./file Wenn kein benutzerdefinierter Loader vorhanden ist, wird die Dateierweiterung nicht durchsucht, z. B. . /file.js oder ./file.mjs" >Intl.NumberFormat(locales, options)
./file Wenn kein benutzerdefinierter Loader vorhanden ist, wird die Dateierweiterung nicht durchsucht, z. B. . /file.js oder ./file.mjs
 Web-Frontend
Web-Frontend
 js-Tutorial
js-Tutorial
 Node.js 19 ist offiziell veröffentlicht, lassen Sie uns über seine 6 Hauptfunktionen sprechen!
Node.js 19 ist offiziell veröffentlicht, lassen Sie uns über seine 6 Hauptfunktionen sprechen!
Node.js 19 ist offiziell veröffentlicht, lassen Sie uns über seine 6 Hauptfunktionen sprechen!
Node 19 wurde offiziell veröffentlicht. Dieser Artikel gibt Ihnen eine detaillierte Erklärung der 6 Hauptfunktionen von Node.js 19. Ich hoffe, dass er für alle hilfreich sein wird!

Übersetzt von: 6 Hauptfunktionen von Node.js 19. Details zu Node.js 19 neuen Funktionen… |. Bessere Programmierung
Node.js 14 wird enden Nach Ablauf der Update-Wartung im April 2023 wird die Update-Wartung für Node.js 16 (LTS) voraussichtlich im September 2023 enden.
Und Node 19 wurde am 18.10.2022 veröffentlicht. [Verwandte Tutorial-Empfehlungen: nodejs-Video-Tutorial]
Wir wissen, dass es zwei Versionen von Node.js gibt: LTS und Current
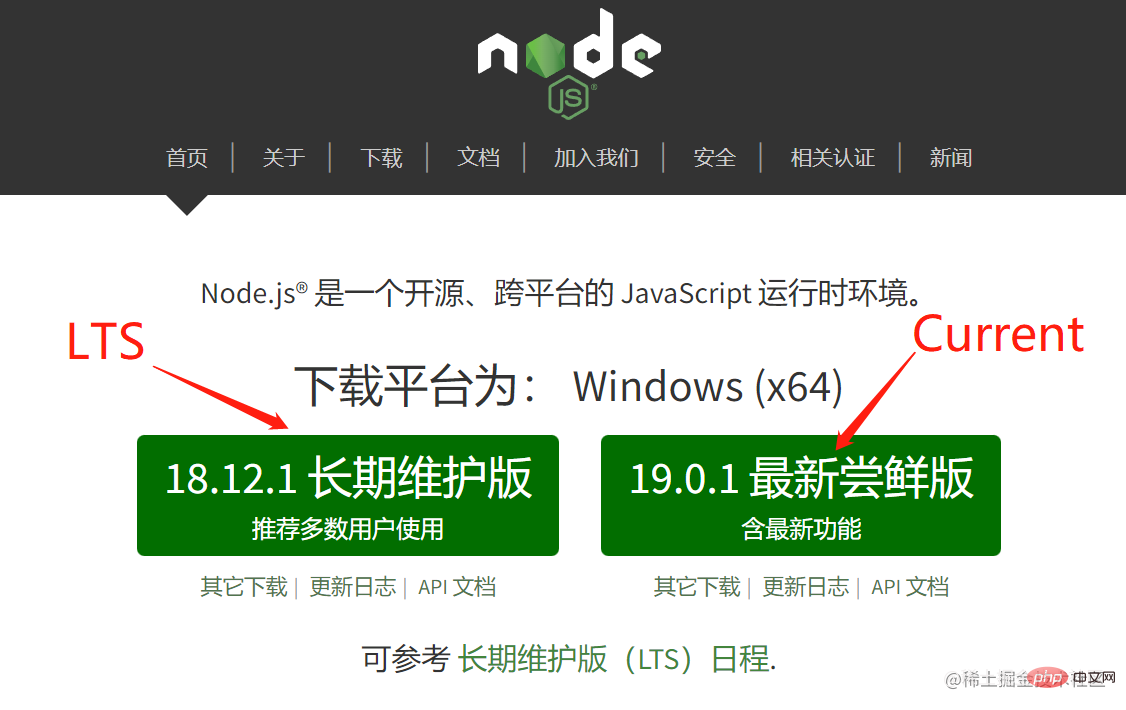
Unter diesen wird die aktuelle Version normalerweise alle 6 Monate veröffentlicht.
