 Backend-Entwicklung
Backend-Entwicklung
 C++
C++
 C/C++-Programm, das mit dem Merge-Sort-Algorithmus geschrieben wurde, um umgekehrte Zahlen in einem Array zu berechnen
C/C++-Programm, das mit dem Merge-Sort-Algorithmus geschrieben wurde, um umgekehrte Zahlen in einem Array zu berechnen
C/C++-Programm, das mit dem Merge-Sort-Algorithmus geschrieben wurde, um umgekehrte Zahlen in einem Array zu berechnen

Die invertierte Darstellung eines Arrays; wie viele Änderungen sind erforderlich, um das Array in seine sortierte Form umzuwandeln. Wenn das Array bereits sortiert ist, sind 0 Umkehrungen erforderlich, während in anderen Fällen, wenn das Array umgekehrt ist, die maximale Anzahl an Umkehrungen erreicht wird.
Um dieses Problem zu lösen, folgen wir der Merge-Sortier-Methode, um die zeitliche Komplexität zu reduzieren, und verwenden den Divide-and-Conquer-Algorithmus.
Eingabe
A sequence of numbers. (1, 5, 6, 4, 20).
Ausgabe
Die Anzahl der Umkehrungen, die erforderlich sind, um die Zahlen in aufsteigender Reihenfolge zu sortieren.
Here the number of inversions are 2. First inversion: (1, 5, 4, 6, 20) Second inversion: (1, 4, 5, 6, 20)
Algorithmus
merge(array, tempArray, left, mid, right)
Input – zwei Arrays, die zusammengeführt wurden, linker, rechter und mittlerer Index.
Ausgabe – zusammengeführte Arrays in sortierter Reihenfolge.
Begin
i := left, j := mid, k := right
count := 0
while i <= mid -1 and j <= right, do
if array[i] <= array[j], then
tempArray[k] := array[i]
increase i and k by 1
else
tempArray[k] := array[j]
increase j and k by 1
count := count + (mid - i)
done
while left part of the array has some extra element, do
tempArray[k] := array[i]
increase i and k by 1
done
while right part of the array has some extra element, do
tempArray[k] := array[j]
increase j and k by 1
done
return count
EndmergeSort(array, tempArray, left, right)
Eingabe - Gegeben ein Array und ein temporäres Array, der linke und der rechte Index des Arrays.
Ausgabe – Die Anzahl der umgekehrt geordneten Paare nach dem Sortieren.
Begin
count := 0
if right > left, then
mid := (right + left)/2
count := mergeSort(array, tempArray, left, mid)
count := count + mergeSort(array, tempArray, mid+1, right)
count := count + merge(array, tempArray, left, mid+1, right)
return count
EndBeispiel
Echtzeitdemonstration
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int merge(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int mid, int right) {
int i, j, k;
int count = 0;
i = left; //i to locate first array location
j = mid; //i to locate second array location
k = left; //i to locate merged array location
while ((i <= mid - 1) && (j <= right)) {
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]){ //when left item is less than right item
temp[k++] = arr[i++];
} else {
temp[k++] = arr[j++];
count += (mid - i); //find how many convertion is performed
}
}
while (i <= mid - 1) //if first list has remaining item, add them in the list
temp[k++] = arr[i++];
while (j <= right) //if second list has remaining item, add them in the list
temp[k++] = arr[j++];
for (i=left; i <= right; i++)
arr[i] = temp[i]; //store temp Array to main array
return count;
}
int mergeSort(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int right){
int mid, count = 0;
if (right > left) {
mid = (right + left)/2; //find mid index of the array
count = mergeSort(arr, temp, left, mid); //merge sort left sub array
count += mergeSort(arr, temp, mid+1, right); //merge sort right sub array
count += merge(arr, temp, left, mid+1, right); //merge two sub arrays
}
return count;
}
int arrInversion(int arr[], int n) {
int temp[n];
return mergeSort(arr, temp, 0, n - 1);
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 5, 6, 4, 20};
int n = 5;
cout << "Number of inversions are "<< arrInversion(arr, n);
}Ausgabe
Number of inversions are 2
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonC/C++-Programm, das mit dem Merge-Sort-Algorithmus geschrieben wurde, um umgekehrte Zahlen in einem Array zu berechnen. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

Video Face Swap
Tauschen Sie Gesichter in jedem Video mühelos mit unserem völlig kostenlosen KI-Gesichtstausch-Tool aus!

