非常简单易用。
但是由于PIL仅支持到 Python 2.7,再加上年久失修,于是一群志愿者在 PIL 的基础上创建了兼容的版本,名字叫 Pillow,支持最新 Python 3.x,又加入了许多新特性,因此,我们可以跳过 PIL,直接安装使用 Pillow。
5、 Pillow
使用 Pillow


NumPy (Numerical Python) ist PythonC-Sprache werden Objekte direkt im Array anstelle von Objektzeigern gespeichert, sodass die Operationseffizienz viel höher ist als bei reinem Python-Code. Wir können die Geschwindigkeit der Berechnung des Sin-Werts einer Liste zwischen
Pure Python und der Verwendung der Numpy-Bibliothek im Beispiel vergleichen: 🎜from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageFilterimport random# 随机字母:def rndChar():
return chr(random.randint(65, 90))# 随机颜色1:def rndColor():
return (random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255))# 随机颜色2:def rndColor2():
return (random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127))# 240 x 60:width = 60 * 6height = 60 * 6image = Image.new('RGB', (width, height), (255, 255, 255))# 创建Font对象:font = ImageFont.truetype('/usr/share/fonts/wps-office/simhei.ttf', 60)# 创建Draw对象:draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)# 填充每个像素:for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
draw.point((x, y), fill=rndColor())# 输出文字:for t in range(6):
draw.text((60 * t + 10, 150), rndChar(), font=font, fill=rndColor2())# 模糊:image = image.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)image.save('code.jpg', 'jpeg')Numpy-Bibliothek ist schneller als in reinem Python geschriebener Code: 🎜from SimpleCV import Image, Color, Display# load an image from imgurimg = Image('http://i.imgur.com/lfAeZ4n.png')# use a keypoint detector to find areas of interestfeats = img.findKeypoints()# draw the list of keypointsfeats.draw(color=Color.RED)# show the resulting image. img.show()# apply the stuff we found to the image.output = img.applyLayers()# save the results.output.save('juniperfeats.png')🎜2, Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)🎜
🎜Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) ist ein Cross- Plattform-Computer-Vision-Bibliothek, die auf Linux-, Windows- und Mac OS-Betriebssystemen ausgeführt werden kann. Es ist leichtgewichtig und effizient – es besteht aus einer Reihe von C-Funktionen und einer kleinen Anzahl von C++-Klassen. Es bietet außerdem eine Python-Schnittstelle zur Implementierung vieler gängiger Algorithmen in der Bildverarbeitung und Computer Vision. Der folgende Code versucht, einige einfache Filter zu verwenden, einschließlich Bildglättung, Gaußsche Unschärfe usw.: 🎜
SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'. Did you mean print('unit test')? 🎜🎜Weitere Informationen zu Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)-Bildverarbeitungsvorgängen finden Sie unter Grundlagen der Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)-Bildverarbeitung (Transformation und Rauschunterdrückung). 🎜
🎜🎜Weitere Informationen zu Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)-Bildverarbeitungsvorgängen finden Sie unter Grundlagen der Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)-Bildverarbeitung (Transformation und Rauschunterdrückung). 🎜🎜3, Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)🎜
🎜scikit-image ist eine Bildverarbeitungsbibliothek basierend auf scipy, die Bilder als numpy verwendet Array zur Verarbeitung. Sie können beispielsweise
scikit-image verwenden, um das Bildverhältnis zu ändern. scikit-image bietet rescale und resize Und Funktionen wie downscale_local_mean. 🎜import numpy as npimport mahotasimport mahotas.demosfrom mahotas.thresholding import soft_thresholdfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltfrom os import path
f = mahotas.demos.load('lena', as_grey=True)f = f[128:,128:]plt.gray()# Show the data:print("Fraction of zeros in original image: {0}".format(np.mean(f==0)))plt.imshow(f)plt.show() 🎜
🎜🎜4、 Python Imaging Library(PIL)🎜
🎜Python Imaging Library(PIL) ist zur De-facto-Bildverarbeitungs-Standardbibliothek von Python geworden Code >PIL ist sehr leistungsfähig, aber die API ist sehr einfach und benutzerfreundlich. Da PIL jedoch nur
Python 2.7 unterstützt und in einem schlechten Zustand ist, hat eine Gruppe von Freiwilligen eine kompatible Version basierend auf PIL mit dem Namen Pillow erstellt unterstützt das neueste Python 3.x und fügt viele neue Funktionen hinzu. Daher können wir PIL überspringen und es direkt installieren und verwenden /code>. 🎜🎜5, Pillow🎜
🎜Verwenden SiePillow, um ein Bild mit einem Buchstabenbestätigungscode zu generieren: 🎜import timeimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe), Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances_argminfrom sklearn.datasets import make_blobs# Generate sample datanp.random.seed(0)batch_size = 45centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]]n_clusters = len(centers)X, labels_true = make_blobs(n_samples=3000, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.7)# Compute clustering with Meansk_means = Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, n_init=10)t0 = time.time()k_means.fit(X)t_batch = time.time() - t0# Compute clustering with MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)mbk = MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, batch_size=batch_size,
n_init=10, max_no_improvement=10, verbose=0)t0 = time.time()mbk.fit(X)t_mini_batch = time.time() - t0# Plot resultfig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.02, right=0.98, bottom=0.05, top=0.9)colors = ['#4EACC5', '#FF9C34', '#4E9A06']# We want to have the same colors for the same cluster from the# MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) and the Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) algorithm. Let's pair the cluster centers per# closest one.k_means_cluster_centers = k_means.cluster_centers_
order = pairwise_distances_argmin(k_means.cluster_centers_,
mbk.cluster_centers_)mbk_means_cluster_centers = mbk.cluster_centers_[order]k_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, k_means_cluster_centers)mbk_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, mbk_means_cluster_centers)# Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)for k, col in zip(range(n_clusters), colors):
my_members = k_means_labels == k
cluster_center = k_means_cluster_centers[k]
plt.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], 'w',
markerfacecolor=col, marker='.')
