Beispielcode für ein Springboot-Projekt zum Konfigurieren mehrerer Kafka
1.spring-kafka
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
2. Informationen zur Konfigurationsdatei
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
3.kafka-Konfigurationsklasse
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 |
|
4
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonBeispielcode für ein Springboot-Projekt zum Konfigurieren mehrerer Kafka. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 So implementieren Sie eine Echtzeit-Aktienanalyse mit PHP und Kafka
Jun 28, 2023 am 10:04 AM
So implementieren Sie eine Echtzeit-Aktienanalyse mit PHP und Kafka
Jun 28, 2023 am 10:04 AM
Mit der Entwicklung des Internets und der Technologie sind digitale Investitionen zu einem Thema mit zunehmender Besorgnis geworden. Viele Anleger erforschen und studieren weiterhin Anlagestrategien in der Hoffnung, eine höhere Kapitalrendite zu erzielen. Im Aktienhandel ist die Aktienanalyse in Echtzeit für die Entscheidungsfindung sehr wichtig, und der Einsatz der Kafka-Echtzeit-Nachrichtenwarteschlange und der PHP-Technologie ist ein effizientes und praktisches Mittel. 1. Einführung in Kafka Kafka ist ein von LinkedIn entwickeltes verteiltes Publish- und Subscribe-Messagingsystem mit hohem Durchsatz. Die Hauptmerkmale von Kafka sind
 Vergleich und Differenzanalyse zwischen SpringBoot und SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Vergleich und Differenzanalyse zwischen SpringBoot und SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot und SpringMVC sind beide häufig verwendete Frameworks in der Java-Entwicklung, es gibt jedoch einige offensichtliche Unterschiede zwischen ihnen. In diesem Artikel werden die Funktionen und Verwendungsmöglichkeiten dieser beiden Frameworks untersucht und ihre Unterschiede verglichen. Lassen Sie uns zunächst etwas über SpringBoot lernen. SpringBoot wurde vom Pivotal-Team entwickelt, um die Erstellung und Bereitstellung von Anwendungen auf Basis des Spring-Frameworks zu vereinfachen. Es bietet eine schnelle und einfache Möglichkeit, eigenständige, ausführbare Dateien zu erstellen
 Fünf Auswahlmöglichkeiten an Visualisierungstools zur Erkundung von Kafka
Feb 01, 2024 am 08:03 AM
Fünf Auswahlmöglichkeiten an Visualisierungstools zur Erkundung von Kafka
Feb 01, 2024 am 08:03 AM
Fünf Optionen für Kafka-Visualisierungstools ApacheKafka ist eine verteilte Stream-Verarbeitungsplattform, die große Mengen an Echtzeitdaten verarbeiten kann. Es wird häufig zum Aufbau von Echtzeit-Datenpipelines, Nachrichtenwarteschlangen und ereignisgesteuerten Anwendungen verwendet. Die Visualisierungstools von Kafka können Benutzern dabei helfen, Kafka-Cluster zu überwachen und zu verwalten und Kafka-Datenflüsse besser zu verstehen. Im Folgenden finden Sie eine Einführung in fünf beliebte Kafka-Visualisierungstools: ConfluentControlCenterConfluent
 Vergleichende Analyse der Kafka-Visualisierungstools: Wie wählt man das am besten geeignete Tool aus?
Jan 05, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
Vergleichende Analyse der Kafka-Visualisierungstools: Wie wählt man das am besten geeignete Tool aus?
Jan 05, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
Wie wählt man das richtige Kafka-Visualisierungstool aus? Vergleichende Analyse von fünf Tools Einführung: Kafka ist ein leistungsstarkes verteiltes Nachrichtenwarteschlangensystem mit hohem Durchsatz, das im Bereich Big Data weit verbreitet ist. Mit der Popularität von Kafka benötigen immer mehr Unternehmen und Entwickler ein visuelles Tool zur einfachen Überwachung und Verwaltung von Kafka-Clustern. In diesem Artikel werden fünf häufig verwendete Kafka-Visualisierungstools vorgestellt und ihre Merkmale und Funktionen verglichen, um den Lesern bei der Auswahl des Tools zu helfen, das ihren Anforderungen entspricht. 1. KafkaManager
 Praktisches Tutorial zur SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos-Entwicklung
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
Praktisches Tutorial zur SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos-Entwicklung
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
In diesem Artikel wird ein detailliertes Beispiel geschrieben, um über die tatsächliche Entwicklung von Dubbo + Nacos + Spring Boot zu sprechen. In diesem Artikel wird nicht zu viel theoretisches Wissen behandelt, sondern das einfachste Beispiel wird geschrieben, um zu veranschaulichen, wie Dubbo in Nacos integriert werden kann, um schnell eine Entwicklungsumgebung aufzubauen.