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
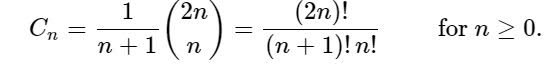 Was ist das C/C++-Programm für die n-te katalanische Zahl?
Sep 11, 2023 pm 10:33 PM
Was ist das C/C++-Programm für die n-te katalanische Zahl?
Sep 11, 2023 pm 10:33 PM
Katalanische Zahlen sind eine Reihe von Zahlen. Katalanische Zahlen sind eine Folge natürlicher Zahlen, die in einer Vielzahl von Zählproblemen vorkommen und häufig rekursiv definierte Objekte beinhalten. Cn ist die Anzahl der Dyck-Wörter der Länge 2n. Ein Dyck-Wort ist eine Zeichenfolge, die aus n Xs und n Ys besteht, sodass die Anzahl der Ys die Anzahl der Xs in keinem Anfangsfragment der Zeichenfolge übersteigt. Das Folgende ist beispielsweise ein Dyck-Wort der Länge 6: XXXYYYXYXXYYXYXYXXYYXXXYXYY Das Symbol neu interpretieren )(())()()()(())()(()())Cn ist kein Faktor, der vollständig sein kann umschlossen durch n+1 Faktoren
 C/C++-Programm, das mit dem Merge-Sort-Algorithmus geschrieben wurde, um umgekehrte Zahlen in einem Array zu berechnen
Aug 25, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
C/C++-Programm, das mit dem Merge-Sort-Algorithmus geschrieben wurde, um umgekehrte Zahlen in einem Array zu berechnen
Aug 25, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
Die invertierte Darstellung eines Arrays; wie viele Änderungen sind erforderlich, um das Array in seine sortierte Form zu konvertieren. Wenn das Array bereits sortiert ist, sind 0 Umkehrungen erforderlich, während in anderen Fällen, wenn das Array umgekehrt ist, die maximale Anzahl an Umkehrungen erreicht wird. Um dieses Problem zu lösen, werden wir der Merge-Sortier-Methode folgen, um die zeitliche Komplexität zu reduzieren, und den Divide-and-Conquer-Algorithmus verwenden. Geben Sie „Asequenceofnumbers.(1,5,6,4,20)“ ein. Geben Sie die Anzahl der Umkehrungen aus, die zum Sortieren der Zahlen in aufsteigender Reihenfolge erforderlich sind. Hier beträgt die Anzahl der Inversionen 2. Erste Inversion: (1,5,4,6,20) Zweite Inversion: (1,4,5,6,20) Algorithmuszusammenführung
 So implementieren Sie die Zusammenführungssortierung in PHP
Oct 21, 2022 am 09:30 AM
So implementieren Sie die Zusammenführungssortierung in PHP
Oct 21, 2022 am 09:30 AM
So implementieren Sie die Zusammenführungssortierung in PHP: 1. Erstellen Sie eine PHP-Beispieldatei. 2. Definieren Sie die Methode „public function handle(){...}“. 3. Verwenden Sie „private function mergeSort($a, $lo, $hi )“ {...}“-Methode, um die Daten schrittweise zu zerlegen. 4. Verwenden Sie die „merge“-Methode, um die zerlegten Daten zu sortieren und sie dann zusammenzuführen.
