MySQL备份命令帮助_MySQL
bitsCN.com
MySQL备份命令帮助
1:输出此信息的命令如下:
Sql代码
E:/Soft/Programs/MySQL/MySQL Server 5.6/bin/mysqldump --help > D:/tmp/mysqldump_help.txt
2:帮助文档信息如下:
mysqldump Ver 10.13 Distrib 5.6.10, for Win32 (x86)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Dumping structure and contents of MySQL databases and tables.
Usage: mysqldump [OPTIONS] database [tables]
OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --databases [OPTIONS] DB1 [DB2 DB3...]
OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --all-databases [OPTIONS]
Default options are read from the following files in the given order:
C:/WINDOWS/my.ini C:/WINDOWS/my.cnf C:/my.ini C:/my.cnf E:/Soft/Programs/MySQL/MySQL Server 5.6/my.ini E:/Soft/Programs/MySQL/MySQL Server 5.6/my.cnf
The following groups are read: mysqldump client
The following options may be given as the first argument:
--print-defaults Print the program argument list and exit.
--no-defaults Don't read default options from any option file,
except for login file.
--defaults-file=# Only read default options from the given file #.
--defaults-extra-file=# Read this file after the global files are read.
--defaults-group-suffix=#
Also read groups with concat(group, suffix)
--login-path=# Read this path from the login file.
-A, --all-databases Dump all the databases. This will be same as --databases
with all databases selected.
-Y, --all-tablespaces
Dump all the tablespaces.
-y, --no-tablespaces
Do not dump any tablespace information.
--add-drop-database Add a DROP DATABASE before each create.
--add-drop-table Add a DROP TABLE before each create.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-add-drop-table to disable.)
--add-drop-trigger Add a DROP TRIGGER before each create.
--add-locks Add locks around INSERT statements.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-add-locks to disable.)
--allow-keywords Allow creation of column names that are keywords.
--apply-slave-statements
Adds 'STOP SLAVE' prior to 'CHANGE MASTER' and 'START
SLAVE' to bottom of dump.
--bind-address=name IP address to bind to.
--character-sets-dir=name
Directory for character set files.
-i, --comments Write additional information.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-comments to disable.)
--compatible=name Change the dump to be compatible with a given mode. By
default tables are dumped in a format optimized for
MySQL. Legal modes are: ansi, mysql323, mysql40,
postgresql, oracle, mssql, db2, maxdb, no_key_options,
no_table_options, no_field_options. One can use several
modes separated by commas. Note: Requires MySQL server
version 4.1.0 or higher. This option is ignored with
earlier server versions.
--compact Give less verbose output (useful for debugging). Disables
structure comments and header/footer constructs. Enables
options --skip-add-drop-table --skip-add-locks
--skip-comments --skip-disable-keys --skip-set-charset.
-c, --complete-insert
Use complete insert statements.
-C, --compress Use compression in server/client protocol.
-a, --create-options
Include all MySQL specific create options.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-create-options to disable.)
-B, --databases Dump several databases. Note the difference in usage; in
this case no tables are given. All name arguments are
regarded as database names. 'USE db_name;' will be
included in the output.
-#, --debug[=#] This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
--debug-check Check memory and open file usage at exit.
--debug-info Print some debug info at exit.
--default-character-set=name
Set the default character set.
--delayed-insert Insert rows with INSERT DELAYED.
--delete-master-logs
Delete logs on master after backup. This automatically
enables --master-data.
-K, --disable-keys '/*!40000 ALTER TABLE tb_name DISABLE KEYS */; and
'/*!40000 ALTER TABLE tb_name ENABLE KEYS */; will be put
in the output.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-disable-keys to disable.)
--dump-slave[=#] This causes the binary log position and filename of the
master to be appended to the dumped data output. Setting
the value to 1, will printit as a CHANGE MASTER command
in the dumped data output; if equal to 2, that command
will be prefixed with a comment symbol. This option will
turn --lock-all-tables on, unless --single-transaction is
specified too (in which case a global read lock is only
taken a short time at the beginning of the dump - don't
forget to read about --single-transaction below). In all
cases any action on logs will happen at the exact moment
of the dump.Option automatically turns --lock-tables off.
