Eine ausführliche Erklärung des Flex-Layouts in CSS3
Dieser Artikel führt Sie durch das Flex-Layout in CSS3, ich hoffe, er wird Ihnen hilfreich sein!

Einführung
Was ist Flex-Layout?
Flex ist die Abkürzung für Flexible Box, auch als flexibles Box-Layout bekannt.
Flex-Layout besteht aus:
- Flex-Container (
Flex-Container) - flex项(
flex items) - 主轴(
main axis) - 交叉轴(
cross axis)
flex container)Flex布局的作用
在flex布局未出现前,网页布局的方式为标准流,浮动,定位等。在解决比较复杂的问题相对麻烦。【学习视频分享:css视频教程、web前端】
而flex布局可以:
- 自动弹性伸缩
- 更轻松地设计灵活的响应式布局结构
- 精确灵活控制块级盒子的布局方式
- 在pc端和移动端都适用
Flex容器(父元素)属性
在使用flex布局之前首先定义 Flex 容器。
display:flex;
定义 Flex 容器后可以使用相应的属性, 改变子元素的布局方式,让子元素可以自动的挤压或拉伸。
相应属性:
1. justify-content 主轴元素对齐方式 2. align-items 交叉轴元素对齐方式 3. flex-direction 设置主轴方向 4. flex-wrap 主轴一行满了换行 5. align-content 交叉轴行对齐方式 6. flex-flow 同时设置 flex-direction和 flex-wrap属性
1. justify-content
容器的justify-content属性可以设置子元素在主轴方向的对齐方式。(记得先display:flex;定义容器)
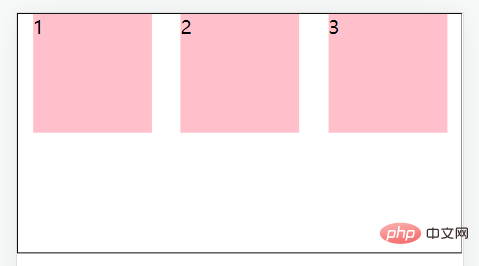
justify-content: center;//居中对齐
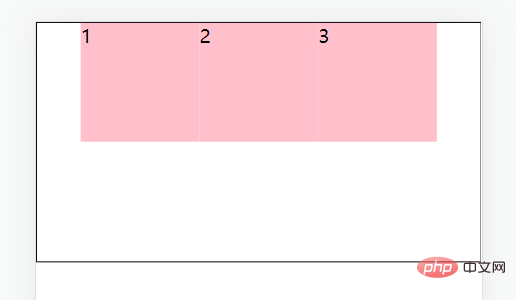
justify-content: space-between;//间距在子元素之间
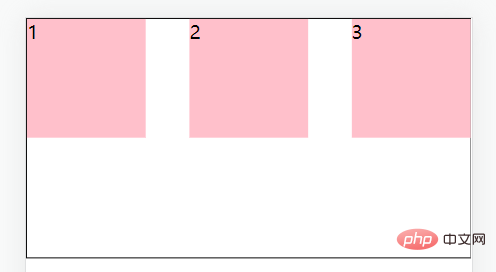
justify-content: space-evenly;//主轴方向所有地方的间距都相等
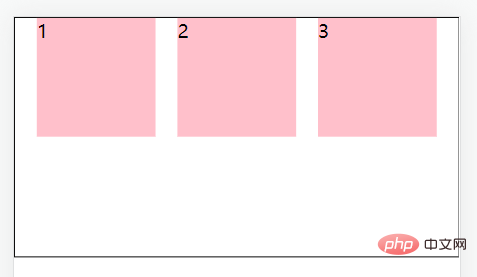
justify-content: space-around;//间距加在子元素的两侧(中间大的是两个子元素的加在一起)
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>主轴对齐方式</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box {
display: flex;
/* justify-content: center; */
/* justify-content: space-between; */
/* justify-content: space-evenly; */
justify-content: space-around;
height: 200px;
margin: auto;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>2. align-items
容器的align-items属性可以设置子元素在交叉轴方向的对齐方式。
由此我们可以设置将容器属性justify-content和 align-items 设置为居中,让元素实现完美居中。
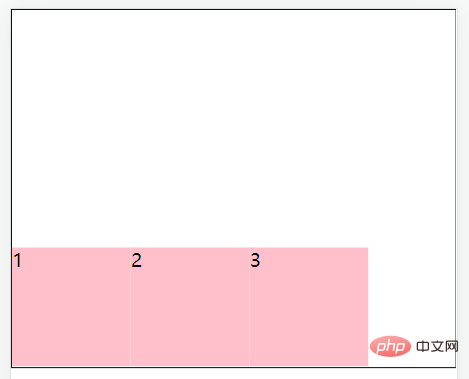
align-items: center;//居中
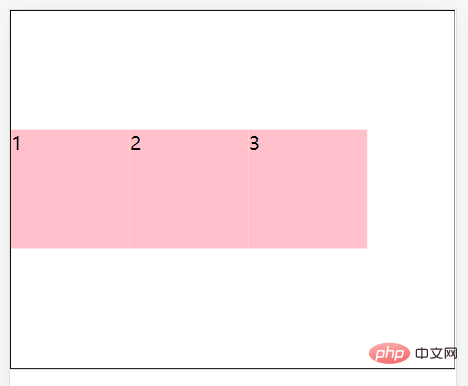
align-items: stretch;//拉伸,默认值(现有状态,这里测试去掉子级的高度)
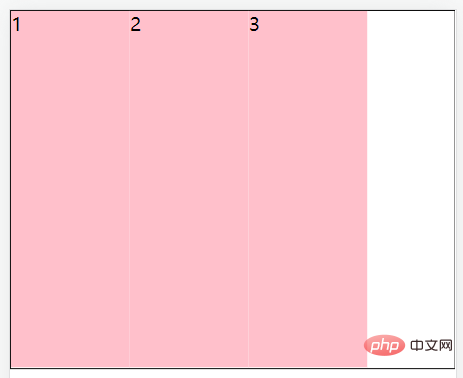
align-items: flex-start;//将子元素在容器顶部对齐
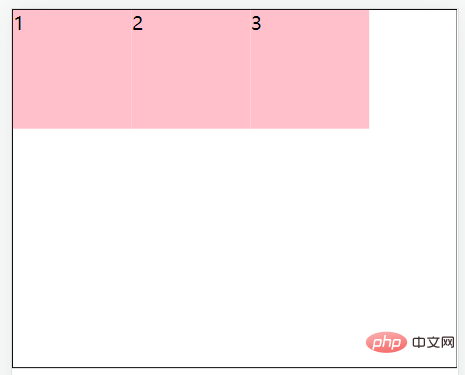
align-items: flex-end;//将子元素在容器底部对齐
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>交叉轴对齐方式</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.father {
display: flex;