plt.plot(cluster_center[0], cluster_center[1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col,
markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6)plt.title('Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)')plt.xticks(())plt.yticks(())plt.show()6、 SimpleCV
SimpleCV 是一个用于构建计算机视觉应用程序的开源框架。使用它,可以访问高性能的计算机视觉库,如 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe),而不必首先了解位深度、文件格式、颜色空间、缓冲区管理、特征值或矩阵等术语。但其对于 Python3 的支持很差很差,在 Python3.7 中使用如下代码:
from SimpleCV import Image, Color, Display# load an image from imgurimg = Image('http://i.imgur.com/lfAeZ4n.png')# use a keypoint detector to find areas of interestfeats = img.findKeypoints()# draw the list of keypointsfeats.draw(color=Color.RED)# show the resulting image. img.show()# apply the stuff we found to the image.output = img.applyLayers()# save the results.output.save('juniperfeats.png')会报如下错误,因此不建议在 Python3 中使用:
SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'. Did you mean print('unit test')?7、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 是一个快速计算机视觉算法库,其构建在 Numpy 之上,目前拥有超过100种图像处理和计算机视觉功能,并在不断增长。
使用 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 加载图像,并对像素进行操作:
import numpy as npimport mahotasimport mahotas.demosfrom mahotas.thresholding import soft_thresholdfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltfrom os import path
f = mahotas.demos.load('lena', as_grey=True)f = f[128:,128:]plt.gray()# Show the data:print("Fraction of zeros in original image: {0}".format(np.mean(f==0)))plt.imshow(f)plt.show()
8、 Ilastik
Ilastik 能够给用户提供良好的基于机器学习的生物信息图像分析服务,利用机器学习算法,轻松地分割,分类,跟踪和计数细胞或其他实验数据。大多数操作都是交互式的,并不需要机器学习专业知识。可以参考https://www.ilastik.org/documentation/basics/installation.html进行安装使用。
9、 Scikit-learn
Scikit-learn 是针对 Python 编程语言的免费软件机器学习库。它具有各种分类,回归和聚类算法,包括支持向量机,随机森林,梯度提升,k均值和 DBSCAN 等多种机器学习算法。
使用Scikit-learn实现Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)算法:
import timeimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe), Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances_argminfrom sklearn.datasets import make_blobs# Generate sample datanp.random.seed(0)batch_size = 45centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]]n_clusters = len(centers)X, labels_true = make_blobs(n_samples=3000, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.7)# Compute clustering with Meansk_means = Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, n_init=10)t0 = time.time()k_means.fit(X)t_batch = time.time() - t0# Compute clustering with MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)mbk = MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, batch_size=batch_size,
n_init=10, max_no_improvement=10, verbose=0)t0 = time.time()mbk.fit(X)t_mini_batch = time.time() - t0# Plot resultfig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.02, right=0.98, bottom=0.05, top=0.9)colors = ['#4EACC5', '#FF9C34', '#4E9A06']# We want to have the same colors for the same cluster from the# MiniBatchEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) and the Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) algorithm. Let's pair the cluster centers per# closest one.k_means_cluster_centers = k_means.cluster_centers_
