So laden Sie Javascript-Dateien sicher asynchron_Javascript-Tipps
Das Beispiel in diesem Artikel beschreibt die Methode zum asynchronen und sicheren Laden von Javascript-Dateien. Teilen Sie es als Referenz mit allen. Die Details lauten wie folgt:
Anwendung:
(function() {
__safeLoadScript("http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.4.2/jquery.min.js", function() {
alert(jQuery);
});
})();
JavaScript-Implementierungscode:
window.__safeLoadScript = function(src, callback) {
function addEvent(obj, type, fn) {
if (obj.attachEvent) {
obj['e' + type + fn] = fn;
obj[type + fn] = function() { obj['e' + type + fn](window.event); }
obj.attachEvent('on' + type, obj[type + fn]);
} else
obj.addEventListener(type, fn, false);
}
function async_load(src, callback) {
var s = document.createElement('script');
s.type = 'text/javascript';
s.async = true;
var protocol = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ? "https://" : "http://");
s.src = protocol + src;
var x = document.getElementsByTagName('script')[0];
x.parentNode.insertBefore(s, x);
s.onload = s.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(callback && (!this.readyState || this.readyState == "loaded" || this.readyState == "complete")) {
callback();
}
};
}
addEvent(window, "load", function() {
async_load(src, callback);
});
};
Ich hoffe, dass dieser Artikel für das JavaScript-Programmierdesign aller hilfreich sein wird.

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

Video Face Swap
Tauschen Sie Gesichter in jedem Video mühelos mit unserem völlig kostenlosen KI-Gesichtstausch-Tool aus!

