 Betrieb und Instandhaltung
Betrieb und Instandhaltung
 Nginx
Nginx
 Beispielanalyse der Nginx-Proxy_Pass-Reverse-Proxy-Konfiguration
Beispielanalyse der Nginx-Proxy_Pass-Reverse-Proxy-Konfiguration
Beispielanalyse der Nginx-Proxy_Pass-Reverse-Proxy-Konfiguration
Das Folgende ist ein kleines Beispiel:
In der Centos7-Systembibliothek gibt es standardmäßig kein Nginx-RPM-Paket, daher müssen wir zuerst die RPM-Abhängigkeitsbibliothek aktualisieren.
1) Die Verwendung von yum zur Installation von Nginx erfordert die Einbindung von Nginx Bibliothek, installieren Sie die Nginx-Bibliothek 3 ist die 192.168 .1.23-Maschine Externe Netzwerk-IP)
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -uvh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/rpms/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm
Sehen Sie sich die folgenden Situationen an: Verwenden Sie http://192.168.1.23/proxy/index.html, um Zugriffstests durchzuführen
Um das Testen zu vereinfachen, verwenden Sie zunächst eine andere Maschine 192.168.1.23 .1.5 Stellen Sie einen Nginx auf Port 8090 bereit. Die Konfiguration lautet wie folgt:
[root@localhost ~]# yum install nginx
Testzugriff (103.110.186.5 ist die externe Netzwerk-IP von 192.168.1.5):
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/
[root@localhost conf.d]# cat test.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
}
[root@localhost conf.d]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
this is page of test!!!!192.168.1 .23 dient als Nginx-Reverse-Proxy-Maschine, Nginx Die Konfiguration ist wie folgt:
1) Der erste Fall:
[root@localhost ~]# service nginx start //或者使用 systemctl start nginx.service
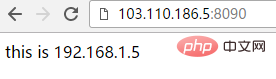
Beachten Sie dies, wenn Sie im Terminal auf http://192.168.1.23/proxy zugreifen (d. h. ohne „/“ danach). ), schlägt der Zugriff fehl! Da „/“ nach der durch „proxy_pass“ konfigurierten URL hinzugefügt wird
[root@localhost conf.d]# curl http://192.168.1.23 this is page of test!!!!
Wenn die Seite auf http://103.110.186.23/proxy zugreift, wird „/“ automatisch hinzugefügt (derselbe Grund ist, dass „/“ nach der URL hinzugefügt wird konfiguriert durch „proxy_pass“) und umgekehrt zum Ergebnis von http://103.110.186.5:8090
2) Im zweiten Fall, wenn „/“ nicht nach der durch „proxy_pass“ konfigurierten URL hinzugefügt wird
[root@bastion-idc ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhosts/haha.conf
server {
listen 8090;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
}
[root@bastion-idc ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
this is 192.168.1.5
[root@bastion-idc ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload, dann besuchen Sie http://192.168.1.23/proxy oder http://192.168.1.23/proxy/ wird fehlschlagen!
Nach dieser Konfiguration ist der Zugriff auf http://192.168.1.23/proxy/ ein Reverse-Proxy zu http://192.168.1.5:8090/proxy/
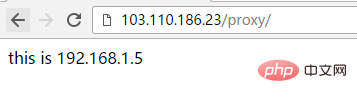
[root@bastion-idc ~]# curl http://192.168.1.5:8090 this is 192.168.1.5
[root@localhost conf.d]# cat test.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
location /proxy/ {
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.5:8090/;
}
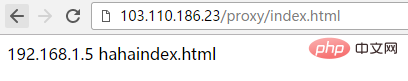
}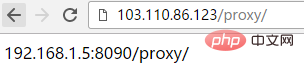 Nach der obigen Konfiguration wird der Zugriff auf http://192.168.1.23/proxy/index.html ein Proxy für http://192.168.1.5:8090/hahaindex.html sein
Nach der obigen Konfiguration wird der Zugriff auf http://192.168.1.23/proxy/index.html ein Proxy für http://192.168.1.5:8090/hahaindex.html seinÄhnlich auch der Zugriff auf http :/ /192.168.1.23/proxy/test.html wird an http://192.168.1.5:8090/hahatest.html weitergeleitet. Beachten Sie, dass in diesem Fall nicht direkt auf http://192.168 zugegriffen werden kann. 1.23/proxy / muss auch die Standarddatei index.html folgen, sonst schlägt der Zugriff fehl!