/* 居中 */
/* align-items: center; */
/* 拉伸,默认值(现有状态,测试的时候去掉子级的高度) */
/* align-items: stretch; */
/* align-items: flex-start; */
align-items: flex-end;
height: 300px;
margin: auto;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.father div {
/* 如果不设置宽,由内容撑开 */
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>3. flex-direction
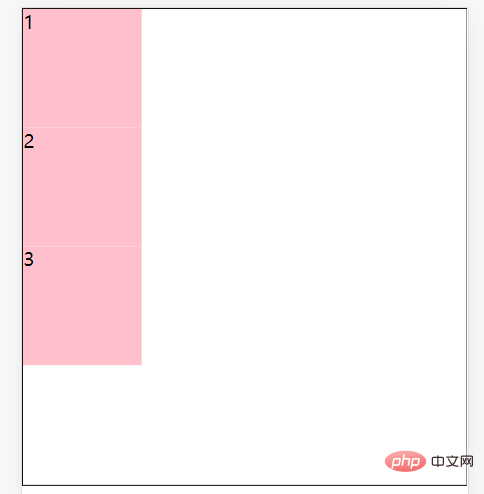
容器的flex-direction属性可以改变flex布局的主轴方向。flex主轴方向默认为水平向右方向。如果修改主轴方向,那么交叉轴方向也会与之改变。
flex-direction: column;//主轴方向为垂直方向(从上到下)
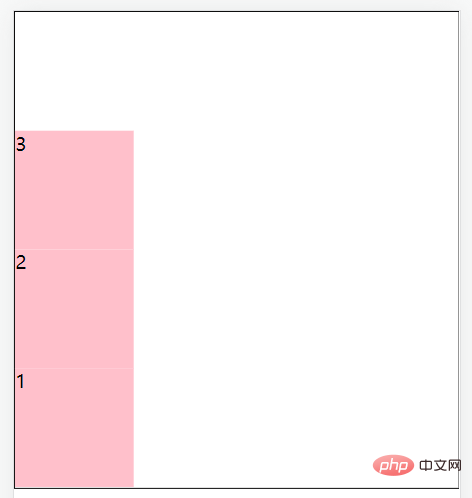
flex-direction: column-reverse;//主轴方向为垂直方向(从下到上)
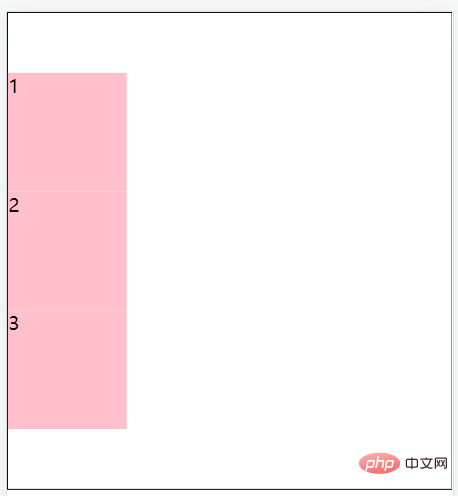
flex-direction: row;//主轴方向为水平方向(从左到右)

flex-direction: row-reverse;//主轴方向为水平方向(从右到左)

修改主轴方向后实现垂直居中:
display:flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center;
4. flex-wrap
当定义flex容器之后,如果子元素过多超出主轴方向宽度,容器内的子元素会自动伸缩。
如:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>弹性盒子换行</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box {
display: flex;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div>4</div>
<div>5</div>
<div>6</div>
<div>7</div>
<div>8</div>
<div>9</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>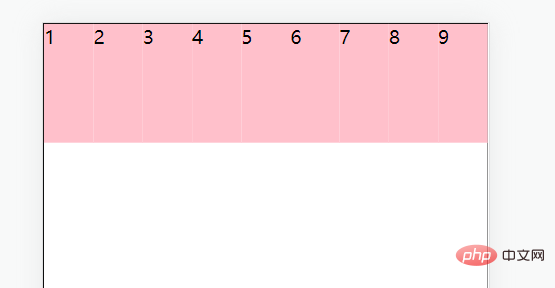
解决:容器的flex-wrap属性可以让超出容器主轴方向的子元素换行显示。
flex-wrap: nowrap;//默认值,不换行 flex-wrap: wrap;//换行,从上到下
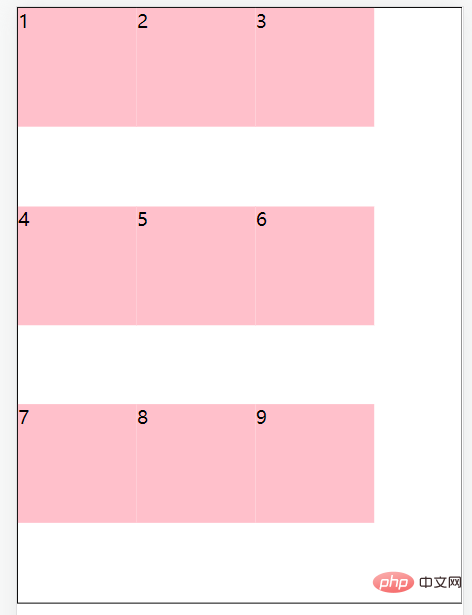
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;//换行,从下到上

5. align-content
容器的align-contentFlex-Elemente (Flex-Elemente)Hauptachse (Hauptachse)Querachse (Querachse)
 🎜🎜🎜Die Rolle des Flex-Layouts🎜🎜🎜Bevor das Flex-Layout erschien, waren die Webseiten-Layoutmethoden Standardfluss, Floating und Positionierung , usw. Es ist relativ mühsam, komplexere Probleme zu lösen. [Teilen von Lernvideos: CSS-Video-Tutorial, web front-end]🎜🎜Und der
🎜🎜🎜Die Rolle des Flex-Layouts🎜🎜🎜Bevor das Flex-Layout erschien, waren die Webseiten-Layoutmethoden Standardfluss, Floating und Positionierung , usw. Es ist relativ mühsam, komplexere Probleme zu lösen. [Teilen von Lernvideos: CSS-Video-Tutorial, web front-end]🎜🎜Und der flex Layout kann sein:🎜🎜 🎜Automatische elastische Skalierung🎜Einfaches Entwerfen flexibler, responsiver Layoutstrukturen🎜Präzises und flexibles Steuern des Layouts von Boxen auf Blockebene🎜Anwendbar sowohl auf PCs als auch auf mobilen Endgeräten< /li> 🎜🎜Eigenschaft des Flex-Containers (übergeordnetes Element)🎜🎜🎜🎜Definieren Sie zunächst den Flex-Container, bevor Sie das Flex-Layout verwenden. 