
Verwenden Sie Springs ResourceUtils, um die JSON-Datei im Ressourcenverzeichnis zu lesen.
Verwenden Sie common-io, um die gelesene Datei in einen JSON-String zu konvertieren.
Verwenden Sie fastjson, um JSON-Strings in Objekte zu deserialisieren.
pom.xml, hauptsächlich common-io , die Einführung von fastjson.
<!-- 资源目录资源文件读取 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 反序列化json字符串 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson2</artifactId>
<version>2.0.14</version>
</dependency>notice.json, listen Sie einfach den zu verwendenden JSON-Inhalt auf.
[
{
"title": "新功能xxx上线",
"content": "支持xxx"
},
{
"title": "旧功能xxx下线",
"content": "不支持xxx"
}
]3.1 definieren. Schnittstelle
package com.example.springbootjson.service;
import com.example.springbootjson.domain.NoticeInfo;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author hongcunlin
*/
public interface NoticeService {
/**
* 获取公告
*
* @return 公告
* @throws IOException 文件
*/
List<NoticeInfo> getNoticeInfoList() throws IOException;
}hier implementieren Man kann sagen, dass es sich um den Kernteil dieses Artikels handelt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie im Code. Die JSON-Datei „notice.json“ wird über ResourceUtils gelesen und die Datei wird über „FileUtils“ von common-io in eine JSON-Zeichenfolge konvertiert. und das JSON-Objekt wird über den JSON von fastjson deserialisiert.
package com.example.springbootjson.service.impl;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import com.example.springbootjson.domain.NoticeInfo;
import com.example.springbootjson.service.NoticeService;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.ResourceUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author hongcunlin
*/
@Service
public class NoticeServiceImpl implements NoticeService {
@Override
public List<NoticeInfo> getNoticeInfoList() throws IOException {
File file = ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:notice.json");
String json = FileUtils.readFileToString(file, "UTF-8");
List<NoticeInfo> noticeInfoList = JSON.parseArray(json, NoticeInfo.class);
return noticeInfoList;
}
}4. Testschnittstelle
package com.example.springbootjson;
import com.example.springbootjson.service.NoticeService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootJsonApplicationTests {
@Resource
private NoticeService noticeService;
@Test
void contextLoads() throws IOException {
System.out.println(noticeService.getNoticeInfoList());
}
}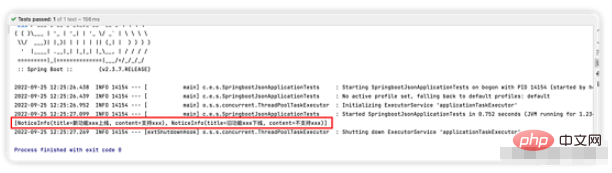 Sie können sehen, dass der Inhalt in der JSON-Datei normal ausgegeben werden kann, was darauf hinweist, dass unser Programm korrekt ist.
Sie können sehen, dass der Inhalt in der JSON-Datei normal ausgegeben werden kann, was darauf hinweist, dass unser Programm korrekt ist.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonWie liest SpringBoot JSON-Dateien im Ressourcenverzeichnis?. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
 JSON-Datenformat
JSON-Datenformat
 Was ist JSON?
Was ist JSON?
 Schritte zur SpringBoot-Projekterstellung
Schritte zur SpringBoot-Projekterstellung
 So bedienen Sie JSON mit JQuery
So bedienen Sie JSON mit JQuery
 Was ist der Unterschied zwischen j2ee und springboot?
Was ist der Unterschied zwischen j2ee und springboot?
 Lösung für das Problem, dass Win11-Download-Software nicht installiert werden kann
Lösung für das Problem, dass Win11-Download-Software nicht installiert werden kann
 Verwendung der Formatierungsfunktion
Verwendung der Formatierungsfunktion
 Win10 unterstützt die Festplattenlayoutlösung der Uefi-Firmware nicht
Win10 unterstützt die Festplattenlayoutlösung der Uefi-Firmware nicht
 Einführung in das von vscode verwendete Framework
Einführung in das von vscode verwendete Framework