 Wie installiere ich Apache Kafka unter Rocky Linux?
Mar 01, 2024 pm 10:37 PM
Wie installiere ich Apache Kafka unter Rocky Linux?
Mar 01, 2024 pm 10:37 PM
Um ApacheKafka auf RockyLinux zu installieren, können Sie die folgenden Schritte ausführen: Aktualisieren Sie das System: Stellen Sie zunächst sicher, dass Ihr RockyLinux-System auf dem neuesten Stand ist. Führen Sie den folgenden Befehl aus, um die Systempakete zu aktualisieren: sudoyumupdate Java installieren: ApacheKafka hängt von Java ab, also von Ihnen Sie müssen zuerst JavaDevelopmentKit (JDK) installieren. OpenJDK kann mit dem folgenden Befehl installiert werden: sudoyuminstalljava-1.8.0-openjdk-devel Herunterladen und dekomprimieren: Besuchen Sie die offizielle Website von ApacheKafka (), um das neueste Binärpaket herunterzuladen. Wählen Sie eine stabile Version
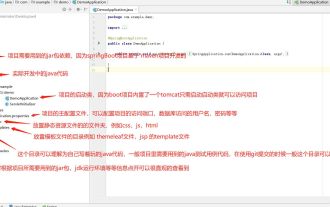 Was sind die am häufigsten verwendeten Verzeichnisse für SpringBoot-Projekte?
Jun 27, 2023 pm 01:42 PM
Was sind die am häufigsten verwendeten Verzeichnisse für SpringBoot-Projekte?
Jun 27, 2023 pm 01:42 PM
Häufig verwendete Verzeichnisse für SpringBoot-Projekte werden auf der Grundlage der Verzeichnisstruktur und Benennungsspezifikationen während der SpringBoot-Entwicklung eingeführt. Durch die Einführung können wir Ihnen bei der tatsächlichen Planung der Verzeichnisstruktur helfen Projekte? Wie können Verzeichnisse standardisierter benannt werden? Was bedeuten die einzelnen Verzeichnisse? Warten Sie drei Fragen. Verzeichnisbeschreibung servicex//Projektname|-admin-ui//Front-End-Code für den Verwaltungsdienst (normalerweise werden UI und SERVICE zur einfachen Verwaltung in einem Projekt zusammengefasst)|-servicex-auth//Modul 1|-servicex-common// Modul 2|-servicex-gateway//Modul 3|
 Die Praxis von Go-Zero und Kafka+Avro: Aufbau eines leistungsstarken interaktiven Datenverarbeitungssystems
Jun 23, 2023 am 09:04 AM
Die Praxis von Go-Zero und Kafka+Avro: Aufbau eines leistungsstarken interaktiven Datenverarbeitungssystems
Jun 23, 2023 am 09:04 AM
In den letzten Jahren haben mit dem Aufkommen von Big Data und aktiven Open-Source-Communities immer mehr Unternehmen begonnen, nach leistungsstarken interaktiven Datenverarbeitungssystemen zu suchen, um den wachsenden Datenanforderungen gerecht zu werden. In dieser Welle von Technologie-Upgrades werden Go-Zero und Kafka+Avro von immer mehr Unternehmen beachtet und übernommen. go-zero ist ein auf der Golang-Sprache entwickeltes Microservice-Framework. Es zeichnet sich durch hohe Leistung, Benutzerfreundlichkeit, einfache Erweiterung und einfache Wartung aus und soll Unternehmen dabei helfen, schnell effiziente Microservice-Anwendungssysteme aufzubauen. sein schnelles Wachstum