🎜🎜align-content: center;//居中对齐 align-content: space-around;//间距加在子元素的两侧(中间大的是两个子元素的加在一起) align-content: space-between;//间距在子元素之间
align-content: stretch;拉伸,默认值(现有状态,这里测试去掉子级的高度)
justify-content-Attribut des Containers kann die Ausrichtung von untergeordneten Elementen in der 🎜Hauptachsenrichtung🎜 festlegen. (Denken Sie daran, zuerst den Container mit display:flex; zu definieren.) .png " alt="Eine ausführliche Erklärung des Flex-Layouts in CSS3"/>🎜flex-flow: row wrap;
 🎜
🎜1. flex-grow 2. flex-shrink 3. flex-basis 4. flex 5. align-self 6. order
 🎜
🎜<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
}
.box1{
/* 没有设置宽度 */
background:red;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.box2{
background:blue;
flex-grow: 2;
}
.box3{
background:orange;
flex-grow: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
background:red;
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
background:blue;
flex-shrink: 2;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
background:orange;
flex-shrink: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>align-items des Containers items🎜🎜🎜 kann die Ausrichtung von untergeordneten Elementen in der 🎜Querachsenrichtung🎜 festlegen. 🎜🎜🎜Daraus können wir die Containerattribute justify-content und align-items so einstellen, dass sie zentriert sind, sodass das Element perfekt zentriert ist. 🎜🎜flex: grow shrink basis;//顺序不能改变,默认值为0 1 auto;
 🎜
🎜<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
align-items: center;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background:red;
align-self: flex-start;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background:blue;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background:orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html> 🎜
🎜<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
background:red;
order: 2;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