-E, --events Dump events.
-e, --extended-insert
Use multiple-row INSERT syntax that include several
VALUES lists.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-extended-insert to disable.)
--fields-terminated-by=name
Fields in the output file are terminated by the given
string.
--fields-enclosed-by=name
Fields in the output file are enclosed by the given
character.
--fields-optionally-enclosed-by=name
Fields in the output file are optionally enclosed by the
given character.
--fields-escaped-by=name
Fields in the output file are escaped by the given
character.
-F, --flush-logs Flush logs file in server before starting dump. Note that
if you dump many databases at once (using the option
--databases= or --all-databases), the logs will be
flushed for each database dumped. The exception is when
using --lock-all-tables or --master-data: in this case
the logs will be flushed only once, corresponding to the
moment all tables are locked. So if you want your dump
and the log flush to happen at the same exact moment you
should use --lock-all-tables or --master-data with
--flush-logs.
--flush-privileges Emit a FLUSH PRIVILEGES statement after dumping the mysql
database. This option should be used any time the dump
contains the mysql database and any other database that
depends on the data in the mysql database for proper
restore.
-f, --force Continue even if we get an SQL error.
-?, --help Display this help message and exit.
--hex-blob Dump binary strings (BINARY, VARBINARY, BLOB) in
hexadecimal format.
-h, --host=name Connect to host.
--ignore-table=name Do not dump the specified table. To specify more than one
table to ignore, use the directive multiple times, once
for each table. Each table must be specified with both
database and table names, e.g.,
--ignore-table=database.table.
--include-master-host-port
Adds 'MASTER_HOST=
MASTER TO..' in dump produced with --dump-slave.
--insert-ignore Insert rows with INSERT IGNORE.
--lines-terminated-by=name
Lines in the output file are terminated by the given
string.
-x, --lock-all-tables
Locks all tables across all databases. This is achieved
by taking a global read lock for the duration of the
whole dump. Automatically turns --single-transaction and
--lock-tables off.
-l, --lock-tables Lock all tables for read.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-lock-tables to disable.)
--log-error=name Append warnings and errors to given file.
--master-data[=#] This causes the binary log position and filename to be
appended to the output. If equal to 1, will print it as a
CHANGE MASTER command; if equal to 2, that command will
be prefixed with a comment symbol. This option will turn
--lock-all-tables on, unless --single-transaction is
specified too (in which case a global read lock is only
taken a short time at the beginning of the dump; don't
forget to read about --single-transaction below). In all
cases, any action on logs will happen at the exact moment
of the dump. Option automatically turns --lock-tables
off.
--max-allowed-packet=#
The maximum packet length to send to or receive from
server.
--net-buffer-length=#
The buffer size for TCP/IP and socket communication.
--no-autocommit Wrap tables with autocommit/commit statements.
-n, --no-create-db Suppress the CREATE DATABASE ... IF EXISTS statement that
normally is output for each dumped database if
--all-databases or --databases is given.
-t, --no-create-info
Don't write table creation info.
-d, --no-data No row information.
-N, --no-set-names Same as --skip-set-charset.
--opt Same as --add-drop-table, --add-locks, --create-options,
--quick, --extended-insert, --lock-tables, --set-charset,
and --disable-keys. Enabled by default, disable with
--skip-opt.
--order-by-primary Sorts each table's rows by primary key, or first unique
key, if such a key exists. Useful when dumping a MyISAM
table to be loaded into an InnoDB table, but will make
the dump itself take considerably longer.
-p, --password[=name]
Password to use when connecting to server. If password is
not given it's solicited on the tty.
-W, --pipe Use named pipes to connect to server.
-P, --port=# Port number to use for connection.
