pip install mediapipe
 Backend-Entwicklung
Backend-Entwicklung
 Python-Tutorial
Python-Tutorial
 So erzielen Sie mit Python+OpenCV den Effekt des Ziehens virtueller Quadrate
So erzielen Sie mit Python+OpenCV den Effekt des Ziehens virtueller Quadrate
So erzielen Sie mit Python+OpenCV den Effekt des Ziehens virtueller Quadrate
1. Projekteffekt
2. Kernprozess
1.
2. Verwenden Sie Mediapipe, um Finger-Schlüsselpunktkoordinaten zu erhalten.
3. Bestimmen Sie anhand der Koordinatenposition des Fingers und der Koordinatenposition des Rechtecks, ob sich der Fingerpunkt auf dem Rechteck befindet. Wenn ja, folgt das Rechteck der Fingerbewegung.
3. Codeprozess
Umgebungsvorbereitung:
Python: 3.8.8
opencv: 4.2.0.32# 🎜🎜#
mediapipe: 0.8.10.1Hinweis: 1. Wenn die OpenCV-Version zu hoch oder zu niedrig ist, können einige Probleme auftreten, z Die Kamera lässt sich nicht öffnen oder stürzt ab. Bei anderen Problemen wirkt sich die Python-Version auf die auswählbare Version von opencv aus. 2. OpenCV kann nach der Installation von pip mediapipe möglicherweise nicht mehr normal verwendet werden. 1. Lesen Sie das Kameravideo und zeichnen Sie ein Rechteckimport cv2
import time
import numpy as np
# 调用摄像头 0 默认摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 初始方块数据
x = 100
y = 100
w = 100
h = 100
# 读取一帧帧照片
while True:
# 返回frame图片
rec,frame = cap.read()
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
# 画矩形
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 255), -1)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()Nach dem Login kopieren
Dies ist ein sehr grundlegender Schritt, wenn wir diesen Code ausführen und die Kamera eingeschaltet ist. Wir werden überrascht sein, wenn wir in Ihrem hübschen Gesicht ein 100*100 großes violettes Rechteck in der oberen linken Ecke sehen. 2. Mediapipe importieren, um Fingerkoordinaten zu verarbeiten import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
# 调用摄像头 0 默认摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 初始方块数据
x = 100
y = 100
w = 100
h = 100
# 读取一帧帧照片
while True:
# 返回frame图片
rec,frame = cap.read()
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
# 画矩形
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 255), -1)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()pip install mediapipe
Nach dem Login kopieren
Es kann zu Problemen kommen, wie zum Beispiel, dass openCV plötzlich unbrauchbar wird. Es spielt keine Rolle, es zu deinstallieren Laden Sie es erneut herunter. mediapipe-Details: Hände – mediapipe (google.github.io)pip install mediapipe
2.1 Konfigurieren Sie einige grundlegende Informationen
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import mediapipe as mp
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles
mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mp_hands.Hands(
static_image_mode=True,
max_num_hands=2,
min_detection_confidence=0.5)2.2 Fügen Sie bei der Verarbeitung jedes Bildrahmens #🎜 🎜 hinzu # frame.flags.writeable = False
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 返回结果
results = hands.process(frame)
frame.flags.writeable = True
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 如果结果不为空
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历双手(根据读取顺序,一只只手遍历、画画)
for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
mp_drawing.draw_landmarks(
frame,
hand_landmarks,
mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS,
mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style(),
mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style())import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import mediapipe as mp
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles
mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mp_hands.Hands(
static_image_mode=True,
max_num_hands=2,
min_detection_confidence=0.5)
# 调用摄像头 0 默认摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 方块初始数组
x = 100
y = 100
w = 100
h = 100
# 读取一帧帧照片
while True:
# 返回frame图片
rec,frame = cap.read()
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
frame.flags.writeable = False
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 返回结果
results = hands.process(frame)
frame.flags.writeable = True
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 如果结果不为空
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历双手(根据读取顺序,一只只手遍历、画画)
# results.multi_hand_landmarks n双手
# hand_landmarks 每只手上21个点信息
for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
mp_drawing.draw_landmarks(
frame,
hand_landmarks,
mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS,
mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style(),
mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style())
# 画矩形
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 255), -1)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
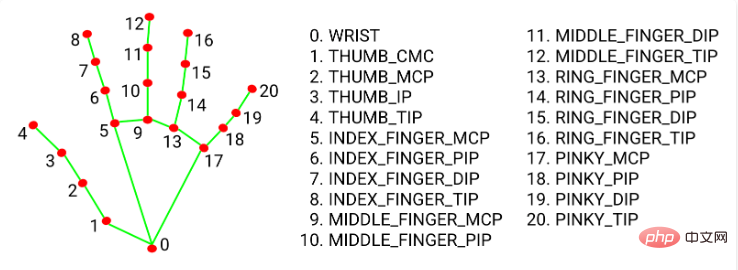
Unser Experiment erfordert das Ziehen Quadratisch wird es sicherlich Zeiten geben, in denen Sie nicht ziehen möchten, also können Sie genauso gut die Position der Spitzen Ihres Zeigefingers (8) und Ihres Mittelfingers (12) entsprechend dem vorherigen Schritt ermitteln, wenn diese nahe beieinander liegen , wir verwenden die Position der Fingerspitzen, wenn sie mit dem Quadrat übereinstimmen. Position ändert die Koordinaten des Blocks.