background:blue;
order: 1;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
background:orange;
order: 3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html> 🎜rrreee🎜
🎜rrreee🎜 🎜 Code: 🎜rrreee🎜🎜3. Eigenschaften von flex-direction🎜🎜🎜container
🎜 Code: 🎜rrreee🎜🎜3. Eigenschaften von flex-direction🎜🎜🎜container flex-direction kann die Hauptachsenrichtung des Flex-Layouts ändern. Die Standardrichtung der flexiblen Spindel ist horizontal nach rechts. Wenn Sie die Richtung der Hauptachse ändern, ändert sich auch die Richtung der Querachse. 🎜rrreee🎜 🎜rrreee🎜
🎜rrreee🎜 🎜rrreee🎜
🎜rrreee🎜 🎜rrreee🎜
🎜rrreee🎜 🎜 Ändern Sie die Richtung der Hauptachse, um eine vertikale Zentrierung zu erreichen: 🎜rrreee🎜
🎜 Ändern Sie die Richtung der Hauptachse, um eine vertikale Zentrierung zu erreichen: 🎜rrreee🎜 🎜🎜🎜4. flex-wrap🎜🎜🎜Wenn der
🎜🎜🎜4. flex-wrap🎜🎜🎜Wenn der flex-Container definiert ist Wenn das untergeordnete Element zu viele Elemente enthält, die die Breite der Hauptachse überschreiten, werden die untergeordneten Elemente im Container automatisch erweitert und verkleinert. 🎜 Wie zum Beispiel: 🎜rrreee🎜 🎜 Lösung: Container Das Attribut
🎜 Lösung: Container Das Attribut flex-wrap kann Unterelemente über die Hauptachse des Containers hinaus umbrechen. 🎜rrreee🎜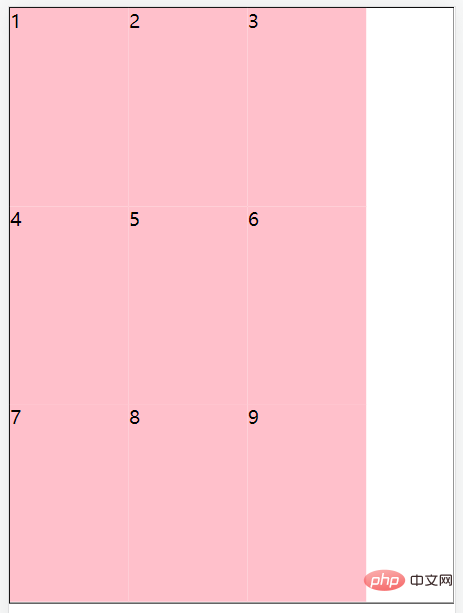 🎜🎜🎜5. content🎜🎜🎜container< Das Attribut code>align-content kann die Ausrichtung von Unterelementzeilen anpassen (🎜Sie müssen zuerst den Zeilenumbruch festlegen🎜). 🎜
🎜🎜🎜5. content🎜🎜🎜container< Das Attribut code>align-content kann die Ausrichtung von Unterelementzeilen anpassen (🎜Sie müssen zuerst den Zeilenumbruch festlegen🎜). 🎜align-content: center;//居中对齐 align-content: space-around;//间距加在子元素的两侧(中间大的是两个子元素的加在一起) align-content: space-between;//间距在子元素之间
前三者的属性跟主轴对齐方式一样就不再赘述。
align-content: stretch;拉伸,默认值(现有状态,这里测试去掉子级的高度)

6.flex-flow
flex-flow属性是用于同时设置 flex-direction 和 flex-wrap 属性的简写属性。
flex-flow: row wrap;
Flex项(子元素)属性
我们可以设置相应属性让flex 容器的直接子元素成为弹性(flex)项目。(在使用flex布局之前首先定义 Flex 容器。)
相应属性:
1. flex-grow 2. flex-shrink 3. flex-basis 4. flex 5. align-self 6. order
1. flex-grow
使用flex-grow属性来定义弹性盒子内部子元素的放大比例(当所有子元素宽度之和小于父元素的宽度时子元素如何分配父元素的剩余空间)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
