
Zu den aktuellen Festplattenklassifizierungen auf dem Markt gehören: IDE-Festplatten (hauptsächlich in PCs verwendet), SATA-Festplatten, SAS-Festplatten, SSD-Festplatten usw. Die meisten Server in Unternehmen sind die beiden letzteren, und SATA-Festplatten werden hauptsächlich in Unternehmen und Unternehmen verwendet SAS-Festplatten werden hauptsächlich für externe Unternehmen verwendet (einige Geschäftsplattformen).
SATA-Festplatten haben derzeit eine maximale Kapazität von 4T, und SAS-Festplatten liegen im Allgemeinen zwischen 300G und 600G. Diese Kapazität wird am häufigsten in Unternehmensproduktionsumgebungen verwendet. Die Verwendung von Festplatten in der tatsächlichen Produktion hängt hauptsächlich von den Leistungsanforderungen ab, also von der Größe der Festplatte.
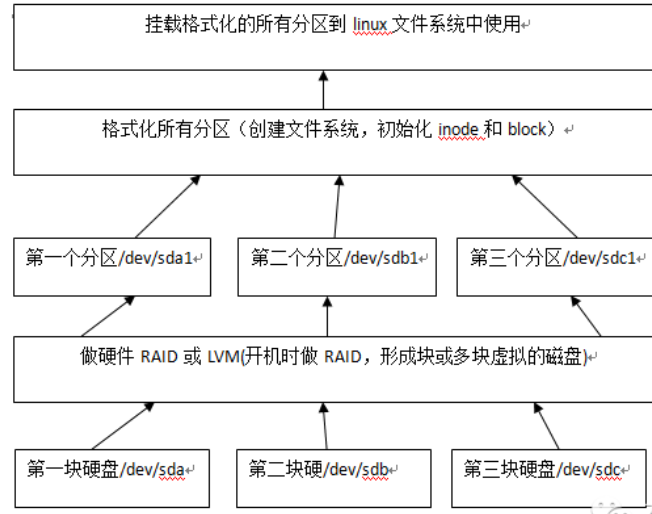
Die Situation mehrerer Festplatten in Servern der Unternehmensebene
Die Struktur einer Festplatte umfasst im Allgemeinen Spuren, Festplattenoberflächen, Sektoren, Header usw.
Die Größe einer Spur = 512 Bytes * Anzahl der Sektoren
Die Größe einer Festplatte = Spurgröße * Anzahl der Spuren
Die Größe einer Festplatte = Festplattengröße * Anzahl der Köpfe
Daher ist die Kapazität einer Festplatte = 512 Bytes * Anzahl der Sektoren * Anzahl der Spuren * Anzahl der Köpfe
Alle Festplattenpartitionsinformationen werden in der Partitionstabelle gespeichert. Das Linux-System unterstützt nur 4 Partitionstabelleninformationen (primäre Partition + erweiterte Partition). Die Größe einer Partitionstabelle beträgt 64 Byte
Linux ist im Allgemeinen in drei Partitionen unterteilt: Boot-Partition, Swap-Partition, /root-PartitionLinux-Partitionsnummer: primäre Partition 1-4, logische Partition beginnt bei 5
Tatsächliche Partitionsanforderungen für die Produktionsumgebung
1. Es müssen mindestens zwei Partitionen vorhanden sein: / und swap
2. Swap (virtueller Speicher) = 1,5 * physische Speichergröße Im Allgemeinen wird die Swap-Partition bei Servern mit weniger als oder gleich 16 GB direkt auf die Größe 16 GB eingestellt
3. Es wird empfohlen, die /boot-Partition, die Linux-Boot-Partition, wie Kerneldateien usw. einzurichten. Im Allgemeinen beträgt die Gesamtgröße aller Dateien nur einige zehn M, daher kann diese Partition auf 100-200 MB eingestellt werden
5. Festplattenpartitionierungstool fdisk
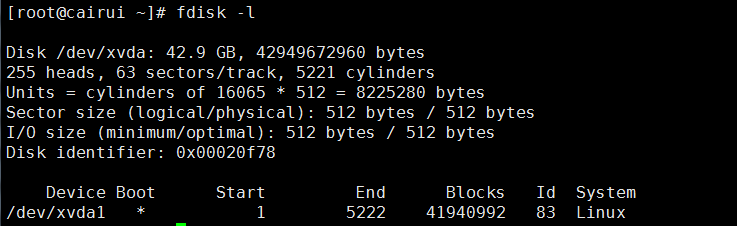
[root@cairui ~]# fdisk --help fdisk: invalid option -- '-' fdisk: Usage: fdisk [options] change partition table fdisk [options] -l list partition table(s) fdisk -s give partition size(s) in blocks Options: -b sector size (512, 1024, 2048 or 4096) -c switch off DOS-compatible mode -h print help -u give sizes in sectors instead of cylinders -v print version -C specify the number of cylinders -H specify the number of heads -S specify the number of sectors per track : Success
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sda1 #对/dev/sda1进行分区操作 Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x02fadd9c. Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable. Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite) WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to sectors (command 'u'). Command (m for help): m Command action a toggle a bootable flag b edit bsd disklabel c toggle the dos compatibility flag d delete a partition #删除一个分区 l list known partition types m print this menu n add a new partition #新建一个分区 o create a new empty DOS partition table p print the partition table #打印出分区表信息 q quit without saving changes #不保存退出 s create a new empty Sun disklabel t change a partition's system id u change display/entry units v verify the partition table w write table to disk and exit #将分区信息写入分区表并退出程序 x extra functionality (experts only)
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1): 设置起始柱面
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610):
设置大小或柱面
Using default value 2610
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
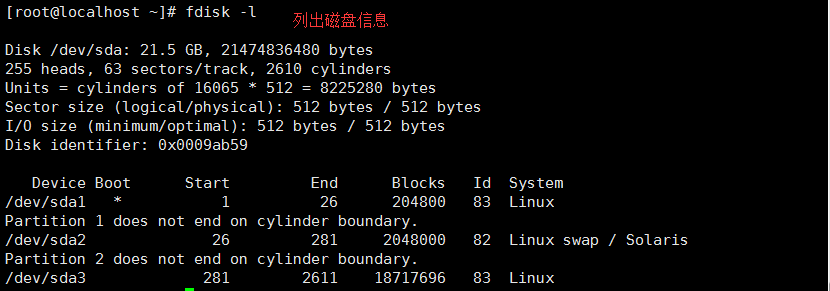
Command (m for help): p 打印分区表信息
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
121 / 753
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xb712cc55
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 2610 20964793+ 83 Linux
分区完成后执行 partprobe 通知系统分区表发生改变
接下来进行格式化分区
[root@Centos ~]# mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
1310720 inodes, 5241198 blocks
262059 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=4294967296