 Vollständiger Code
Vollständiger Code
import cv2
import time
import math
import numpy as np
import mediapipe as mp
# mediapipe配置
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles
mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mp_hands.Hands(
static_image_mode=True,
max_num_hands=2,
min_detection_confidence=0.5)
# 调用摄像头 0 默认摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# cv2.namedWindow("frame", 0)
# cv2.resizeWindow("frame", 960, 640)
# 获取画面宽度、高度
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# 方块初始数组
x = 100
y = 100
w = 100
h = 100
L1 = 0
L2 = 0
on_square = False
square_color = (0, 255, 0)
# 读取一帧帧照片
while True:
# 返回frame图片
rec,frame = cap.read()
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
frame.flags.writeable = False
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 返回结果
results = hands.process(frame)
frame.flags.writeable = True
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 如果结果不为空
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历双手(根据读取顺序,一只只手遍历、画画)
# results.multi_hand_landmarks n双手
# hand_landmarks 每只手上21个点信息
for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
mp_drawing.draw_landmarks(
frame,
hand_landmarks,
mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS,
mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style(),
mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style())
# 记录手指每个点的x y 坐标
x_list = []
y_list = []
for landmark in hand_landmarks.landmark:
x_list.append(landmark.x)
y_list.append(landmark.y)
# 获取食指指尖
index_finger_x, index_finger_y = int(x_list[8] * width),int(y_list[8] * height)
# 获取中指
middle_finger_x,middle_finger_y = int(x_list[12] * width), int(y_list[12] * height)
# 计算两指尖距离
finger_distance = math.hypot((middle_finger_x - index_finger_x), (middle_finger_y - index_finger_y))
# 如果双指合并(两之间距离近)
if finger_distance < 60:
# X坐标范围 Y坐标范围
if (index_finger_x > x and index_finger_x < (x + w)) and (
index_finger_y > y and index_finger_y < (y + h)):
if on_square == False:
L1 = index_finger_x - x
L2 = index_finger_y - y
square_color = (255, 0, 255)
on_square = True
else:
# 双指不合并/分开
on_square = False
square_color = (0, 255, 0)
# 更新坐标
if on_square:
x = index_finger_x - L1
y = index_finger_y - L2
# 图像融合 使方块不遮挡视频图片
overlay = frame.copy()
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), square_color, -1)
frame = cv2.addWeighted(overlay, 0.5, frame, 1 - 0.5, 0)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo erzielen Sie mit Python+OpenCV den Effekt des Ziehens virtueller Quadrate. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Was ist der Grund, warum PS immer wieder Laden zeigt?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
Was ist der Grund, warum PS immer wieder Laden zeigt?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS "Laden" Probleme werden durch Probleme mit Ressourcenzugriff oder Verarbeitungsproblemen verursacht: Die Lesegeschwindigkeit von Festplatten ist langsam oder schlecht: Verwenden Sie Crystaldiskinfo, um die Gesundheit der Festplatte zu überprüfen und die problematische Festplatte zu ersetzen. Unzureichender Speicher: Upgrade-Speicher, um die Anforderungen von PS nach hochauflösenden Bildern und komplexen Schichtverarbeitung zu erfüllen. Grafikkartentreiber sind veraltet oder beschädigt: Aktualisieren Sie die Treiber, um die Kommunikation zwischen PS und der Grafikkarte zu optimieren. Dateipfade sind zu lang oder Dateinamen haben Sonderzeichen: Verwenden Sie kurze Pfade und vermeiden Sie Sonderzeichen. Das eigene Problem von PS: Installieren oder reparieren Sie das PS -Installateur neu.
 Wie löst ich das Problem des Ladens beim Starten von PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
Wie löst ich das Problem des Ladens beim Starten von PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
Ein PS, der beim Booten auf "Laden" steckt, kann durch verschiedene Gründe verursacht werden: Deaktivieren Sie korrupte oder widersprüchliche Plugins. Eine beschädigte Konfigurationsdatei löschen oder umbenennen. Schließen Sie unnötige Programme oder aktualisieren Sie den Speicher, um einen unzureichenden Speicher zu vermeiden. Upgrade auf ein Solid-State-Laufwerk, um die Festplatte zu beschleunigen. PS neu installieren, um beschädigte Systemdateien oder ein Installationspaketprobleme zu reparieren. Fehlerinformationen während des Startprozesses der Fehlerprotokollanalyse anzeigen.