order = pairwise_distances_argmin(k_means.cluster_centers_,
mbk.cluster_centers_)mbk_means_cluster_centers = mbk.cluster_centers_[order]k_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, k_means_cluster_centers)mbk_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, mbk_means_cluster_centers)# Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)for k, col in zip(range(n_clusters), colors):
my_members = k_means_labels == k
cluster_center = k_means_cluster_centers[k]
plt.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], 'w',
markerfacecolor=col, marker='.')
plt.plot(cluster_center[0], cluster_center[1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col,
markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6)plt.title('Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)')plt.xticks(())plt.yticks(())plt.show()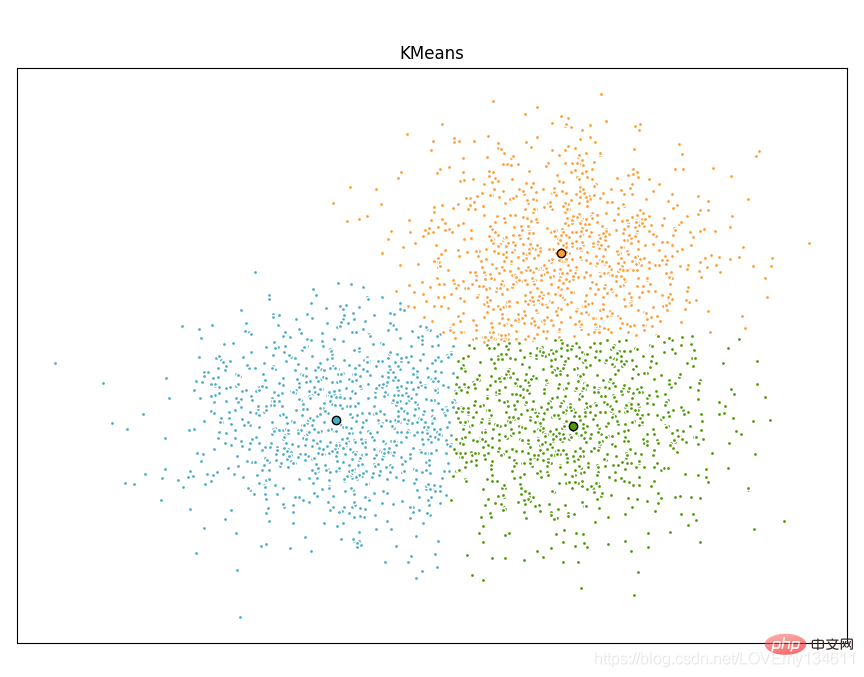
10、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 库提供了许多用户友好和高效的数值计算,如数值积分、插值、优化、线性代数等。Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 库定义了许多数学物理的特殊函数,包括椭圆函数、贝塞尔函数、伽马函数、贝塔函数、超几何函数、抛物线圆柱函数等等。
from scipy import specialimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npdef drumhead_height(n, k, distance, angle, t):
kth_zero = special.jn_zeros(n, k)[-1]
return np.cos(t) * np.cos(n*angle) * special.jn(n, distance*kth_zero)theta = np.r_[0:2*np.pi:50j]radius = np.r_[0:1:50j]x = np.array([r * np.cos(theta) for r in radius])y = np.array([r * np.sin(theta) for r in radius])z = np.array([drumhead_height(1, 1, r, theta, 0.5) for r in radius])fig = plt.figure()ax = fig.add_axes(rect=(0, 0.05, 0.95, 0.95), projection='3d')ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='RdBu_r', vmin=-0.5, vmax=0.5)ax.set_xlabel('X')ax.set_ylabel('Y')ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-1, 1.1, 0.5))ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-1, 1.1, 0.5))ax.set_zlabel('Z')plt.show()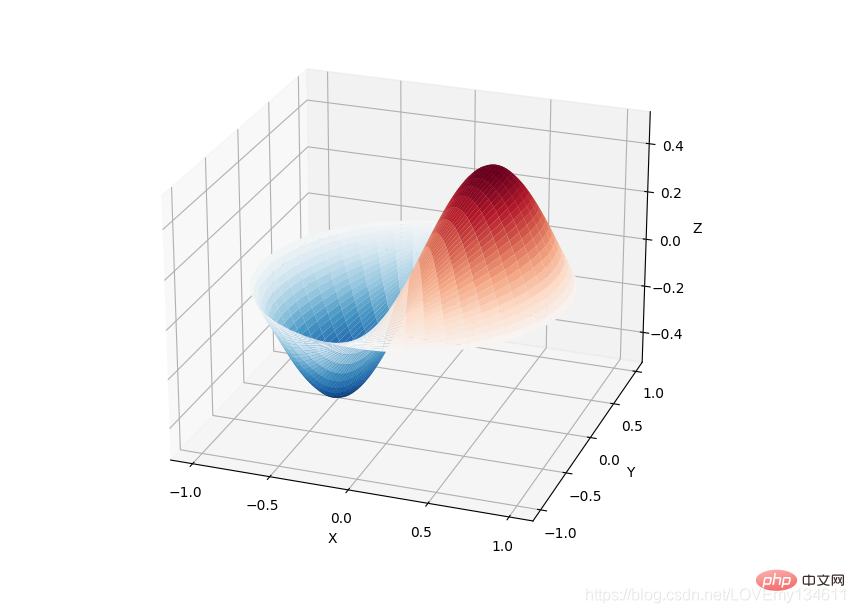
11、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 是构建Python程序以处理自然语言的库。它为50多个语料库和词汇资源(如 WordNet )提供了易于使用的接口,以及一套用于分类、分词、词干、标记、解析和语义推理的文本处理库、工业级自然语言处理 (Natural Language Processing, NLP) 库的包装器。
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)被称为 “a wonderful tool for teaching, and working in, computational linguistics using Python”。
import nltkfrom nltk.corpus import treebank# 首次使用需要下载nltk.download('punkt')nltk.download('averaged_perceptron_tagger')nltk.download('maxent_ne_chunker')nltk.download('words')nltk.download('treebank')sentence = """At eight o'clock on Thursday morning Arthur didn't feel very good."""# Tokenizetokens = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)tagged = nltk.pos_tag(tokens)# Identify named entitiesentities = nltk.chunk.ne_chunk(tagged)# Display a parse treet = treebank.parsed_sents('wsj_0001.mrg')[0]t.draw()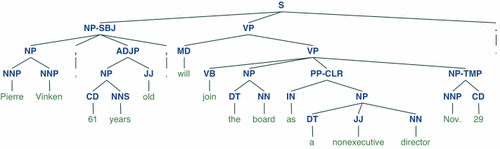
12、 spaCy
spaCy 是一个免费的开源库,用于 Python 中的高级 NLP。它可以用于构建处理大量文本的应用程序;也可以用来构建信息提取或自然语言理解系统,或者对文本进行预处理以进行深度学习。