--protocol=name The protocol to use for connection (tcp, socket, pipe,
memory).
-q, --quick Don't buffer query, dump directly to stdout.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-quick to disable.)
-Q, --quote-names Quote table and column names with backticks (`).
(Defaults to on; use --skip-quote-names to disable.)
--replace Use REPLACE INTO instead of INSERT INTO.
-r, --result-file=name
Direct output to a given file. This option should be used
in systems (e.g., DOS, Windows) that use carriage-return
linefeed pairs (/r/n) to separate text lines. This option
ensures that only a single newline is used.
-R, --routines Dump stored routines (functions and procedures).
--set-charset Add 'SET NAMES default_character_set' to the output.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-set-charset to disable.)
--set-gtid-purged[=name]
Add 'SET @@GLOBAL.GTID_PURGED' to the output. Possible
values for this option are ON, OFF and AUTO. If ON is
used and GTIDs are not enabled on the server, an error is
generated. If OFF is used, this option does nothing. If
AUTO is used and GTIDs are enabled on the server, 'SET
@@GLOBAL.GTID_PURGED' is added to the output. If GTIDs
are disabled, AUTO does nothing. Default is AUTO.
--shared-memory-base-name=name
Base name of shared memory.
--single-transaction
Creates a consistent snapshot by dumping all tables in a
single transaction. Works ONLY for tables stored in
storage engines which support multiversioning (currently
only InnoDB does); the dump is NOT guaranteed to be
consistent for other storage engines. While a
--single-transaction dump is in process, to ensure a
valid dump file (correct table contents and binary log
position), no other connection should use the following
statements: ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, RENAME TABLE,
TRUNCATE TABLE, as consistent snapshot is not isolated
from them. Option automatically turns off --lock-tables.
--dump-date Put a dump date to the end of the output.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-dump-date to disable.)
--skip-opt Disable --opt. Disables --add-drop-table, --add-locks,
--create-options, --quick, --extended-insert,
--lock-tables, --set-charset, and --disable-keys.
-S, --socket=name The socket file to use for connection.
--ssl Enable SSL for connection (automatically enabled with
other flags).
--ssl-ca=name CA file in PEM format (check OpenSSL docs, implies
--ssl).
--ssl-capath=name CA directory (check OpenSSL docs, implies --ssl).
--ssl-cert=name X509 cert in PEM format (implies --ssl).
--ssl-cipher=name SSL cipher to use (implies --ssl).
--ssl-key=name X509 key in PEM format (implies --ssl).
--ssl-crl=name Certificate revocation list (implies --ssl).
--ssl-crlpath=name Certificate revocation list path (implies --ssl).
--ssl-verify-server-cert
Verify server's "Common Name" in its cert against
hostname used when connecting. This option is disabled by
default.
-T, --tab=name Create tab-separated textfile for each table to given
path. (Create .sql and .txt files.) NOTE: This only works
if mysqldump is run on the same machine as the mysqld
server.
--tables Overrides option --databases (-B).
--triggers Dump triggers for each dumped table.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-triggers to disable.)
--tz-utc SET TIME_ZONE='+00:00' at top of dump to allow dumping of
TIMESTAMP data when a server has data in different time
zones or data is being moved between servers with
different time zones.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-tz-utc to disable.)
-u, --user=name User for login if not current user.
-v, --verbose Print info about the various stages.
-V, --version Output version information and exit.
-w, --where=name Dump only selected records. Quotes are mandatory.
-X, --xml Dump a database as well formed XML.
--plugin-dir=name Directory for client-side plugins.
--default-auth=name Default authentication client-side plugin to use.