----------------------------------------------------------- ------ ---------------------------------------- Die oben genannten vier Methoden stimmen alle überein. Fügen Sie „/“ nach dem Pfad hinzu. Sprechen wir über die Situation ohne „/“ nach dem Pfad:
Die oben genannten vier Methoden stimmen alle überein. Fügen Sie „/“ nach dem Pfad hinzu. Sprechen wir über die Situation ohne „/“ nach dem Pfad:
1) Im ersten Fall hat die URL nach „proxy_pass“ „/“:
[root@localhost conf.d]# curl http://192.168.1.23/proxy/ this is 192.168.1.5 [root@localhost conf.d]# curl http://192.168.1.23/proxy <html> <head><title>301 moved permanently</title></head> <body bgcolor="white"> <center><h1>301 moved permanently</h1></center> <hr><center>nginx/1.10.3</center> </body> </html>
 2) Im zweiten Fall, wenn die URL nach „proxy_pass“ nicht „/“ enthält
2) Im zweiten Fall, wenn die URL nach „proxy_pass“ nicht „/“ enthält
[root@localhost conf.d]# cat test.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
location /proxy/ {
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.5:8090;
}
}
[root@localhost conf.d]# service nginx restart
redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart nginx.service[root@localhost conf.d]# cat test.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
location /proxy/ {
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.5:8090/haha/;
}
}
[root@localhost conf.d]# service nginx restart
redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart nginx.service
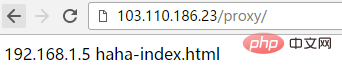
[root@localhost conf.d]# curl http://192.168.1.23/proxy/
192.168.1.5 haha-index.html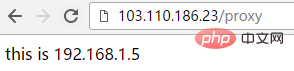 Wenn auf diese Weise konfiguriert, wird auf http://103.110 zugegriffen .186.23/proxy fügt automatisch „/“ hinzu (das heißt, es wird http://103.110.186.23/proxy/), Proxy für http://192.168.1.5:8090/haha/
Wenn auf diese Weise konfiguriert, wird auf http://103.110 zugegriffen .186.23/proxy fügt automatisch „/“ hinzu (das heißt, es wird http://103.110.186.23/proxy/), Proxy für http://192.168.1.5:8090/haha/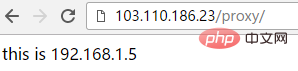
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonBeispielanalyse der Nginx-Proxy_Pass-Reverse-Proxy-Konfiguration. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1378
1378
 52
52
 So starten Sie Nginx unter Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
So starten Sie Nginx unter Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Schritte zum Starten von Nginx unter Linux: Überprüfen Sie, ob Nginx installiert ist. Verwenden Sie SystemCTL Start Nginx, um den Nginx -Dienst zu starten. Verwenden Sie SystemCTL aktivieren NGINX, um das automatische Start von NGINX beim Systemstart zu aktivieren. Verwenden Sie den SystemCTL -Status NGINX, um zu überprüfen, ob das Startup erfolgreich ist. Besuchen Sie http: // localhost in einem Webbrowser, um die Standard -Begrüßungsseite anzuzeigen.
 So konfigurieren Sie Nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
So konfigurieren Sie Nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Wie konfiguriere ich Nginx in Windows? Installieren Sie NGINX und erstellen Sie eine virtuelle Hostkonfiguration. Ändern Sie die Hauptkonfigurationsdatei und geben Sie die Konfiguration der virtuellen Host ein. Starten oder laden Nginx neu. Testen Sie die Konfiguration und sehen Sie sich die Website an. Aktivieren Sie selektiv SSL und konfigurieren Sie SSL -Zertifikate. Stellen Sie die Firewall selektiv fest, damit Port 80 und 443 Verkehr.