 Wie löste ich das Problem des Ladens, wenn die PS die Datei öffnet?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
Wie löste ich das Problem des Ladens, wenn die PS die Datei öffnet?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
Das Laden von Stottern tritt beim Öffnen einer Datei auf PS auf. Zu den Gründen gehören: zu große oder beschädigte Datei, unzureichender Speicher, langsame Festplattengeschwindigkeit, Probleme mit dem Grafikkarten-Treiber, PS-Version oder Plug-in-Konflikte. Die Lösungen sind: Überprüfen Sie die Dateigröße und -integrität, erhöhen Sie den Speicher, aktualisieren Sie die Festplatte, aktualisieren Sie den Grafikkartentreiber, deinstallieren oder deaktivieren Sie verdächtige Plug-Ins und installieren Sie PS. Dieses Problem kann effektiv gelöst werden, indem die PS -Leistungseinstellungen allmählich überprüft und genutzt wird und gute Dateimanagementgewohnheiten entwickelt werden.
 So verwenden Sie MySQL nach der Installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
So verwenden Sie MySQL nach der Installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Der Artikel führt den Betrieb der MySQL -Datenbank vor. Zunächst müssen Sie einen MySQL -Client wie MySQLworkBench oder Befehlszeilen -Client installieren. 1. Verwenden Sie den Befehl mySQL-uroot-P, um eine Verbindung zum Server herzustellen und sich mit dem Stammkonto-Passwort anzumelden. 2. Verwenden Sie die Erstellung von Createdatabase, um eine Datenbank zu erstellen, und verwenden Sie eine Datenbank aus. 3.. Verwenden Sie CreateTable, um eine Tabelle zu erstellen, Felder und Datentypen zu definieren. 4. Verwenden Sie InsertInto, um Daten einzulegen, Daten abzufragen, Daten nach Aktualisierung zu aktualisieren und Daten nach Löschen zu löschen. Nur indem Sie diese Schritte beherrschen, lernen, mit gemeinsamen Problemen umzugehen und die Datenbankleistung zu optimieren, können Sie MySQL effizient verwenden.
 Wie kontrolliert PS -Federn die Weichheit des Übergangs?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Wie kontrolliert PS -Federn die Weichheit des Übergangs?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Der Schlüssel zur Federkontrolle liegt darin, seine allmähliche Natur zu verstehen. PS selbst bietet nicht die Möglichkeit, die Gradientenkurve direkt zu steuern, aber Sie können den Radius und die Gradientenweichheit flexius durch mehrere Federn, Matching -Masken und feine Selektionen anpassen, um einen natürlichen Übergangseffekt zu erzielen.
 So optimieren Sie die Datenbankleistung nach der MySQL -Installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
So optimieren Sie die Datenbankleistung nach der MySQL -Installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
Die MySQL -Leistungsoptimierung muss von drei Aspekten beginnen: Installationskonfiguration, Indexierung und Abfrageoptimierung, Überwachung und Abstimmung. 1. Nach der Installation müssen Sie die my.cnf -Datei entsprechend der Serverkonfiguration anpassen, z. 2. Erstellen Sie einen geeigneten Index, um übermäßige Indizes zu vermeiden und Abfrageanweisungen zu optimieren, z. B. den Befehl Erklärung zur Analyse des Ausführungsplans; 3. Verwenden Sie das eigene Überwachungstool von MySQL (ShowProcessList, Showstatus), um die Datenbankgesundheit zu überwachen und die Datenbank regelmäßig zu sichern und zu organisieren. Nur durch kontinuierliche Optimierung dieser Schritte kann die Leistung der MySQL -Datenbank verbessert werden.
 Muss MySQL bezahlen?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Muss MySQL bezahlen?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL hat eine kostenlose Community -Version und eine kostenpflichtige Enterprise -Version. Die Community -Version kann kostenlos verwendet und geändert werden, die Unterstützung ist jedoch begrenzt und für Anwendungen mit geringen Stabilitätsanforderungen und starken technischen Funktionen geeignet. Die Enterprise Edition bietet umfassende kommerzielle Unterstützung für Anwendungen, die eine stabile, zuverlässige Hochleistungsdatenbank erfordern und bereit sind, Unterstützung zu bezahlen. Zu den Faktoren, die bei der Auswahl einer Version berücksichtigt werden, gehören Kritikalität, Budgetierung und technische Fähigkeiten von Anwendungen. Es gibt keine perfekte Option, nur die am besten geeignete Option, und Sie müssen die spezifische Situation sorgfältig auswählen.
 Wie richte ich PS -Federn ein?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Wie richte ich PS -Federn ein?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
PS Federn ist ein Bildkantenschwärcheneffekt, der durch den gewichteten Durchschnitt der Pixel im Randbereich erreicht wird. Das Einstellen des Federradius kann den Grad der Unschärfe steuern und je größer der Wert ist, desto unscharfer ist er. Eine flexible Einstellung des Radius kann den Effekt entsprechend den Bildern und Bedürfnissen optimieren. Verwenden Sie beispielsweise einen kleineren Radius, um Details bei der Verarbeitung von Charakterfotos zu erhalten und einen größeren Radius zu verwenden, um ein dunstiges Gefühl bei der Verarbeitung von Kunst zu erzeugen. Es ist jedoch zu beachten, dass zu groß der Radius leicht an Kantendetails verlieren kann, und zu klein ist der Effekt nicht offensichtlich. Der Federneffekt wird von der Bildauflösung beeinflusst und muss anhand des Bildverständnisses und des Griffs von Effekten angepasst werden.