Variables (--variable-name=value)
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
--------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
all-databases FALSE
all-tablespaces FALSE
no-tablespaces FALSE
add-drop-database FALSE
add-drop-table TRUE
add-drop-trigger FALSE
add-locks TRUE
allow-keywords FALSE
apply-slave-statements FALSE
bind-address (No default value)
character-sets-dir (No default value)
comments TRUE
compatible (No default value)
compact FALSE
complete-insert FALSE
compress FALSE
create-options TRUE
databases FALSE
debug-check FALSE
debug-info FALSE
default-character-set utf8
delayed-insert FALSE
delete-master-logs FALSE
disable-keys TRUE
dump-slave 0
events FALSE
extended-insert TRUE
fields-terminated-by (No default value)
fields-enclosed-by (No default value)
fields-optionally-enclosed-by (No default value)
fields-escaped-by (No default value)
flush-logs FALSE
flush-privileges FALSE
force FALSE
hex-blob FALSE
host (No default value)
include-master-host-port FALSE
insert-ignore FALSE
lines-terminated-by (No default value)
lock-all-tables FALSE
lock-tables TRUE
log-error (No default value)
master-data 0
max-allowed-packet 25165824
net-buffer-length 1046528
no-autocommit FALSE
no-create-db FALSE
no-create-info FALSE
no-data FALSE
order-by-primary FALSE
port 0
quick TRUE
quote-names TRUE
replace FALSE
routines FALSE
set-charset TRUE
shared-memory-base-name (No default value)
single-transaction FALSE
dump-date TRUE
socket (No default value)
ssl FALSE
ssl-ca (No default value)
ssl-capath (No default value)
ssl-cert (No default value)
ssl-cipher (No default value)
ssl-key (No default value)
ssl-crl (No default value)
ssl-crlpath (No default value)
ssl-verify-server-cert FALSE
tab (No default value)
triggers TRUE
tz-utc TRUE
user (No default value)
verbose FALSE
where (No default value)
plugin-dir (No default value)
default-auth (No default value)
bitsCN.com

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 So entfernen Sie Informationen zum Autor und zur letzten Änderung in Microsoft Word
Apr 15, 2023 am 11:43 AM
So entfernen Sie Informationen zum Autor und zur letzten Änderung in Microsoft Word
Apr 15, 2023 am 11:43 AM
Microsoft Word-Dokumente enthalten beim Speichern einige Metadaten. Diese Details werden zur Identifizierung des Dokuments verwendet, z. B. wann es erstellt wurde, wer der Autor war, Datum der Änderung usw. Es enthält auch andere Informationen wie die Anzahl der Zeichen, die Anzahl der Wörter, die Anzahl der Absätze und mehr. Wenn Sie den Autor oder die zuletzt geänderten Informationen oder andere Informationen entfernen möchten, damit andere Personen die Werte nicht kennen, gibt es eine Möglichkeit. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie, wie Sie Informationen zum Autor und zur letzten Änderung aus einem Dokument entfernen. Entfernen Sie den Autor und die zuletzt geänderten Informationen aus dem Microsoft Word-Dokument. Schritt 1 – Gehen Sie zu
 So teilen Sie Kontaktdaten mit NameDrop: Anleitung für iOS 17
Sep 16, 2023 pm 06:09 PM
So teilen Sie Kontaktdaten mit NameDrop: Anleitung für iOS 17
Sep 16, 2023 pm 06:09 PM
In iOS 17 gibt es eine neue AirDrop-Funktion, mit der Sie Kontaktinformationen mit jemandem austauschen können, indem Sie zwei iPhones berühren. Es heißt NameDrop und so funktioniert es. Anstatt die Nummer einer neuen Person einzugeben, um sie anzurufen oder ihr eine SMS zu schicken, können Sie mit NameDrop Ihr iPhone einfach in die Nähe der Person halten, um Kontaktdaten auszutauschen, damit sie Ihre Nummer hat. Wenn Sie die beiden Geräte zusammenfügen, wird automatisch die Schnittstelle zum Teilen von Kontakten angezeigt. Wenn Sie auf das Popup klicken, werden die Kontaktinformationen einer Person und ihr Kontaktposter angezeigt (Sie können Ihre eigenen Fotos anpassen und bearbeiten, ebenfalls eine neue Funktion von iOS17). Dieser Bildschirm enthält auch Optionen zum „Nur Empfangen“ oder zum Teilen Ihrer eigenen Kontaktinformationen als Antwort.
