
Java五子棋设计流程:
1.创建窗口和设计一个棋盘界面
2.实现鼠标点击,棋子出现,黑白棋轮流下
3.能够判断输赢
4.添加按钮功能
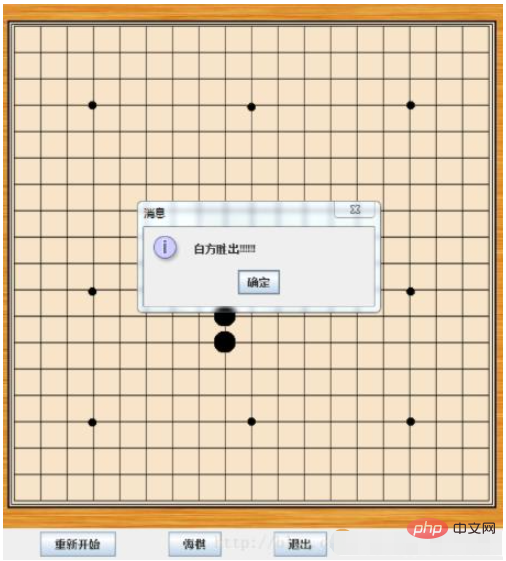
实现结果图:
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Cursor;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.KeyListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame();
}
}
class MyFrame extends JFrame implements MouseListener{
//保存坐标
int x;
int y;
int x1;
int y1;
//黑子数
//白子数
//1是黑下,2是白下
//默认开始是黑旗先下
int flag=1;
//表示游戏是否结束
//true游戏开始,false游戏结束,不能再下
boolean canPlay=true;
//保存之前下过的棋子的坐标
//'0'代表没有棋子,'1'代表黑棋,'2'代表白棋
int [][]allChess=new int[19][19];
//int [][]allChess=new int[25][25];
//当前棋子的总数
int chessSum=0;
BufferedImage bgImage =null;
JButton withdraw=new JButton("悔棋");
JButton restart=new JButton("重新开始");
JButton exit=new JButton("退出");
JPanel south=new JPanel();
public MyFrame() {
this.setTitle("五子棋");
setSize(630,700);
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
try {
bgImage=ImageIO.read(new File("C:\\Users\\us\\Desktop\\1.jpg"));
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
addMouseListener(this);//将窗体加入监听
south.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT,60,30));
south.add(restart);
south.add(withdraw);
south.add(exit);
//初始化按钮事件监听器内部类
MybuttonListener buttonListener =new MybuttonListener();
//将三个按钮事件注册监听事件
restart.addActionListener(buttonListener);
withdraw.addActionListener(buttonListener);
exit.addActionListener(buttonListener);
//将按钮面板加到窗体的南部
this.add(south,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setVisible(true);
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
int tempSum=chessSum;
//棋盘
g.drawImage(bgImage,8,30,this);
for(int colum=58;colum<600 ;colum=colum+30){//行
g.drawLine(38,colum,578,colum);
}
for(int rand=38;rand<600;rand=rand+30){//列
g.drawLine(rand, 58,rand, 598);
}
//黑点
g.fillOval(122, 143, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(484, 143, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(122, 504, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(303, 353, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(484, 503, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(122, 355, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(484, 355, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(303, 145, 10, 10);
g.fillOval(303, 503, 10, 10);
for(int i=0;i<allChess.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<allChess.length;++j) {
//下黑子
if(allChess[i][j]==1) {
int tempX=i*30+38;//左边界到棋盘的距离
int tempY=j*30+58;//上边界到棋盘的距离
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.fillOval(tempX-13,tempY-13,25,25);
}
//下白子
if(allChess[i][j]==2) {
int tempX=i*30+38;
int tempY=j*30+58;
g.setColor(Color.white);
g.fillOval(tempX-13,tempY-13,25,25);
}
}
}
//最后棋子用红框表示
if(chessSum>0) {
g.setColor(Color.red);
g.drawRect(x*30+38-13, y*30+58-13, 25,25);
}
//g.setColor(Color.red);
//g.drawRect(x1*30+38-13, y1*30+58-13, 25,25);
chessSum++;
System.out.println("总数为"+(chessSum-1));
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
x=e.getX();
y=e.getY();
//System.out.println("x="+e.getX()+" "+"y="+e.getY());
if(canPlay) {
if(x>=38&&x<=588&&y>=58&&y<=620) {
x=(x-38)/30;//38起点,适应19x19
y=(y-58)/30;
if(allChess[x][y]==0){//此点没有棋子,才可下
//判断该由哪方下棋
if(flag==1) {//'1'代表由黑方下
allChess[x][y]=1;//'1'表示此处放黑棋
this.checkFive();//判断黑棋是否五子相连
flag=2;
}
else {
allChess[x][y]=2;//'2'表示此处放白棋
this.checkFive();//判断白棋是否五子相连
flag=1;//'1'代表由黑方下
}
this.repaint();
}
}
}
}
//判断五子相连
public void checkFive(){
//把要下的棋子颜色保存
int color=allChess[x][y];
//计算已连棋子个数
int count=1;
//判断横向右边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(x>=15)
break;
if(color==allChess[x+i][y]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
//判断横向左边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(x<=3)//当棋子左边无法连成五子,直接退出
break;
if(color==allChess[x-i][y]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
//判断竖向下边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(y>=15)//当棋子左边无法连成五子,直接退出
break;
if(color==allChess[x][y+i]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
//判断竖向上边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(y<=3)//当棋子竖向上边无法连成五子,直接退出
break;
if(color==allChess[x][y-i]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
//判断右斜上边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(y<=3||x>=15)//当棋子右斜上边无法连成五子,直接退出
break;
if(color==allChess[x+i][y-i]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
//判断左斜向下边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(x<=3||y>=15)//当棋子左斜向下边无法连成五子,直接退出
break;
if(color==allChess[x-i][y+i]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
//判断左斜向上边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(x<=3||y<=3)
break;
if(color==allChess[x-i][y-i]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
//判断右斜向下边是否五子
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
if(y>=15||x>=15)
break;
if(color==allChess[x+i][y+i]) {
count++;
}
checkWin(count);
}
count=1;
}
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {
x1=e.getX();
y1=e.getY();
if(x1>=38&&x1<=588&&y1>=58&&y1<=620) {
setCursor(new Cursor(Cursor.HAND_CURSOR));
}
}
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent arg0) {
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
}
public void checkWin(int count) {
if(count>=5) {//五子相连
if(allChess[x][y]==1) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "黑方胜出!!!!!!");
}
if(allChess[x][y]==2) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "白方胜出!!!!!!");
}
canPlay=false;//游戏结束
}
}
//重新开始
public void restartGame(){
for(int i=0;i<allChess.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<allChess.length;j++) {
allChess[i][j]=0;
}
}
flag=1;//默认开始是黑旗先下
canPlay=true;
repaint();
}
//悔棋
public void goback() {
if(allChess[x][y]!=0) {//当棋盘有棋子,才能悔棋
allChess[x][y]=0;
if(flag==1) {
flag=2;
repaint();
}
else {
flag=1;
repaint();
}
}
}
//按钮事件监听器内部类
class MybuttonListener implements ActionListener{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(e.getSource()==restart) {
restartGame();
}
if(e.getSource()==withdraw) {
goback();
}
if(e.getSource()==exit) {
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo implementieren Sie die eigenständige Version von Backgammon in Java. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!