Neue Versionen mit geraden Nummern werden jeden April veröffentlicht.
Neue Versionen mit ungeraden Nummern werden jedes Jahr im Oktober veröffentlicht von 6 Tolle Funktionen.
1. HTTP(S)/1.1 KeepAlive ist standardmäßig auf true eingestelltNode.js v19 setzt den KeepAlive-Standardwert auf true, was bedeutet, dass alle ausgehenden HTTP(s)-Verbindungen HTTP 1.1 KeepAlive verwenden, Standardzeit für 5S ;
Codetest:
const http = require('node:http'); console.log(http.globalAgent); const https = require('node:https'); console.log(https.globalAgent);
Wir können die Unterschiede in der Knotenserver-Agentenkonfiguration zwischen Version 16 und Version 19 vergleichen:
V16% nvm use 16 Now using node v16.0.0 (npm v7.10.0) % node server Agent { _events: [Object: null prototype] { free: [Function (anonymous)], newListener: [Function: maybeEnableKeylog] }, _eventsCount: 2, _maxListeners: undefined, defaultPort: 80, protocol: 'http:', options: [Object: null prototype] { path: null }, requests: [Object: null prototype] {}, sockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, freeSockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, keepAliveMsecs: 1000, keepAlive : false, maxSockets: Infinity, maxFreeSockets: 256, scheduling: 'lifo', maxTotalSockets: Infinity, totalSocketCount: 0, [Symbol(kCapture)]: false } Agent { _events: [Object: null prototype] { free: [Function (anonymous)], newListener: [Function: maybeEnableKeylog] }, _eventsCount: 2, _maxListeners: undefined, defaultPort: 443, protocol: 'https:', options: [Object: null prototype] { path: null }, requests: [Object: null prototype] {}, sockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, freeSockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, keepAliveMsecs: 1000, keepAlive: false, maxSockets: Infinity, maxFreeSockets: 256, scheduling: 'lifo', maxTotalSockets: Infinity, totalSocketCount: 0, maxCachedSessions: 100, _sessionCache: { map: {}, list: [] }, [Symbol(kCapture)]: false }Nach dem Login kopierenZeilen 18 und 40, keepAlive ist standardmäßig auf false gesetzt;
-
% nvm use 19 Now using node v19.0.0 (npm v8.19.2) % node server Agent { _events: [Object: null prototype] { free: [Function (anonymous)], newListener: [Function: maybeEnableKeylog] }, _eventsCount: 2, _maxListeners: undefined, defaultPort: 80, protocol: 'http:', options: [Object: null prototype] { keepAlive: true, scheduling: 'lifo', timeout: 5000, noDelay: true, path: null }, requests: [Object: null prototype] {}, sockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, freeSockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, keepAliveMsecs: 1000, keepAlive: true, maxSockets: Infinity, maxFreeSockets: 256, scheduling: 'lifo', maxTotalSockets: Infinity, totalSocketCount: 0, [Symbol(kCapture)]: false } Agent { _events: [Object: null prototype] { free: [Function (anonymous)], newListener: [Function: maybeEnableKeylog] }, _eventsCount: 2, _maxListeners: undefined, defaultPort: 443, protocol: 'https:', options: [Object: null prototype] { keepAlive: true, scheduling: 'lifo', timeout: 5000, noDelay: true, path: null }, requests: [Object: null prototype] {}, sockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, freeSockets: [Object: null prototype] {}, keepAliveMsecs: 1000, keepAlive: true, maxSockets: Infinity, maxFreeSockets: 256, scheduling: 'lifo', maxTotalSockets: Infinity, totalSocketCount: 0, maxCachedSessions: 100, _sessionCache: { map: {}, list: [] }, [Symbol(kCapture)]: false }Nach dem Login kopierenDie Zeilen 14, 16, 42 und 44 legen den Standardwert und die Standardzeit von keepAlive fest.