import spacy
texts = [
"Net income was $9.4 million compared to the prior year of $2.7 million.",
"Revenue exceeded twelve billion dollars, with a loss of $1b.",
]
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
for doc in nlp.pipe(texts, disable=["tok2vec", "tagger", "parser", "attribute_ruler", "lemmatizer"]):
# Do something with the doc here
print([(ent.text, ent.label_) for ent in doc.ents])nlp.pipe 生成 Doc 对象,因此我们可以对它们进行迭代并访问命名实体预测:
[('$9.4 million', 'MONEY'), ('the prior year', 'DATE'), ('$2.7 million', 'MONEY')][('twelve billion dollars', 'MONEY'), ('1b', 'MONEY')]13、 LibROSA
librosa 是一个用于音乐和音频分析的 Python 库,它提供了创建音乐信息检索系统所必需的功能和函数。
# Beat tracking exampleimport librosa# 1. Get the file path to an included audio examplefilename = librosa.example('nutcracker')# 2. Load the audio as a waveform `y`# Store the sampling rate as `sr`y, sr = librosa.load(filename)# 3. Run the default beat trackertempo, beat_frames = librosa.beat.beat_track(y=y, sr=sr)print('Estimated tempo: {:.2f} beats per minute'.format(tempo))# 4. Convert the frame indices of beat events into timestampsbeat_times = librosa.frames_to_time(beat_frames, sr=sr)14、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 是一个快速、强大、灵活且易于使用的开源数据分析和操作工具, Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 可以从各种文件格式比如 CSV、JSON、SQL、Microsoft Excel 导入数据,可以对各种数据进行运算操作,比如归并、再成形、选择,还有数据清洗和数据加工特征。Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 广泛应用在学术、金融、统计学等各个数据分析领域。
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdimport numpy as np
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000), index=pd.date_range("1/1/2000", periods=1000))ts = ts.cumsum()df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 4), index=ts.index, columns=list("ABCD"))df = df.cumsum()df.plot()plt.show()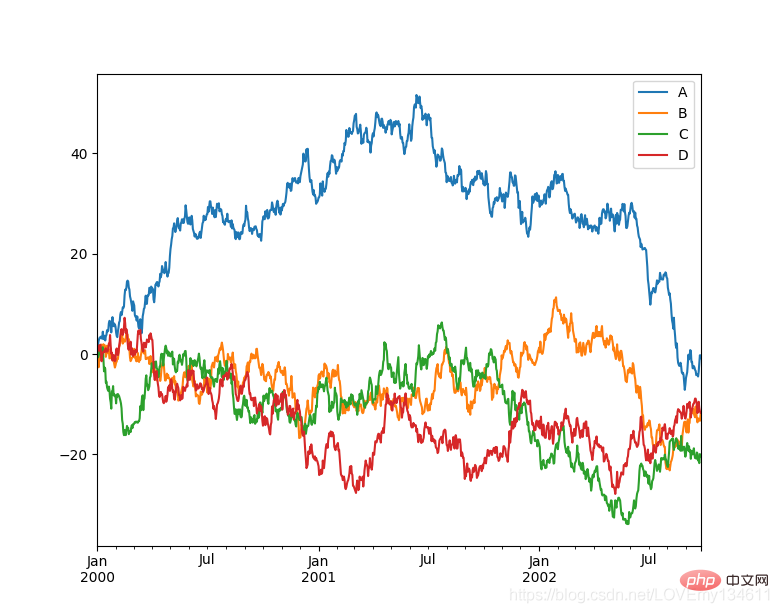
15、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 是Python的绘图库,它提供了一整套和 matlab 相似的命令 API,可以生成出版质量级别的精美图形,Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 使绘图变得非常简单,在易用性和性能间取得了优异的平衡。
使用 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 绘制多曲线图:
# plot_multi_curve.pyimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.linspace(0.1, 2 * np.pi, 100)y_1 = x y_2 = np.square(x)y_3 = np.log(x)y_4 = np.sin(x)plt.plot(x,y_1)plt.plot(x,y_2)plt.plot(x,y_3)plt.plot(x,y_4)plt.show()
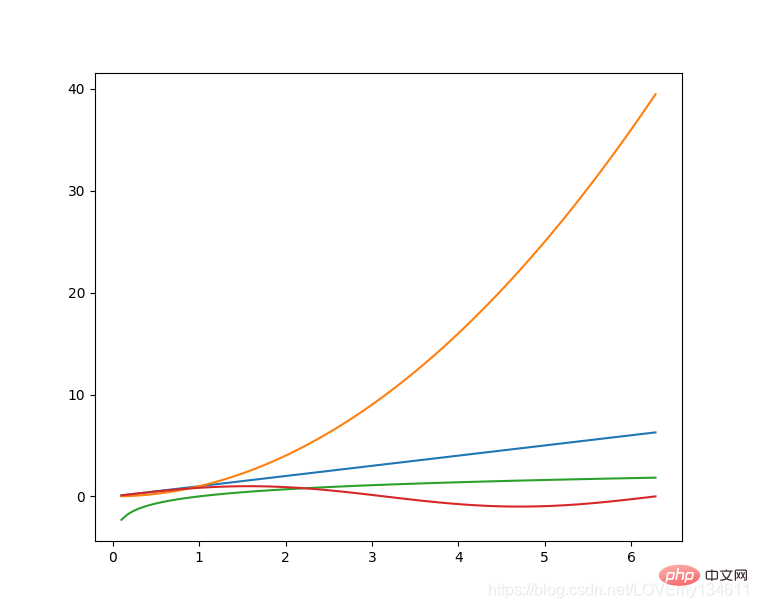 有关更多
有关更多Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)绘图的介绍可以参考此前博文———Python-Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)可视化。
16、 Seaborn
Seaborn 是在 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 的基础上进行了更高级的API封装的Python数据可视化库,从而使得作图更加容易,应该把 Seaborn 视为 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 的补充,而不是替代物。
import Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")df = sns.load_dataset("penguins")sns.pairplot(df, hue="species")plt.show()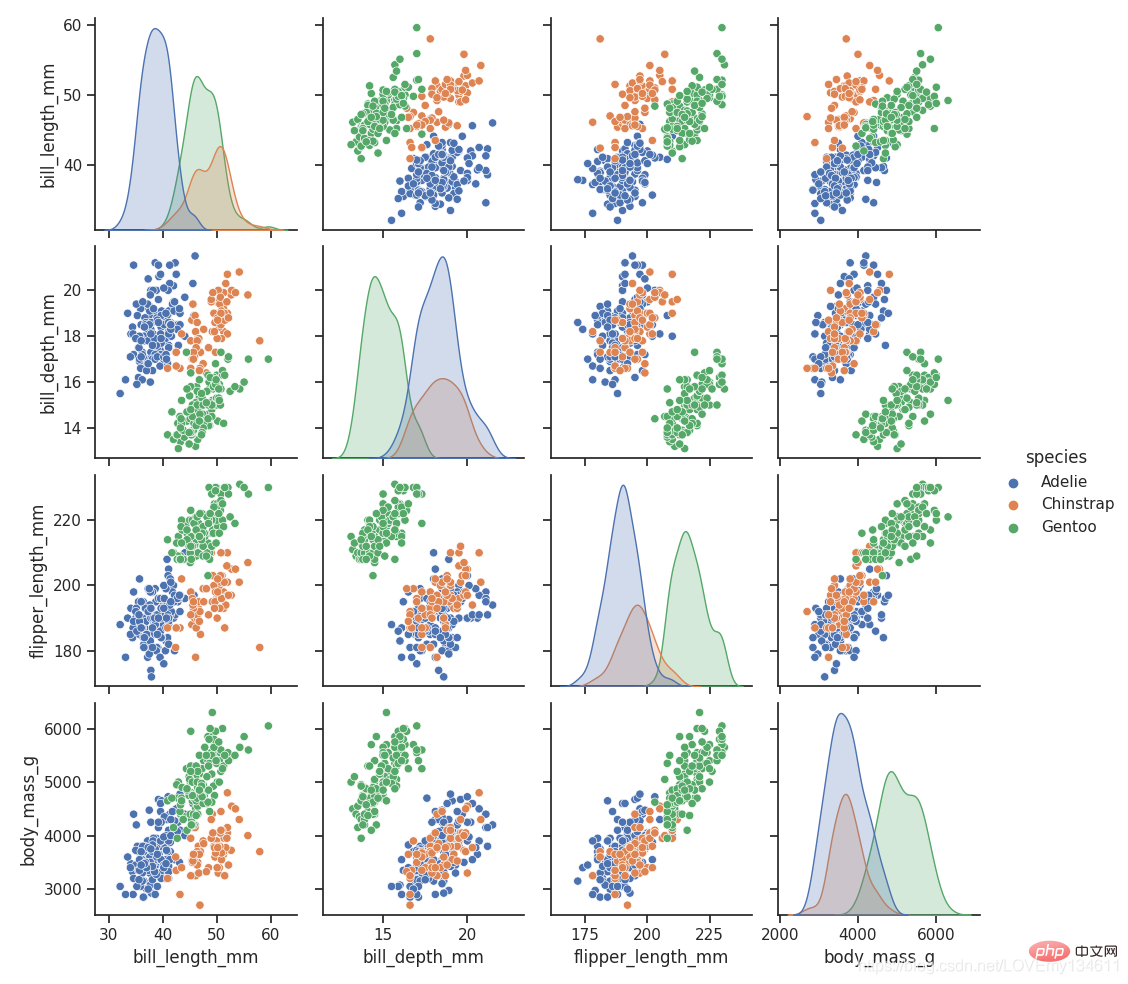
17、 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)
Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 是一个开源的数据挖掘和机器学习软件,提供了一系列的数据探索、可视化、预处理以及建模组件。Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 拥有漂亮直观的交互式用户界面,非常适合新手进行探索性数据分析和可视化展示;同时高级用户也可以将其作为 Python 的一个编程模块进行数据操作和组件开发。
使用 pip 即可安装 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe),好评~
$ pip install orange3
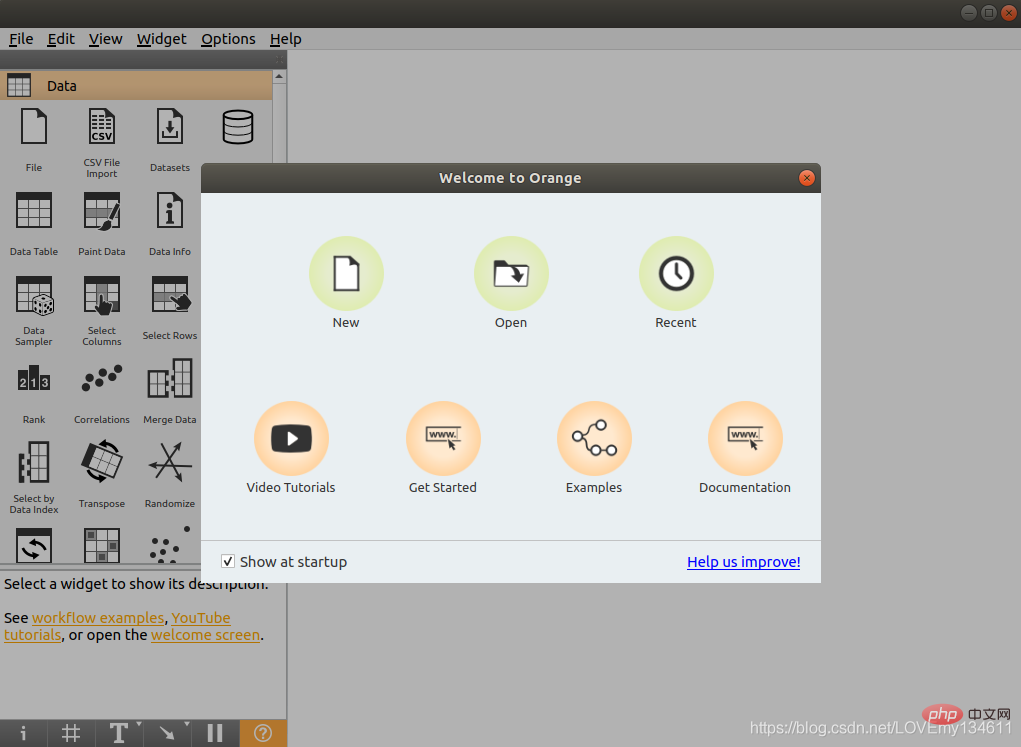
安装完成后,在命令行输入 orange-canvas 命令即可启动 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 图形界面:
$ orange-canvas
启动完成后,即可看到 Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) 图形界面,进行各种操作。
18、 PyBrain
PyBrain 是 Python 的模块化机器学习库。它的目标是为机器学习任务和各种预定义的环境提供灵活、易于使用且强大的算法来测试和比较算法。PyBrain 是 Python-Based Reinforcement Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Neural Network Library 的缩写。
我们将利用一个简单的例子来展示 PyBrain 的用法,构建一个多层感知器 (Multi Layer Perceptron, MLP)。
首先,我们创建一个新的前馈网络对象:
from pybrain.structure import FeedForwardNetwork n = FeedForwardNetwork()
接下来,构建输入、隐藏和输出层:
from pybrain.structure import LinearLayer, SigmoidLayer inLayer = LinearLayer(2)hiddenLayer = SigmoidLayer(3)outLayer = LinearLayer(1)
为了使用所构建的层,必须将它们添加到网络中:
n.addInputModule(inLayer)n.addModule(hiddenLayer)n.addOutputModule(outLayer)
可以添加多个输入和输出模块。为了向前计算和反向误差传播,网络必须知道哪些层是输入、哪些层是输出。
这就需要明确确定它们应该如何连接。为此,我们使用最常见的连接类型,全连接层,由 FullConnection 类实现:
from pybrain.structure import FullConnection in_to_hidden = FullConnection(inLayer, hiddenLayer)hidden_to_out = FullConnection(hiddenLayer, outLayer)
与层一样,我们必须明确地将它们添加到网络中:
n.addConnection(in_to_hidden)n.addConnection(hidden_to_out)
所有元素现在都已准备就位,最后,我们需要调用.sortModules()方法使MLP可用:
n.sortModules()
这个调用会执行一些内部初始化,这在使用网络之前是必要的。
19、 Milk
MILK(MACHINE LEARNING TOOLKIT) 是 Python 语言的机器学习工具包。它主要是包含许多分类器比如 SVMS、K-NN、随机森林以及决策树中使用监督分类法,它还可执行特征选择,可以形成不同的例如无监督学习、密切关系传播和由 MILK 支持的 K-means 聚类等分类系统。
使用 MILK 训练一个分类器:
import numpy as npimport milk features = np.random.rand(100,10)labels = np.zeros(100)features[50:] += .5labels[50:] = 1learner = milk.defaultclassifier()model = learner.train(features, labels)# Now you can use the model on new examples:example = np.random.rand(10)print(model.apply(example))example2 = np.random.rand(10)example2 += .5print(model.apply(example2))
20、 TensorFlow
TensorFlow 是一个端到端开源机器学习平台。它拥有一个全面而灵活的生态系统,一般可以将其分为 TensorFlow1.x 和 TensorFlow2.x,TensorFlow1.x 与 TensorFlow2.x 的主要区别在于 TF1.x 使用静态图而 TF2.x 使用Eager Mode动态图。
这里主要使用TensorFlow2.x作为示例,展示在 TensorFlow2.x 中构建卷积神经网络 (Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)。
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, models# 数据加载(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = datasets.cifar10.load_data()# 数据预处理train_images, test_images = train_images / 255.0, test_images / 255.0# 模型构建model = models.Sequential()model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)))model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))model.add(layers.Flatten())model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))model.add(layers.Dense(10))# 模型编译与训练model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True), metrics=['accuracy'])history = model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10, validation_data=(test_images, test_labels))
想要了解更多Tensorflow2.x的示例,可以参考专栏 Tensorflow.
