Bei n Knoten besteht die Aufgabe darin, das Produkt aller Knoten in einer einfach verknüpften Liste auszugeben. Das Programm muss alle Knoten der einseitig verknüpften Liste beginnend beim Anfangsknoten durchlaufen, bis NULL nicht mehr gefunden wird.
Beispiel
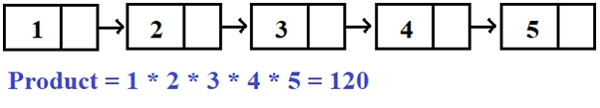
1 2 | Input -: 1 2 3 4 5
Output -: 120
|
Nach dem Login kopieren
Im obigen Beispiel ist ihr Produkt ausgehend vom ersten Knoten und beim Durchlaufen aller Knoten, d. h. 1, 2 3, 4, 5, 6, 1*2*3*4*5*6 = 120
< p>
Die unten verwendete Methode lautet wie folgt: Holen Sie sich einen temporären Zeiger, z. B. temp vom Knotentyp temp wechselt zu temp ->next.
Set Product=product*(temp->data)- Algorithmus
- H2>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 | Start
Step 1 -> create structure of a node and temp, next and head as pointer to a structure node
struct node
int data
struct node *next, *head, *temp
End
Step 2 -> declare function to insert a node in a list
void insert(int val)
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node))
newnode->data = val
IF head= NULL
set head = newnode
set head->next = NULL
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp->next!=NULL
Set temp=temp->next
End
Set newnode->next=NULL
Set temp->next=newnode
End
Step 3 -> Declare a function to display list
void display()
IF head=NULL
Print no node
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp!=NULL
Print temp->data
Set temp=temp->next
End
End
Step 4 -> declare a function to find alternate nodes
void product_nodes()
declare int product=1
Set temp=head
Loop While temp!=NULL
Set product=product * (temp->data)
Set temp=temp->next
End
Print product
Step 5 -> in main()
Create nodes using struct node* head = NULL;
Call function insert(10) to insert a node
Call display() to display the list
Call product_nodes() to find alternate nodes product
Stop
|
Nach dem Login kopieren
Beispiel1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 | #include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}*head,*temp;
void insert(int val){
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = val;
newnode->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL){
head = newnode;
temp = head;
} else {
temp->next=newnode;
temp=temp->next;
}
}
void display(){
if(head==NULL)
printf("no node ");
else{
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL){
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
}
}
void product_nodes(){
int product=1;
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL){
product=product * (temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("</p><p>product of nodes is : %d" ,product);
}
int main(){
struct node* head = NULL;
insert(1);
insert(2);
insert(3);
insert(4);
insert(5);
insert(6);
printf("linked list is : ");
display();
Product_nodes();
return 0;
}
|
Nach dem Login kopieren
1 2 | linked list is : 1 2 3 4 5 6
product of nodes is : 720
|
Nach dem Login kopieren
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonKnotenprodukt einer einfach verknüpften Liste. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!