Durch die Aktivierung von keepAlive können Verbindungen wiederverwendet und der Netzwerkdurchsatz verbessert werden.
Darüber hinaus trennt der Server automatisch inaktive Clients, wenn er close() aufruft, was intern durch die Verwendung der API http(s).Server.close implementiert wird;
Diese Modifikationen optimieren das Erlebnis und die Leistung weiter. close() 自动断开空闲的客户端,内部依靠 http(s).Server.close API 实现;
这些修改,进一步优化了体验和性能。
2. 稳定的 WebCrypto API
WebCrypto API 是一个使用密码学构建的系统接口,在 node.js v19 趋于稳定(除 Ed25519、Ed448、X25519、X448 外)。
我们可以通过调用 globalThis.crypto 或 require('node:crypto').webcrypto 来访问,下面以 subtle 加密函数为例;
const { subtle } = globalThis.crypto;
(async function() {
const key = await subtle.generateKey({
name: 'HMAC',
hash: 'SHA-256',
length: 256
}, true, ['sign', 'verify']);
console.log('key =', key);
const enc = new TextEncoder();
const message = enc.encode('I love cupcakes');
console.log('message =', message);
const digest = await subtle.sign({
name: 'HMAC'
}, key, message);
console.log('digest =', digest);
})();首先生成 HMAC 密钥,生成的密钥可同时用于验证消息数据完整性和真实性;
然后,对字符串 I love cupcakes 加密;
最后创建 消息摘要,它是一种加密散列函数;
在控制台显示:key 、message 、digest 信息
% node server
key = CryptoKey {
type: 'secret',
extractable: true,
algorithm: { name: 'HMAC', length: 256, hash: [Object] },
usages: [ 'sign', 'verify' ]
}
message = Uint8Array(15) [ 73, 32, 108, 111, 118, 101, 32, 99, 117, 112, 99, 97, 107, 101, 115]
digest = ArrayBuffer {
[Uint8Contents]: <30 01 7a 5c d9 e2 82 55 6b 55 90 4f 1d de 36 d7 89 dd fb fb 1a 9e a0 cc 5d d8 49 13 38 2f d1 bc>,
byteLength: 32
}3. 自定义 ESM resolution 调整
Node.js 已经删除 --experimental-specifier-resolution ,其功能现在可以通过自定义加载器实现。
可以在这个库中测试:nodejs/loaders-test: Examples demonstrating the Node.js ECMAScript Modules Loaders API
git clone https://github.com/nodejs/loaders-test.git % cd loaders-test/commonjs-extension-resolution-loader % yarn install
比如 loaders-test/commonjs-extension-resolution-loader/test/basic-fixtures/index.js 文件:
import { version } from 'process';
import { valueInFile } from './file';
import { valueInFolderIndex } from './folder';
console.log(valueInFile);
console.log(valueInFolderIndex);./file 如果没有自定义加载器,不会去查找文件的扩展名,比如 ./file.js 或 ./file.mjs
2. Stabile WebCrypto-API
Die WebCrypto-API ist eine mit Kryptografie erstellte Systemschnittstelle, die in node.js v19 tendenziell stabil ist (außer Ed25519, Ed448, X25519, außer X448).