}
.box1{
/* 没有设置宽度 */
background:red;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.box2{
background:blue;
flex-grow: 2;
}
.box3{
background:orange;
flex-grow: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2. flex-shrink
使用flex-shrink属性来定义弹性盒子内部子元素的缩小比例(当所有子元素宽度之和大于父元素的宽度时子元素如何缩小自己的宽度)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
background:red;
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
background:blue;
flex-shrink: 2;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
background:orange;
flex-shrink: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3. flex-basis
使用flex-basis属性来设置子元素的宽度,默认值为auto(作用跟width一样,优先级比width高,就算width在后面也会显示flex-basis)。
4. flex
使用flex属性来同时设置flex-grow、flex-shrink、flex-basis这3个属性,flex属性就是一个复合属性。
实际应用一般用复合属性。
语法:
flex: grow shrink basis;//顺序不能改变,默认值为0 1 auto;
5. align-self
使用align-self属性设置子元素项目的对齐方式。
注意:align-self属性会覆盖容器的 align-items 属性所设置的对齐方式。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
align-items: center;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background:red;
align-self: flex-start;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background:blue;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background:orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>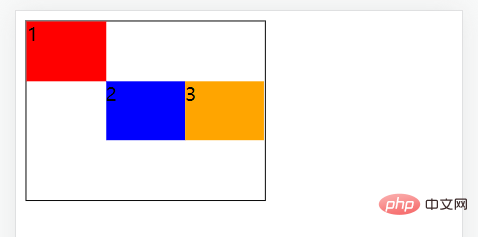
6. order
使用order属性来定义子元素的排列顺序。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
display:flex;
width:200px;
height:150px;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
background:red;
order: 2;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
background:blue;
order: 1;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
background:orange;
order: 3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonEine ausführliche Erklärung des Flex-Layouts in CSS3. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1377
1377
 52
52
 So ändern Sie Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
So ändern Sie Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
Um die Größe der Elemente in Bootstrap anzupassen, können Sie die Dimensionsklasse verwenden, einschließlich: Einstellbreite:.