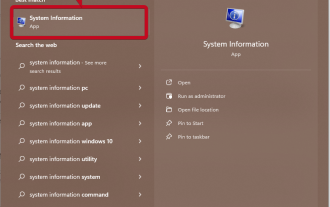 So erhalten Sie die GPU in Windows 11 und überprüfen die Grafikkartendetails
Nov 07, 2023 am 11:21 AM
So erhalten Sie die GPU in Windows 11 und überprüfen die Grafikkartendetails
Nov 07, 2023 am 11:21 AM
Systeminformationen verwenden Klicken Sie auf Start und geben Sie Systeminformationen ein. Klicken Sie einfach auf das Programm, wie im Bild unten gezeigt. Hier finden Sie die meisten Systeminformationen und unter anderem Informationen zur Grafikkarte. Erweitern Sie im Systeminformationsprogramm Komponenten und klicken Sie dann auf Anzeigen. Lassen Sie das Programm alle notwendigen Informationen sammeln und sobald es fertig ist, können Sie den grafikkartenspezifischen Namen und andere Informationen auf Ihrem System finden. Auch wenn Sie über mehrere Grafikkarten verfügen, finden Sie hier die meisten Inhalte zu dedizierten und integrierten Grafikkarten, die an Ihren Computer angeschlossen sind. Verwenden des Geräte-Managers von Windows 11 Wie bei den meisten anderen Windows-Versionen können Sie auch die Grafikkarte auf Ihrem Computer über den Geräte-Manager finden. Klicken Sie auf Start und dann
 Der Single-View-NeRF-Algorithmus S^3-NeRF verwendet Multi-Beleuchtungsinformationen, um Szenengeometrie und Materialinformationen wiederherzustellen.
Apr 13, 2023 am 10:58 AM
Der Single-View-NeRF-Algorithmus S^3-NeRF verwendet Multi-Beleuchtungsinformationen, um Szenengeometrie und Materialinformationen wiederherzustellen.
Apr 13, 2023 am 10:58 AM
Aktuelle 3D-Bildrekonstruktionsarbeiten verwenden normalerweise eine Multi-View-Stereo-Rekonstruktionsmethode (Multi-View-Stereo), die die Zielszene aus mehreren Blickwinkeln (Multi-View) unter konstanten natürlichen Lichtbedingungen erfasst. Diese Methoden gehen jedoch normalerweise von Lambertschen Oberflächen aus und haben Schwierigkeiten, hochfrequente Details wiederherzustellen. Ein weiterer Ansatz zur Szenenrekonstruktion besteht darin, Bilder zu verwenden, die von einem festen Standpunkt, aber mit unterschiedlichen Punktlichtern aufgenommen wurden. Photometrische Stereomethoden nutzen beispielsweise diesen Aufbau und nutzen seine Schattierungsinformationen, um die Oberflächendetails von Nicht-Lambertschen Objekten zu rekonstruieren. Bestehende Einzelansichtsmethoden verwenden jedoch normalerweise Normalkarten oder Tiefenkarten, um das Sichtbare darzustellen
 Was ist der Grund für die Verzögerung beim Empfang von Nachrichten auf WeChat?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 03:02 PM
Was ist der Grund für die Verzögerung beim Empfang von Nachrichten auf WeChat?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 03:02 PM
Der Grund für die Verzögerung beim Empfang von Informationen durch WeChat können Netzwerkprobleme, Serverlast, Versionsprobleme, Geräteprobleme, Probleme beim Senden von Nachrichten oder andere Faktoren sein. Detaillierte Einführung: 1. Netzwerkprobleme können mit der Netzwerkverbindung zusammenhängen. Wenn die Netzwerkverbindung instabil ist oder das Signal schwach ist, kann es zu Verzögerungen bei der Informationsübertragung kommen mit einem stabilen Netzwerk verbunden und die Netzwerksignalstärke ist gut. 2. Wenn die Auslastung des WeChat-Servers hoch ist, kann es zu Verzögerungen bei der Informationsübertragung kommen, insbesondere wenn eine große Anzahl von Benutzern WeChat verwendet gleichzeitig usw.