Wir können darauf zugreifen, indem wir globalThis.crypto oder require('node:crypto').webcrypto aufrufen. Das Folgende ist die subtile-Verschlüsselung Funktion: Beispiel;
import { isBuiltin } from 'node:module';
import { dirname } from 'node:path';
import { cwd } from 'node:process';
import { fileURLToPath, pathToFileURL } from 'node:url';
import { promisify } from 'node:util';
import resolveCallback from 'resolve/async.js';
const resolveAsync = promisify(resolveCallback);
const baseURL = pathToFileURL(cwd() + '/').href;
export async function resolve(specifier, context, next) {
const { parentURL = baseURL } = context;
if (isBuiltin(specifier)) {
return next(specifier, context);
}
// `resolveAsync` works with paths, not URLs
if (specifier.startsWith('file://')) {
specifier = fileURLToPath(specifier);
}
const parentPath = fileURLToPath(parentURL);
let url;
try {
const resolution = await resolveAsync(specifier, {
basedir: dirname(parentPath),
// For whatever reason, --experimental-specifier-resolution=node doesn't search for .mjs extensions
// but it does search for index.mjs files within directories
extensions: ['.js', '.json', '.node', '.mjs'],
});
url = pathToFileURL(resolution).href;
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'MODULE_NOT_FOUND') {
// Match Node's error code
error.code = 'ERR_MODULE_NOT_FOUND';
}
throw error;
}
return next(url, context);
}Generieren Sie zuerst den HMAC-Schlüssel, und der generierte Schlüssel kann verwendet werden, um die Integrität und Authentizität der Nachrichtendaten zu überprüfen. Verschlüsseln Sie dann die Zeichenfolge I love Cupcakes;
Erstellen Sie abschließend einen Nachrichtenauszug, bei dem es sich um eine kryptografische Hash-Funktion handelt. Anzeige in der Konsole: Schlüssel, Nachricht, Zusammenfassungsinformationen Node.js hat --experimental-specifier-resolution entfernt und seine Funktionalität ist jetzt über einen benutzerdefinierten Loader verfügbar.
Kann in dieser Bibliothek getestet werden: nodejs/loaders-test: Beispiele zur Veranschaulichung der Node.js ECMAScript Module Loaders API
% node --loader=./loader.js test/basic-fixtures/index (node:56149) ExperimentalWarning: Custom ESM Loaders is an experimental feature. This feature could change at any time (Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created) hello from file.js
loaders-test/commonjs-extension-resolution- Loader /test/basic-fixtures/index.js Datei: Intl.NumberFormat(locales, options)
Nach dem Login kopieren./file Wenn kein benutzerdefinierter Loader vorhanden ist, wird die Dateierweiterung nicht durchsucht, z. B. . /file.js oder ./file.mjs
Nach dem Einrichten eines benutzerdefinierten Loaders kann das obige Problem gelöst werden: Intl.NumberFormat(locales, options)
const number = 123456.789;
console.log(new Intl.NumberFormat('de-DE', { style: 'currency', currency: 'EUR' }).format(number));
console.log(new Intl.NumberFormat('ja-JP', { style: 'currency', currency: 'JPY' }).format(number));
console.log(new Intl.NumberFormat('ar-SA', { style: 'currency', currency: 'EGP' }).format(number));
console.log(new Intl.NumberFormat('zh-CN', { style: 'currency', currency: 'CNY' }).format(number));const express = require("express");
const path = require("path");
const app = express();
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, "../build")));
app.listen(8080, () =>
console.log("Express server is running on localhost:8080")
);4. Unterstützung für DTrace/SystemTap/ETW entfernt
In Node.js v19 wurde die Unterstützung für DTrace/SystemTap/ETW entfernt, hauptsächlich aufgrund von Problemen mit der Ressourcenpriorität. 🎜🎜Die Daten zeigen, dass nur wenige Menschen DTrace, SystemTap oder ETW verwenden und es wenig Sinn macht, sie zu pflegen. 🎜🎜Wenn Sie die Nutzung wieder aufnehmen möchten, können Sie Probleme melden => 🎜github.com/nodejs/node…🎜🎜🎜🎜5. Aktualisieren Sie die V8-Engine auf 10.7🎜🎜🎜Node.js v19 Aktualisieren Sie die V8-JavaScript-Engine auf V8 10.7, Es enthält eine neue Funktion Intl.NumberFormat zum Formatieren sensibler Zahlen. 🎜% node --watch server (node:67643) ExperimentalWarning: Watch mode is an experimental feature. This feature could change at any time (Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created) Express server is running on localhost:8080
在 "watch" 模式下运行,当导入的文件被改变时,会重新启动进程。
比如:
const express = require("express");
const path = require("path");