 So fügen Sie Bilder auf Bootstrap ein
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
So fügen Sie Bilder auf Bootstrap ein
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
Es gibt verschiedene Möglichkeiten, Bilder in Bootstrap einzufügen: Bilder direkt mit dem HTML -IMG -Tag einfügen. Mit der Bootstrap -Bildkomponente können Sie reaktionsschnelle Bilder und weitere Stile bereitstellen. Legen Sie die Bildgröße fest und verwenden Sie die IMG-Fluid-Klasse, um das Bild anpassungsfähig zu machen. Stellen Sie den Rand mit der img-beliebten Klasse ein. Stellen Sie die abgerundeten Ecken ein und verwenden Sie die IMG-Rund-Klasse. Setzen Sie den Schatten, verwenden Sie die Schattenklasse. Größen Sie die Größe und positionieren Sie das Bild im CSS -Stil. Verwenden Sie mit dem Hintergrundbild die CSS-Eigenschaft im Hintergrund.
 So verwenden Sie die Bootstrap -Taste
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
So verwenden Sie die Bootstrap -Taste
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
Wie benutze ich die Bootstrap -Taste? Führen Sie Bootstrap -CSS ein, um Schaltflächenelemente zu erstellen, und fügen Sie die Schaltfläche "Bootstrap" hinzu, um Schaltflächentext hinzuzufügen
 So richten Sie das Framework für Bootstrap ein
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
So richten Sie das Framework für Bootstrap ein
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
Um das Bootstrap -Framework einzurichten, müssen Sie die folgenden Schritte befolgen: 1. Verweisen Sie die Bootstrap -Datei über CDN; 2. Laden Sie die Datei auf Ihrem eigenen Server herunter und hosten Sie sie. 3.. Fügen Sie die Bootstrap -Datei in HTML hinzu; 4. Kompilieren Sie Sass/weniger bei Bedarf; 5. Importieren Sie eine benutzerdefinierte Datei (optional). Sobald die Einrichtung abgeschlossen ist, können Sie die Grid -Systeme, -Komponenten und -stile von Bootstrap verwenden, um reaktionsschnelle Websites und Anwendungen zu erstellen.
 So schreiben Sie geteilte Zeilen auf Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
So schreiben Sie geteilte Zeilen auf Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Es gibt zwei Möglichkeiten, eine Bootstrap -Split -Zeile zu erstellen: Verwenden des Tags, das eine horizontale Split -Linie erstellt. Verwenden Sie die CSS -Border -Eigenschaft, um benutzerdefinierte Style Split -Linien zu erstellen.
 Die Rollen von HTML, CSS und JavaScript: Kernverantwortung
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
Die Rollen von HTML, CSS und JavaScript: Kernverantwortung
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML definiert die Webstruktur, CSS ist für Stil und Layout verantwortlich, und JavaScript ergibt eine dynamische Interaktion. Die drei erfüllen ihre Aufgaben in der Webentwicklung und erstellen gemeinsam eine farbenfrohe Website.
 So sehen Sie das Datum der Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
So sehen Sie das Datum der Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
ANTWORT: Sie können die Datumsauswahlkomponente von Bootstrap verwenden, um Daten auf der Seite anzuzeigen. Schritte: Stellen Sie das Bootstrap -Framework ein. Erstellen Sie ein Eingangsfeld für Datumsauswahl in HTML. Bootstrap fügt dem Selektor automatisch Stile hinzu. Verwenden Sie JavaScript, um das ausgewählte Datum zu erhalten.
 So verwenden Sie Bootstrap in Vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
So verwenden Sie Bootstrap in Vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Die Verwendung von Bootstrap in Vue.js ist in fünf Schritte unterteilt: Startstrap installieren. Bootstrap in main.js. Verwenden Sie die Bootstrap -Komponente direkt in der Vorlage. Optional: benutzerdefinierter Stil. Optional: Verwenden Sie Plug-Ins.