21、 PyTorch
PyTorch 的前身是 Torch,其底层和 Torch 框架一样,但是使用 Python 重新写了很多内容,不仅更加灵活,支持动态图,而且提供了 Python 接口。
# 导入库import torchfrom torch import nnfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoaderfrom torchvision import datasetsfrom torchvision.transforms import ToTensor, Lambda, Composeimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 模型构建device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"print("Using {} device".format(device))# Define modelclass NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear_relu_stack = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 10),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.flatten(x)
logits = self.linear_relu_stack(x)
return logits
model = NeuralNetwork().to(device)# 损失函数和优化器loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)# 模型训练def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# Compute prediction error
pred = model(X)
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
# Backpropagation
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch % 100 == 0:
loss, current = loss.item(), batch * len(X)
print(f"loss: {loss:>7f} [{current:>5d}/{size:>5d}]")22、 Theano
Theano 是一个 Python 库,它允许定义、优化和有效地计算涉及多维数组的数学表达式,建在 NumPy 之上。
在 Theano 中实现计算雅可比矩阵:
import theanoimport theano.tensor as T
x = T.dvector('x')y = x ** 2J, updates = theano.scan(lambda i, y,x : T.grad(y[i], x), sequences=T.arange(y.shape[0]), non_sequences=[y,x])f = theano.function([x], J, updates=updates)f([4, 4])23、 Keras
Keras 是一个用 Python 编写的高级神经网络 API,它能够以 TensorFlow, CNTK, 或者 Theano 作为后端运行。Keras 的开发重点是支持快速的实验,能够以最小的时延把想法转换为实验结果。
from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import Dense# 模型构建model = Sequential()model.add(Dense(units=64, activation='relu', input_dim=100))model.add(Dense(units=10, activation='softmax'))# 模型编译与训练model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='sgd', metrics=['accuracy'])model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5, batch_size=32)
24、 Caffe
在 Caffe2 官方网站上,这样说道:Caffe2 现在是 PyTorch 的一部分。虽然这些 api 将继续工作,但鼓励使用 PyTorch api。
25、 MXNet
MXNet 是一款设计为效率和灵活性的深度学习框架。它允许混合符号编程和命令式编程,从而最大限度提高效率和生产力。
使用 MXNet 构建手写数字识别模型:
import mxnet as mxfrom mxnet import gluonfrom mxnet.gluon import nnfrom mxnet import autograd as agimport mxnet.ndarray as F# 数据加载mnist = mx.test_utils.get_mnist()batch_size = 100train_data = mx.io.NDArrayIter(mnist['train_data'], mnist['train_label'], batch_size, shuffle=True)val_data = mx.io.NDArrayIter(mnist['test_data'], mnist['test_label'], batch_size)# CNN模型class Net(gluon.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Net, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2D(20, kernel_size=(5,5))
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides = (2,2))
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2D(50, kernel_size=(5,5))
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides = (2,2))
self.fc1 = nn.Dense(500)
self.fc2 = nn.Dense(10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool1(F.tanh(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool2(F.tanh(self.conv2(x)))
# 0 means copy over size from corresponding dimension.
# -1 means infer size from the rest of dimensions.
x = x.reshape((0, -1))
x = F.tanh(self.fc1(x))
x = F.tanh(self.fc2(x))
return x
net = Net()# 初始化与优化器定义# set the context on GPU is available otherwise CPUctx = [mx.gpu() if mx.test_utils.list_gpus() else mx.cpu()]net.initialize(mx.init.Xavier(magnitude=2.24), ctx=ctx)trainer = gluon.Trainer(net.collect_params(), 'sgd', {'learning_rate': 0.03})# 模型训练# Use Accuracy as the evaluation metric.metric = mx.metric.Accuracy()softmax_cross_entropy_loss = gluon.loss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()for i in range(epoch):
# Reset the train data iterator.
train_data.reset()
for batch in train_data:
data = gluon.utils.split_and_load(batch.data[0], ctx_list=ctx, batch_axis=0)
label = gluon.utils.split_and_load(batch.label[0], ctx_list=ctx, batch_axis=0)
outputs = []
# Inside training scope
with ag.record():
for x, y in zip(data, label):
z = net(x)
# Computes softmax cross entropy loss.
loss = softmax_cross_entropy_loss(z, y)
# Backpropogate the error for one iteration.
loss.backward()
outputs.append(z)
metric.update(label, outputs)
trainer.step(batch.data[0].shape[0])
# Gets the evaluation result.
name, acc = metric.get()
# Reset evaluation result to initial state.
metric.reset()
print('training acc at epoch %d: %s=%f'%(i, name, acc))26、 PaddlePaddle
飞桨 (PaddlePaddle) 以百度多年的深度学习技术研究和业务应用为基础,集深度学习核心训练和推理框架、基础模型库、端到端开发套件、丰富的工具组件于一体。是中国首个自主研发、功能完备、开源开放的产业级深度学习平台。
使用 PaddlePaddle 实现 LeNtet5:
# 导入需要的包import paddleimport numpy as npfrom paddle.nn import Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Linear## 组网import paddle.nn.functional as F# 定义 LeNet 网络结构class LeNet(paddle.nn.Layer): def __init__(self, num_classes=1): super(LeNet, self).__init__() # 创建卷积和池化层 # 创建第1个卷积层 self.conv1 = Conv2D(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5) self.max_pool1 = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 尺寸的逻辑:池化层未改变通道数;当前通道数为6 # 创建第2个卷积层 self.conv2 = Conv2D(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5) self.max_pool2 = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 创建第3个卷积层 self.conv3 = Conv2D(in_channels=16, out_channels=120, kernel_size=4) # 尺寸的逻辑:输入层将数据拉平[B,C,H,W] -> [B,C*H*W] # 输入size是[28,28],经过三次卷积和两次池化之后,C*H*W等于120 self.fc1 = Linear(in_features=120, out_features=64) # 创建全连接层,第一个全连接层的输出神经元个数为64, 第二个全连接层输出神经元个数为分类标签的类别数 self.fc2 = Linear(in_features=64, out_features=num_classes) # 网络的前向计算过程 def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) # 每个卷积层使用Sigmoid激活函数,后面跟着一个2x2的池化 x = F.sigmoid(x) x = self.max_pool1(x) x = F.sigmoid(x) x = self.conv2(x) x = self.max_pool2(x) x = self.conv3(x) # 尺寸的逻辑:输入层将数据拉平[B,C,H,W] -> [B,C*H*W] x = paddle.reshape(x, [x.shape[0], -1]) x = self.fc1(x) x = F.sigmoid(x) x = self.fc2(x) return x
27、 CNTK