const app = express();
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, "../build")));
app.listen(8080, () =>
console.log("Express server is running on localhost:8080")
);% node --watch server (node:67643) ExperimentalWarning: Watch mode is an experimental feature. This feature could change at any time (Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created) Express server is running on localhost:8080
Node.js 14 将在 2023 年 4 月结束更新维护,Node.js 16 (LTS) 预计将在 2023 年 9 月结束更新维护。
建议大家开始计划将版本按需升级到 Node.js 16(LTS)或 Node.js 18(LTS)。
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonNode.js 19 ist offiziell veröffentlicht, lassen Sie uns über seine 6 Hauptfunktionen sprechen!. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1377
1377
 52
52
 PHP und Vue: eine perfekte Kombination von Front-End-Entwicklungstools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP und Vue: eine perfekte Kombination von Front-End-Entwicklungstools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP und Vue: eine perfekte Kombination von Front-End-Entwicklungstools In der heutigen Zeit der rasanten Entwicklung des Internets ist die Front-End-Entwicklung immer wichtiger geworden. Da Benutzer immer höhere Anforderungen an das Erlebnis von Websites und Anwendungen stellen, müssen Frontend-Entwickler effizientere und flexiblere Tools verwenden, um reaktionsfähige und interaktive Schnittstellen zu erstellen. Als zwei wichtige Technologien im Bereich der Front-End-Entwicklung können PHP und Vue.js in Kombination als perfekte Waffe bezeichnet werden. In diesem Artikel geht es um die Kombination von PHP und Vue sowie um detaillierte Codebeispiele, die den Lesern helfen sollen, diese beiden besser zu verstehen und anzuwenden
 Häufig gestellte Fragen von Front-End-Interviewern
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Häufig gestellte Fragen von Front-End-Interviewern
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In Front-End-Entwicklungsinterviews decken häufige Fragen ein breites Themenspektrum ab, darunter HTML/CSS-Grundlagen, JavaScript-Grundlagen, Frameworks und Bibliotheken, Projekterfahrung, Algorithmen und Datenstrukturen, Leistungsoptimierung, domänenübergreifende Anfragen, Front-End-Engineering, Designmuster sowie neue Technologien und Trends. Interviewerfragen sollen die technischen Fähigkeiten, die Projekterfahrung und das Verständnis des Kandidaten für Branchentrends beurteilen. Daher sollten Kandidaten in diesen Bereichen umfassend vorbereitet sein, um ihre Fähigkeiten und Fachkenntnisse unter Beweis zu stellen.
 Einfaches JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie den HTTP-Statuscode
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Einfaches JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie den HTTP-Statuscode
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie HTTP-Statuscode. Es sind spezifische Codebeispiele erforderlich. Vorwort: Bei der Webentwicklung ist häufig die Dateninteraktion mit dem Server erforderlich. Bei der Kommunikation mit dem Server müssen wir häufig den zurückgegebenen HTTP-Statuscode abrufen, um festzustellen, ob der Vorgang erfolgreich ist, und die entsprechende Verarbeitung basierend auf verschiedenen Statuscodes durchführen. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit JavaScript HTTP-Statuscodes abrufen und einige praktische Codebeispiele bereitstellen. Verwenden von XMLHttpRequest
 Ist Django Front-End oder Back-End? Hör zu!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Ist Django Front-End oder Back-End? Hör zu!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Django ist ein in Python geschriebenes Webanwendungs-Framework, das Wert auf schnelle Entwicklung und saubere Methoden legt. Obwohl Django ein Web-Framework ist, müssen Sie zur Beantwortung der Frage, ob Django ein Front-End oder ein Back-End ist, ein tiefes Verständnis der Konzepte von Front-End und Back-End haben. Das Front-End bezieht sich auf die Schnittstelle, mit der Benutzer direkt interagieren, und das Back-End bezieht sich auf serverseitige Programme. Sie interagieren mit Daten über das HTTP-Protokoll. Wenn das Front-End und das Back-End getrennt sind, können die Front-End- und Back-End-Programme unabhängig voneinander entwickelt werden, um Geschäftslogik bzw. interaktive Effekte sowie den Datenaustausch zu implementieren.