 Detaillierte Erläuterung des Merge-Sort-Algorithmus in PHP
Jul 08, 2023 pm 05:03 PM
Detaillierte Erläuterung des Merge-Sort-Algorithmus in PHP
Jul 08, 2023 pm 05:03 PM
Detaillierte Erläuterung des Merge-Sort-Algorithmus in PHP Einführung: Das Sortieren ist eines der häufigsten Grundprobleme in der Informatik. Die geordnete Anordnung von Daten kann die Effizienz von Abruf-, Such- und Änderungsvorgängen verbessern. Unter den Sortieralgorithmen ist die Zusammenführungssortierung ein hocheffizienter und stabiler Algorithmus. In diesem Artikel wird der Merge-Sortier-Algorithmus in PHP anhand von Codebeispielen ausführlich vorgestellt. Prinzip der Zusammenführungssortierung Bei der Zusammenführungssortierung handelt es sich um einen Divide-and-Conquer-Algorithmus, der das zu sortierende Array in zwei Unterarrays aufteilt, jeweils eine Zusammenführungssortierung für die beiden Unterarrays durchführt und dann die sortierten Unterarrays zu einem zusammenführt
 So implementieren Sie den Merge-Sort-Algorithmus in C#
Sep 19, 2023 am 09:45 AM
So implementieren Sie den Merge-Sort-Algorithmus in C#
Sep 19, 2023 am 09:45 AM
So implementieren Sie den Merge-Sort-Algorithmus in C#. Merge-Sort ist ein klassischer Sortieralgorithmus, der auf der Divide-and-Conquer-Idee basiert. Er vervollständigt die Sortierung, indem er ein großes Problem in mehrere kleine Probleme aufteilt, die kleinen Probleme dann schrittweise löst und die Ergebnisse zusammenführt. Im Folgenden wird die Implementierung des Zusammenführungssortierungsalgorithmus in C# vorgestellt und spezifische Codebeispiele bereitgestellt. Die Grundidee der Zusammenführungssortierung besteht darin, die zu sortierende Sequenz in mehrere Teilsequenzen aufzuteilen, diese separat zu sortieren und die sortierten Teilsequenzen dann zu einer geordneten Sequenz zusammenzuführen. Der Schlüssel zu diesem Algorithmus besteht darin, die Aufteilungs- und Zusammenführungsoperationen von Teilsequenzen zu implementieren.
 Konvertieren Sie C/C++-Programme in Präprozessorcode
Sep 11, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
Konvertieren Sie C/C++-Programme in Präprozessorcode
Sep 11, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
Hier erfahren Sie, wie Sie aus dem Quellcode eines C- oder C++-Programms Vorverarbeitungs- oder Präprozessorcode generieren. Um vorverarbeiteten Code mit dem G++-Compiler anzuzeigen, müssen wir die Option „-E“ mit g++ verwenden. Der Präprozessor enthält alle #-Direktiven im Code und erweitert auch die MACRO-Funktion. Syntax g++-Eprogram.cpp example#define PI 3.1415int main() { float a = PI,&nb
 So implementieren Sie den Zusammenführungssortierungsalgorithmus mit Java
Sep 19, 2023 am 11:33 AM
So implementieren Sie den Zusammenführungssortierungsalgorithmus mit Java
Sep 19, 2023 am 11:33 AM
So implementieren Sie den Merge-Sort-Algorithmus mit Java. Einführung: Merge-Sort ist ein klassischer Sortieralgorithmus, der auf der Divide-and-Conquer-Methode basiert. Die Idee besteht darin, das zu sortierende Array Schicht für Schicht in kleinere Unterarrays zu unterteilen und diese dann zusammenzuführen Unterarrays werden nacheinander durch die Zusammenführungsoperation zu einem sortierten Gesamtarray zusammengeführt. In diesem Artikel stellen wir detailliert vor, wie der Merge-Sortier-Algorithmus mit Java implementiert wird, und stellen spezifische Codebeispiele bereit. Algorithmusschritte: Der Zusammenführungssortierungsalgorithmus umfasst hauptsächlich drei Schritte: Teilen, Zusammenführen und Sortieren. Split: Zuerst brauchen wir
 Sortieralgorithmus zum Zusammenführen in Java: Prinzipien und praktische Anwendungen
Feb 18, 2024 pm 03:17 PM
Sortieralgorithmus zum Zusammenführen in Java: Prinzipien und praktische Anwendungen
Feb 18, 2024 pm 03:17 PM
Detaillierte Erläuterung des Merge-Sortieralgorithmus und seiner Anwendung in Java 1. Einführung Merge-Sort ist ein klassischer Sortieralgorithmus. Er nutzt die Idee des Teilens und Eroberns, um das Array in zwei Unterarrays zu unterteilen und die Unterarrays dann rekursiv zu sortieren -Arrays und kombinieren Sie schließlich die beiden sortierten Unterarrays zu einem sortierten Array. In diesem Artikel werden der Merge-Sort-Algorithmus und seine Anwendungen in Java im Detail analysiert und spezifische Codebeispiele gegeben. 2. Algorithmusprinzip Die Hauptidee der Zusammenführungssortierung besteht darin, ein großes Array in zwei Unterarrays zu unterteilen, die beiden Unterarrays entsprechend zu sortieren und schließlich die beiden geordneten zu kombinieren