CNTK(Cognitive Toolkit) 是一个深度学习工具包,通过有向图将神经网络描述为一系列计算步骤。在这个有向图中,叶节点表示输入值或网络参数,而其他节点表示对其输入的矩阵运算。CNTK 可以轻松地实现和组合流行的模型类型,如 CNN 等。CNTK 用网络描述语言 (network description language, NDL) 描述一个神经网络。 简单的说,要描述输入的 feature,输入的 label,一些参数,参数和输入之间的计算关系,以及目标节点是什么。
NDLNetworkBuilder=[ run=ndlLR ndlLR=[ # sample and label dimensions SDim=$dimension$ LDim=1 features=Input(SDim, 1) labels=Input(LDim, 1) # parameters to learn B0 = Parameter(4) W0 = Parameter(4, SDim) B = Parameter(LDim) W = Parameter(LDim, 4) # operations t0 = Times(W0, features) z0 = Plus(t0, B0) s0 = Sigmoid(z0) t = Times(W, s0) z = Plus(t, B) s = Sigmoid(z) LR = Logistic(labels, s) EP = SquareError(labels, s) # root nodes FeatureNodes=(features) LabelNodes=(labels) CriteriaNodes=(LR) EvalNodes=(EP) OutputNodes=(s,t,z,s0,W0) ] ]
总结与分类
python 常用机器学习及深度学习库总结
| 库名 | 官方网站 | 简介 |
|---|---|---|
| NumPy | http://www.numpy.org/ | 提供对大型多维阵列的支持,NumPy是计算机视觉中的一个关键库,因为图像可以表示为多维数组,将图像表示为NumPy数组有许多优点 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https://opencv.org/ | 开源的计算机视觉库 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https:// scikit-image.org/ | 图像处理算法的集合,由scikit-image操作的图像只能是NumPy数组 |
| Python Imaging Library(PIL) | http://www.pythonware.com/products/pil/ | 图像处理库,提供强大的图像处理和图形功能 |
| Pillow | https://pillow.readthedocs.io/ | PIL的一个分支 |
| SimpleCV | http://simplecv.org/ | 计算机视觉框架,提供了处理图像处理的关键功能 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https://mahotas.readthedocs.io/ | 提供了用于图像处理和计算机视觉的一组函数,它最初是为生物图像信息学而设计的;但是,现在它在其他领域也发挥了重要作用,它完全基于numpy数组作为其数据类型 |
| Ilastik | http://ilastik.org/ | 用户友好且简单的交互式图像分割、分类和分析工具 |
| Scikit-learn | http://scikit-learn.org/ | 机器学习库,具有各种分类、回归和聚类算法 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https://www.scipy.org/ | 科学和技术计算库 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https://www.nltk.org/ | 处理自然语言数据的库和程序 |
| spaCy | https://spacy.io/ | 开源软件库,用于Python中的高级自然语言处理 |
| LibROSA | https://librosa.github.io/librosa/ | 用于音乐和音频处理的库 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https://pandas.pydata.org/ | 构建在NumPy之上的库,提供高级数据计算工具和易于使用的数据结构 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https://matplotlib.org | 绘图库,它提供了一整套和 matlab 相似的命令 API,可以生成所需的出版质量级别的图形 |
| Seaborn | https://Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe).pydata.org/ | 是建立在Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe)之上的绘图库 |
| Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | https://orange.biolab.si/ | 面向新手和专家的开源机器学习和数据可视化工具包 |
| PyBrain | http://pybrain.org/ | 机器学习库,为机器学习提供易于使用的最新算法 |
| Milk | http://luispedro.org/software/milk/ | 机器学习工具箱,主要用于监督学习中的多分类问题 |
| TensorFlow | https://www.tensorflow.org/ | 开源的机器学习和深度学习库 |
| PyTorch | https://pytorch.org/ | 开源的机器学习和深度学习库 |
| Theano | http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/ | 用于快速数学表达式、求值和计算的库,已编译为可在CPU和GPU架构上运行 |
| Keras | https://keras.io/ | 高级深度学习库,可以在 TensorFlow、CNTK、Theano 或 Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit 之上运行 |
| Caffe2 | https://caffe2.ai/ | Caffe2 是一个兼具表现力、速度和模块性的深度学习框架,是 Caffe 的实验性重构,能以更灵活的方式组织计算 |
| MXNet | https://mxnet.apache.org/ | 设计为效率和灵活性的深度学习框架,允许混合符号编程和命令式编程 |
| PaddlePaddle | https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn | 以百度多年的深度学习技术研究和业务应用为基础,集深度学习核心训练和推理框架、基础模型库、端到端开发套件、丰富的工具组件于一体 |
| CNTK | https://cntk.ai/ | 深度学习工具包,通过有向图将神经网络描述为一系列计算步骤。在这个有向图中,叶节点表示输入值或网络参数,而其他节点表示对其输入的矩阵运算 |
Klassifizierung
Diese Bibliotheken können nach ihrem Hauptzweck klassifiziert werden:
| Kategorie | Bibliotheken |
|---|---|
| Bildverarbeitung | NumPy, Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe), Scikit Image, PIL, Pillow, SimpleCV, Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) , ilastik |
| Textverarbeitung | Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe), spaCy, NumPy, scikit learn, PyTorch |
| Audioverarbeitung | LibROSA |
| Maschinelles Lernen | pandas, scikit-learn, Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe), PyBrain, Milch |
| Datenanzeige | Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe), Seaborn, scikit-learn, Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) |
| Deep Learning | TensorFlow, Pytorch, Theano, Keras, Caffe2, MXNet, PaddlePaddle, CNTK |
| Wissenschaftliches Rechnen | Einführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe) | .
Empfohlenes Lernen: Python-Video-Tutorial
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonEinführung in häufig verwendete Bibliotheken für maschinelles Lernen und Deep Learning in Python (Zusammenfassungsfreigabe). Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1382
1382
 52
52
 PHP und Python: Code Beispiele und Vergleich
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP und Python: Code Beispiele und Vergleich
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP und Python haben ihre eigenen Vor- und Nachteile, und die Wahl hängt von den Projektbedürfnissen und persönlichen Vorlieben ab. 1.PHP eignet sich für eine schnelle Entwicklung und Wartung großer Webanwendungen. 2. Python dominiert das Gebiet der Datenwissenschaft und des maschinellen Lernens.