 Wie NameDrop auf dem iPhone funktioniert (und wie man es deaktiviert)
Nov 30, 2023 am 11:53 AM
Wie NameDrop auf dem iPhone funktioniert (und wie man es deaktiviert)
Nov 30, 2023 am 11:53 AM
In iOS17 gibt es eine neue AirDrop-Funktion, die es Ihnen ermöglicht, Kontaktinformationen mit jemandem auszutauschen, indem Sie zwei iPhones gleichzeitig berühren. Es heißt NameDrop und hier erfahren Sie, wie es tatsächlich funktioniert. NameDrop macht es überflüssig, die Nummer einer neuen Person einzugeben, um sie anzurufen oder ihr eine SMS zu schicken, damit sie Ihre Nummer hat. Sie können Ihr iPhone einfach in die Nähe der Person halten, um Kontaktinformationen auszutauschen. Wenn Sie die beiden Geräte zusammenfügen, wird automatisch die Schnittstelle zum Teilen von Kontakten angezeigt. Wenn Sie auf das Popup klicken, werden die Kontaktinformationen einer Person und ihr Kontaktposter angezeigt (ein eigenes Foto, das Sie anpassen und bearbeiten können, ebenfalls neu in iOS 17). Dieser Bildschirm enthält auch die Option „Nur Empfangen“ oder das Teilen Ihrer eigenen Kontaktinformationen als Antwort
 Was ist die Einheit zur Übertragung von Informationen in einem Computernetzwerk?
Dec 07, 2020 pm 05:26 PM
Was ist die Einheit zur Übertragung von Informationen in einem Computernetzwerk?
Dec 07, 2020 pm 05:26 PM
Die Übertragung von Informationen in Computernetzwerken basiert auf „Wörtern“; Wörter sind die Grundeinheit der Datenübertragung. Computernetzwerke haben zwei Hauptfunktionen: Datenkommunikation und gemeinsame Nutzung von Ressourcen, und die bei der Datenkommunikation übertragenen Informationen werden in Form von Binärdaten ausgedrückt. Datenkommunikation ist eine Kommunikationsmethode und ein Kommunikationsdienst, die Datenübertragungstechnologie verwenden, um Dateninformationen zwischen zwei Terminals gemäß einem bestimmten Kommunikationsprotokoll zu übertragen.
 iOS 17 NameDrop: So teilen Sie Ihre Kontaktinformationen ganz einfach auf dem iPhone
Jul 30, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
iOS 17 NameDrop: So teilen Sie Ihre Kontaktinformationen ganz einfach auf dem iPhone
Jul 30, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
Apple hat eine sehr schnelle (wenn nicht die schnellste) Möglichkeit eingeführt, Ihre Kontaktinformationen über NameDrop mit einem anderen iPhone zu teilen. Hier finden Sie alles, was Sie wissen müssen. Was ist NameDrop? iOS 17 führt NameDrop ein, eine revolutionäre Funktion, die Kontaktposter nutzt. Diese personalisierten Karten können für Sie selbst und andere Kontakte erstellt werden und werden bei jedem Anruf angezeigt. Mit mehreren anpassbaren Optionen wie Fotos, Memojis, Monogrammen und mehr können Sie Ihr Kontaktposter mithilfe Ihres bevorzugten Farbschemas und Ihrer bevorzugten Schriftarten an Ihre Persönlichkeit anpassen. NameDrop teilt Ihr Poster automatisch, wenn sich Ihr iPhone in der Nähe anderer Benutzer befindet, sodass beide Parteien dies mühelos tun können