 So überprüfen Sie, ob Nginx gestartet wird
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
So überprüfen Sie, ob Nginx gestartet wird
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
So bestätigen Sie, ob Nginx gestartet wird: 1. Verwenden Sie die Befehlszeile: SystemCTL Status Nginx (Linux/Unix), Netstat -ano | FindStr 80 (Windows); 2. Überprüfen Sie, ob Port 80 geöffnet ist; 3. Überprüfen Sie die Nginx -Startmeldung im Systemprotokoll. 4. Verwenden Sie Tools von Drittanbietern wie Nagios, Zabbix und Icinga.
 So starten Sie den Nginx -Server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
So starten Sie den Nginx -Server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Das Starten eines Nginx-Servers erfordert unterschiedliche Schritte gemäß verschiedenen Betriebssystemen: Linux/UNIX-System: Installieren Sie das NGINX-Paket (z. B. mit APT-Get oder Yum). Verwenden Sie SystemCTL, um einen Nginx -Dienst zu starten (z. B. sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows -System: Laden Sie Windows -Binärdateien herunter und installieren Sie sie. Starten Sie Nginx mit der ausführbaren Datei nginx.exe (z. B. nginx.exe -c conf \ nginx.conf). Unabhängig davon, welches Betriebssystem Sie verwenden, können Sie auf die Server -IP zugreifen
 So lösen Sie Nginx403 -Fehler
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
So lösen Sie Nginx403 -Fehler
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Der Server verfügt nicht über die Berechtigung, auf die angeforderte Ressource zuzugreifen, was zu einem NGINX 403 -Fehler führt. Zu den Lösungen gehören: Überprüfung der Dateiberechtigungen. Überprüfen Sie die Konfiguration .htaccess. Überprüfen Sie die Nginx -Konfiguration. Konfigurieren Sie Selinux -Berechtigungen. Überprüfen Sie die Firewall -Regeln. Fehlerbehebung bei anderen Ursachen wie Browserproblemen, Serverausfällen oder anderen möglichen Fehlern.
 So lösen Sie Nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
So lösen Sie Nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
Wie fixiere ich Nginx 403 Verbotener Fehler? Überprüfen Sie die Datei- oder Verzeichnisberechtigungen; 2.Htaccess -Datei prüfen; 3. Überprüfen Sie die Konfigurationsdatei der Nginx; 4. Starten Sie Nginx neu. Weitere mögliche Ursachen sind Firewall -Regeln, Selinux -Einstellungen oder Anwendungsprobleme.
 So lösen Sie Nginx304 Fehler
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
So lösen Sie Nginx304 Fehler
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Antwort auf die Frage: 304 Nicht geänderter Fehler gibt an, dass der Browser die neueste Ressourcenversion der Client -Anfrage zwischengespeichert hat. Lösung: 1. Löschen Sie den Browser -Cache; 2. Deaktivieren Sie den Browser -Cache; 3. Konfigurieren Sie Nginx, um den Client -Cache zu ermöglichen. 4. Überprüfen Sie die Dateiberechtigungen; 5. Datei Hash prüfen; 6. Deaktivieren Sie CDN oder Reverse Proxy -Cache; 7. Starten Sie Nginx neu.
 Wie kann ich überprüfen, ob Nginx begonnen wird?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Wie kann ich überprüfen, ob Nginx begonnen wird?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Verwenden Sie unter Linux den folgenden Befehl, um zu überprüfen, ob Nginx gestartet wird: SystemCTL -Status Nginx Richter basierend auf der Befehlsausgabe: Wenn "aktiv: aktiv (lief) angezeigt wird, wird Nginx gestartet. Wenn "Active: Inactive (Dead)" angezeigt wird, wird Nginx gestoppt.