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 1389
1389
 52
52
![Fehler beim Laden des Plugins in Illustrator [Behoben]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/170831522770626.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Fehler beim Laden des Plugins in Illustrator [Behoben]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:00 PM
Fehler beim Laden des Plugins in Illustrator [Behoben]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:00 PM
Erscheint beim Starten von Adobe Illustrator eine Meldung über einen Fehler beim Laden des Plug-Ins? Bei einigen Illustrator-Benutzern ist dieser Fehler beim Öffnen der Anwendung aufgetreten. Der Meldung folgt eine Liste problematischer Plugins. Diese Fehlermeldung weist darauf hin, dass ein Problem mit dem installierten Plug-In vorliegt, es kann jedoch auch andere Gründe haben, beispielsweise eine beschädigte Visual C++-DLL-Datei oder eine beschädigte Einstellungsdatei. Wenn dieser Fehler auftritt, werden wir Sie in diesem Artikel bei der Behebung des Problems unterstützen. Lesen Sie daher weiter unten weiter. Fehler beim Laden des Plug-Ins in Illustrator Wenn Sie beim Versuch, Adobe Illustrator zu starten, die Fehlermeldung „Fehler beim Laden des Plug-Ins“ erhalten, können Sie Folgendes verwenden: Als Administrator
 So implementieren Sie ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
So implementieren Sie ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem mit WebSocket und JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
So implementieren Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem. Einführung: Mit der kontinuierlichen Weiterentwicklung der Technologie ist die Spracherkennungstechnologie zu einem wichtigen Bestandteil des Bereichs der künstlichen Intelligenz geworden. Das auf WebSocket und JavaScript basierende Online-Spracherkennungssystem zeichnet sich durch geringe Latenz, Echtzeit und plattformübergreifende Eigenschaften aus und hat sich zu einer weit verbreiteten Lösung entwickelt. In diesem Artikel wird erläutert, wie Sie mit WebSocket und JavaScript ein Online-Spracherkennungssystem implementieren.
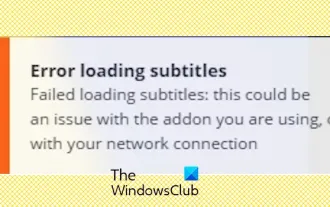 Stremio-Untertitel funktionieren nicht; Fehler beim Laden der Untertitel
Feb 24, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Stremio-Untertitel funktionieren nicht; Fehler beim Laden der Untertitel
Feb 24, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Untertitel funktionieren bei Stremio auf Ihrem Windows-PC nicht? Einige Stremio-Benutzer berichteten, dass in den Videos keine Untertitel angezeigt wurden. Viele Benutzer berichteten, dass ihnen die Fehlermeldung „Fehler beim Laden der Untertitel“ angezeigt wurde. Hier ist die vollständige Fehlermeldung, die bei diesem Fehler angezeigt wird: Beim Laden der Untertitel ist ein Fehler aufgetreten. Untertitel konnten nicht geladen werden: Dies könnte ein Problem mit dem von Ihnen verwendeten Plugin oder Ihrem Netzwerk sein. Wie in der Fehlermeldung angegeben, könnte es Ihre Internetverbindung sein, die den Fehler verursacht. Überprüfen Sie daher bitte Ihre Netzwerkverbindung und stellen Sie sicher, dass Ihr Internet ordnungsgemäß funktioniert. Abgesehen davon könnte es auch andere Gründe für diesen Fehler geben, darunter ein widersprüchliches Untertitel-Add-on, nicht unterstützte Untertitel für bestimmte Videoinhalte und eine veraltete Stremio-App. wie
 WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Implementierung von Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Implementierung von Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket und JavaScript: Schlüsseltechnologien zur Realisierung von Echtzeit-Überwachungssystemen Einführung: Mit der rasanten Entwicklung der Internet-Technologie wurden Echtzeit-Überwachungssysteme in verschiedenen Bereichen weit verbreitet eingesetzt. Eine der Schlüsseltechnologien zur Erzielung einer Echtzeitüberwachung ist die Kombination von WebSocket und JavaScript. In diesem Artikel wird die Anwendung von WebSocket und JavaScript in Echtzeitüberwachungssystemen vorgestellt, Codebeispiele gegeben und deren Implementierungsprinzipien ausführlich erläutert. 1. WebSocket-Technologie
 Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Einführung in die Verwendung von JavaScript und WebSocket zur Implementierung eines Online-Bestellsystems in Echtzeit: Mit der Popularität des Internets und dem Fortschritt der Technologie haben immer mehr Restaurants damit begonnen, Online-Bestelldienste anzubieten. Um ein Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystem zu implementieren, können wir JavaScript und WebSocket-Technologie verwenden. WebSocket ist ein Vollduplex-Kommunikationsprotokoll, das auf dem TCP-Protokoll basiert und eine bidirektionale Kommunikation zwischen Client und Server in Echtzeit realisieren kann. Im Echtzeit-Online-Bestellsystem, wenn der Benutzer Gerichte auswählt und eine Bestellung aufgibt
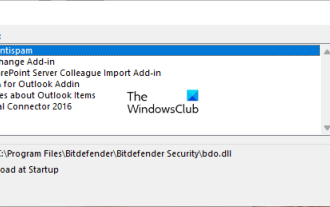 Outlook friert beim Einfügen eines Hyperlinks ein
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Outlook friert beim Einfügen eines Hyperlinks ein
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Wenn beim Einfügen von Hyperlinks in Outlook Probleme beim Einfrieren auftreten, kann dies an instabilen Netzwerkverbindungen, alten Outlook-Versionen, Störungen durch Antivirensoftware oder Add-In-Konflikten liegen. Diese Faktoren können dazu führen, dass Outlook Hyperlink-Vorgänge nicht ordnungsgemäß verarbeitet. Beheben, dass Outlook beim Einfügen von Hyperlinks einfriert. Verwenden Sie die folgenden Korrekturen, um das Einfrieren von Outlook beim Einfügen von Hyperlinks zu beheben: Überprüfen Sie installierte Add-Ins. Aktualisieren Sie Outlook. Deaktivieren Sie vorübergehend Ihre Antivirensoftware und versuchen Sie dann, ein neues Benutzerprofil zu erstellen. Office-Apps reparieren. Programm deinstallieren und neu installieren. Los geht's. 1] Überprüfen Sie die installierten Add-Ins. Möglicherweise verursacht ein in Outlook installiertes Add-In das Problem.
 JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript und WebSocket: Aufbau eines effizienten Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystems Einführung: Heutzutage ist die Genauigkeit von Wettervorhersagen für das tägliche Leben und die Entscheidungsfindung von großer Bedeutung. Mit der Weiterentwicklung der Technologie können wir genauere und zuverlässigere Wettervorhersagen liefern, indem wir Wetterdaten in Echtzeit erhalten. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit JavaScript und WebSocket-Technologie ein effizientes Echtzeit-Wettervorhersagesystem aufbauen. In diesem Artikel wird der Implementierungsprozess anhand spezifischer Codebeispiele demonstriert. Wir
 Einfaches JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie den HTTP-Statuscode
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Einfaches JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie den HTTP-Statuscode
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript-Tutorial: So erhalten Sie HTTP-Statuscode. Es sind spezifische Codebeispiele erforderlich. Vorwort: Bei der Webentwicklung ist häufig die Dateninteraktion mit dem Server erforderlich. Bei der Kommunikation mit dem Server müssen wir häufig den zurückgegebenen HTTP-Statuscode abrufen, um festzustellen, ob der Vorgang erfolgreich ist, und die entsprechende Verarbeitung basierend auf verschiedenen Statuscodes durchführen. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit JavaScript HTTP-Statuscodes abrufen und einige praktische Codebeispiele bereitstellen. Verwenden von XMLHttpRequest