 Erkundung der Front-End-Technologie der Go-Sprache: eine neue Vision für die Front-End-Entwicklung
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Erkundung der Front-End-Technologie der Go-Sprache: eine neue Vision für die Front-End-Entwicklung
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Als schnelle und effiziente Programmiersprache erfreut sich Go im Bereich der Backend-Entwicklung großer Beliebtheit. Allerdings assoziieren nur wenige Menschen die Go-Sprache mit der Front-End-Entwicklung. Tatsächlich kann die Verwendung der Go-Sprache für die Front-End-Entwicklung nicht nur die Effizienz verbessern, sondern Entwicklern auch neue Horizonte eröffnen. In diesem Artikel wird die Möglichkeit der Verwendung der Go-Sprache für die Front-End-Entwicklung untersucht und spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt, um den Lesern ein besseres Verständnis dieses Bereichs zu erleichtern. In der traditionellen Frontend-Entwicklung werden häufig JavaScript, HTML und CSS zum Erstellen von Benutzeroberflächen verwendet
 Kombination von Golang- und Front-End-Technologie: Entdecken Sie, welche Rolle Golang im Front-End-Bereich spielt
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Kombination von Golang- und Front-End-Technologie: Entdecken Sie, welche Rolle Golang im Front-End-Bereich spielt
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Kombination von Golang und Front-End-Technologie: Um zu untersuchen, welche Rolle Golang im Front-End-Bereich spielt, sind spezifische Codebeispiele erforderlich. Mit der rasanten Entwicklung des Internets und mobiler Anwendungen ist die Front-End-Technologie immer wichtiger geworden. Auch in diesem Bereich kann Golang als leistungsstarke Back-End-Programmiersprache eine wichtige Rolle spielen. In diesem Artikel wird untersucht, wie Golang mit Front-End-Technologie kombiniert wird, und sein Potenzial im Front-End-Bereich anhand spezifischer Codebeispiele demonstriert. Die Rolle von Golang im Front-End-Bereich ist effizient, prägnant und leicht zu erlernen
 So erhalten Sie auf einfache Weise HTTP-Statuscode in JavaScript
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
So erhalten Sie auf einfache Weise HTTP-Statuscode in JavaScript
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Einführung in die Methode zum Abrufen des HTTP-Statuscodes in JavaScript: Bei der Front-End-Entwicklung müssen wir uns häufig mit der Interaktion mit der Back-End-Schnittstelle befassen, und der HTTP-Statuscode ist ein sehr wichtiger Teil davon. Das Verstehen und Abrufen von HTTP-Statuscodes hilft uns, die von der Schnittstelle zurückgegebenen Daten besser zu verarbeiten. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie Sie mithilfe von JavaScript HTTP-Statuscodes erhalten, und es werden spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. 1. Was ist ein HTTP-Statuscode? HTTP-Statuscode bedeutet, dass der Dienst den Dienst anfordert, wenn er eine Anfrage an den Server initiiert
 Django: Ein magisches Framework, das sowohl Front-End- als auch Back-End-Entwicklung bewältigen kann!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Django: Ein magisches Framework, das sowohl Front-End- als auch Back-End-Entwicklung bewältigen kann!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Django: Ein magisches Framework, das sowohl Front-End- als auch Back-End-Entwicklung bewältigen kann! Django ist ein effizientes und skalierbares Webanwendungs-Framework. Es unterstützt mehrere Webentwicklungsmodelle, einschließlich MVC und MTV, und kann problemlos hochwertige Webanwendungen entwickeln. Django unterstützt nicht nur die Back-End-Entwicklung, sondern kann auch schnell Front-End-Schnittstellen erstellen und durch die Vorlagensprache eine flexible Ansichtsanzeige erreichen. Django kombiniert Front-End-Entwicklung und Back-End-Entwicklung zu einer nahtlosen Integration, sodass sich Entwickler nicht auf das Lernen spezialisieren müssen