 Wie ist die GPU -Unterstützung für Pytorch bei CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Wie ist die GPU -Unterstützung für Pytorch bei CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Aktivieren Sie die Pytorch -GPU -Beschleunigung am CentOS -System erfordert die Installation von CUDA-, CUDNN- und GPU -Versionen von Pytorch. Die folgenden Schritte führen Sie durch den Prozess: Cuda und Cudnn Installation Bestimmen Sie die CUDA-Version Kompatibilität: Verwenden Sie den Befehl nvidia-smi, um die von Ihrer NVIDIA-Grafikkarte unterstützte CUDA-Version anzuzeigen. Beispielsweise kann Ihre MX450 -Grafikkarte CUDA11.1 oder höher unterstützen. Download und installieren Sie Cudatoolkit: Besuchen Sie die offizielle Website von Nvidiacudatoolkit und laden Sie die entsprechende Version gemäß der höchsten CUDA -Version herunter und installieren Sie sie, die von Ihrer Grafikkarte unterstützt wird. Installieren Sie die Cudnn -Bibliothek:
 Detaillierte Erklärung des Docker -Prinzips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detaillierte Erklärung des Docker -Prinzips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker verwendet Linux -Kernel -Funktionen, um eine effiziente und isolierte Anwendungsumgebung zu bieten. Sein Arbeitsprinzip lautet wie folgt: 1. Der Spiegel wird als schreibgeschützte Vorlage verwendet, die alles enthält, was Sie für die Ausführung der Anwendung benötigen. 2. Das Union File System (UnionFS) stapelt mehrere Dateisysteme, speichert nur die Unterschiede, speichert Platz und beschleunigt. 3. Der Daemon verwaltet die Spiegel und Container, und der Kunde verwendet sie für die Interaktion. 4. Namespaces und CGroups implementieren Container -Isolation und Ressourcenbeschränkungen; 5. Mehrere Netzwerkmodi unterstützen die Containerverbindung. Nur wenn Sie diese Kernkonzepte verstehen, können Sie Docker besser nutzen.
 Python gegen JavaScript: Community, Bibliotheken und Ressourcen
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python gegen JavaScript: Community, Bibliotheken und Ressourcen
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python und JavaScript haben ihre eigenen Vor- und Nachteile in Bezug auf Gemeinschaft, Bibliotheken und Ressourcen. 1) Die Python-Community ist freundlich und für Anfänger geeignet, aber die Front-End-Entwicklungsressourcen sind nicht so reich wie JavaScript. 2) Python ist leistungsstark in Bibliotheken für Datenwissenschaft und maschinelles Lernen, während JavaScript in Bibliotheken und Front-End-Entwicklungsbibliotheken und Frameworks besser ist. 3) Beide haben reichhaltige Lernressourcen, aber Python eignet sich zum Beginn der offiziellen Dokumente, während JavaScript mit Mdnwebdocs besser ist. Die Wahl sollte auf Projektbedürfnissen und persönlichen Interessen beruhen.
 Miniopen CentOS -Kompatibilität
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
Miniopen CentOS -Kompatibilität
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
Minio-Objektspeicherung: Hochleistungs-Bereitstellung im Rahmen von CentOS System Minio ist ein hochleistungsfähiges, verteiltes Objektspeichersystem, das auf der GO-Sprache entwickelt wurde und mit Amazons3 kompatibel ist. Es unterstützt eine Vielzahl von Kundensprachen, darunter Java, Python, JavaScript und Go. In diesem Artikel wird kurz die Installation und Kompatibilität von Minio zu CentOS -Systemen vorgestellt. CentOS -Versionskompatibilitätsminio wurde in mehreren CentOS -Versionen verifiziert, einschließlich, aber nicht beschränkt auf: CentOS7.9: Bietet einen vollständigen Installationshandbuch für die Clusterkonfiguration, die Umgebungsvorbereitung, die Einstellungen von Konfigurationsdateien, eine Festplattenpartitionierung und Mini
 Wie man eine verteilte Schulung von Pytorch auf CentOS betreibt
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
Wie man eine verteilte Schulung von Pytorch auf CentOS betreibt
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
Pytorch Distributed Training on CentOS -System erfordert die folgenden Schritte: Pytorch -Installation: Die Prämisse ist, dass Python und PIP im CentOS -System installiert sind. Nehmen Sie abhängig von Ihrer CUDA -Version den entsprechenden Installationsbefehl von der offiziellen Pytorch -Website ab. Für CPU-Schulungen können Sie den folgenden Befehl verwenden: PipinstallTorChTorChVisionTorChaudio Wenn Sie GPU-Unterstützung benötigen, stellen Sie sicher, dass die entsprechende Version von CUDA und CUDNN installiert ist und die entsprechende Pytorch-Version für die Installation verwenden. Konfiguration der verteilten Umgebung: Verteiltes Training erfordert in der Regel mehrere Maschinen oder mehrere Maschinen-Mehrfach-GPUs. Ort
 So wählen Sie die Pytorch -Version auf CentOS aus
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
So wählen Sie die Pytorch -Version auf CentOS aus
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Bei der Installation von PyTorch am CentOS -System müssen Sie die entsprechende Version sorgfältig auswählen und die folgenden Schlüsselfaktoren berücksichtigen: 1. Kompatibilität der Systemumgebung: Betriebssystem: Es wird empfohlen, CentOS7 oder höher zu verwenden. CUDA und CUDNN: Pytorch -Version und CUDA -Version sind eng miteinander verbunden. Beispielsweise erfordert Pytorch1.9.0 CUDA11.1, während Pytorch2.0.1 CUDA11.3 erfordert. Die Cudnn -Version muss auch mit der CUDA -Version übereinstimmen. Bestimmen Sie vor der Auswahl der Pytorch -Version unbedingt, dass kompatible CUDA- und CUDNN -Versionen installiert wurden. Python -Version: Pytorch Official Branch
 So installieren Sie Nginx in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
So installieren Sie Nginx in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
Die Installation von CentOS-Installationen erfordert die folgenden Schritte: Installieren von Abhängigkeiten wie Entwicklungstools, PCRE-Devel und OpenSSL-Devel. Laden Sie das Nginx -Quellcode -Paket herunter, entpacken Sie es, kompilieren Sie es und installieren Sie es und geben Sie den Installationspfad als/usr/local/nginx an. Erstellen Sie NGINX -Benutzer und Benutzergruppen und setzen Sie Berechtigungen. Ändern Sie die Konfigurationsdatei nginx.conf und konfigurieren Sie den Hörport und den Domänennamen/die IP -Adresse. Starten Sie den Nginx -Dienst. Häufige Fehler müssen beachtet werden, z. B. Abhängigkeitsprobleme, Portkonflikte und Konfigurationsdateifehler. Die Leistungsoptimierung muss entsprechend der spezifischen Situation angepasst werden, z. B. das Einschalten des Cache und die Anpassung der Anzahl der Arbeitsprozesse.