160 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 24 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@Centos ~]# tune2fs -c -1 /dev/sdb1
tune2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Setting maximal mount count to -1
[root@Centos ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt 挂载分区至/mnt 下
[root@Centos ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 50G 3.5G 44G 8% /
tmpfs 932M 0 932M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 39M 421M 9% /boot
122 / 753
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_home 26G 215M 24G 1% /home
/dev/sdb1 20G 172M 19G 1% /mnt
 6. Festplattenpartitionierungstool getrennt
6. Festplattenpartitionierungstool getrennt
[root@Centos ~]# parted /dev/sdb mklabel gpt 将磁盘转换成 gpt 的格式 [root@Centos ~]# parted /dev/sdb mkpart primary 0 200(200M) Warning: The resulting partition is not properly aligned for best performance. Ignore/Cancel? Ignore [root@Centos ~]# parted /dev/sdb p 打印分区表信息 Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi) Disk /dev/sdb: 1074MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 200MB 200MB primary [root@Centos ~]# parted /dev/sdb mkpart primary 201 1073 分区并设置大小 Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab. [root@Centos ~]# parted /dev/sdb p 打印分区表信息 Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi) Disk /dev/sdb: 1074MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 200MB 200MB primary 2 201MB 1073MB 871MB primary [root@Centos ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=1024 (log=0) Fragment size=1024 (log=0) 123 / 753 Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 48960 inodes, 195296 blocks 9764 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=1 Maximum filesystem blocks=67371008 24 block groups 8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group 2040 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 8193, 24577, 40961, 57345, 73729 Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (4096 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 36 mounts or 180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override. [root@Centos ~]# tune2fs -c -1 /dev/sdb1 tune2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Setting maximal mount count to -1 [root@Centos ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt [root@Centos ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 50G 3.5G 44G 8% / tmpfs 932M 0 932M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 485M 39M 421M 9% /boot /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_home 26G 215M 24G 1% /home /dev/sdb1 185M 5.6M 170M 4% /mnt
[root@cairui ~]# parted --help Usage: parted [OPTION]... [DEVICE [COMMAND [PARAMETERS]...]...] Apply COMMANDs with PARAMETERS to DEVICE. If no COMMAND(s) are given, run in interactive mode. OPTIONs: -h, --help displays this help message -l, --list lists partition layout on all block devices -m, --machine displays machine parseable output -s, --script never prompts for user intervention -v, --version displays the version -a, --align=[none|cyl|min|opt] alignment for new partitions COMMANDs: align-check TYPE N check partition N for TYPE(min|opt) alignment check NUMBER do a simple check on the file system cp [FROM-DEVICE] FROM-NUMBER TO-NUMBER copy file system to another partition help [COMMAND] print general help, or help on COMMAND mklabel,mktable LABEL-TYPE create a new disklabel (partition table) mkfs NUMBER FS-TYPE make a FS-TYPE file system on partition NUMBER mkpart PART-TYPE [FS-TYPE] START END make a partition mkpartfs PART-TYPE FS-TYPE START END make a partition with a file system move NUMBER START END move partition NUMBER name NUMBER NAME name partition NUMBER as NAME print [devices|free|list,all|NUMBER] display the partition table, available devices, free space, all found partitions, or a particular partition quit exit program rescue START END rescue a lost partition near START and END resize NUMBER START END resize partition NUMBER and its file system rm NUMBER delete partition NUMBER select DEVICE choose the device to edit set NUMBER FLAG STATE change the FLAG on partition NUMBER toggle [NUMBER [FLAG]] toggle the state of FLAG on partition NUMBER unit UNIT set the default unit to UNIT version display the version number and copyright information of GNU Parted
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonDetaillierte Erläuterung der Linux-Systemfestplatte. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!




