Listen Sie alle in die Bash-Shell integrierten Befehle auf
Ein in die Shell integrierter Befehl ist ein Befehl oder eine Funktion, die von der Shell aufgerufen und direkt in der Shell ausgeführt wird. Die Bash-Shell führt den Befehl direkt aus, ohne andere Programme aufzurufen. Mit dem Befehl „help“ können Sie Informationen zu den in Bash integrierten Befehlen anzeigen. Nachfolgend finden Sie verschiedene Arten integrierter Befehle.
Typen sind wie folgt:
Integrierte Bourne Shell-Befehle: Integrierte Befehle werden von Bourne Shell geerbt.
Integrierte Bash-Befehle: Eine Liste Bash-spezifischer integrierter Befehle.
Shell-Verhalten ändern: Integrierte Befehle, die Shell-Eigenschaften und optionales Verhalten ändern.
Spezielle integrierte Befehle: Integrierte Befehle, die von POSIX speziell klassifiziert werden.
Es gibt folgende Befehle:
$ help $ help | less $ help | grep read
Beispielausgabe:
GNU bash, version 4.1.5(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
These shell commands are defined internally. Type `help' to see this list.
Type `help name' to find out more about the function `name'.
Use `info bash' to find out more about the shell in general.
Use `man -k' or `info' to find out more about commands not in this list.
A star (*) next to a name means that the command is disabled.
job_spec [&] history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or hist>
(( expression )) if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif C>
. filename [arguments] jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs >
: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigs>
[ arg... ] let arg [arg ...]
[[ expression ]] local [option] name[=value] ...
alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ] logout [n]
bg [job_spec ...] mapfile [-n count] [-O origin] [-s c>
bind [-lpvsPVS] [-m keymap] [-f filen> popd [-n] [+N | -N]
break [n] printf [-v var] format [arguments]
builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]] pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
caller [expr] pwd [-LP]
case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...)> read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [->
cd [-L|-P] [dir] readarray [-n count] [-O origin] [-s>
command [-pVv] command [arg ...] readonly [-af] [name[=value] ...] or>
compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] > return [n]
complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DE] > select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMM>
compopt [-o|+o option] [-DE] [name ..> set [--abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option>
continue [n] shift [n]
coproc [NAME] command [redirections] shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...]
declare [-aAfFilrtux] [-p] [name[=val> source filename [arguments]
dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] suspend [-f]
disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ...] test [expr]
echo [-neE] [arg ...] time [-p] pipeline
enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [na> times
eval [arg ...] trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...]
exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [argume> true
exit [n] type [-afptP] name [name ...]
export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or ex> typeset [-aAfFilrtux] [-p] name[=val>
false ulimit [-SHacdefilmnpqrstuvx] [limit>
fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] o> umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
fg [job_spec] unalias [-a] name [name ...]
for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMAND> unset [-f] [-v] [name ...]
for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMAN> until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
function name { COMMANDS ; } or name > variables - Names and meanings of so>
getopts optstring name [arg] wait [id]
hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name > while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
help [-dms] [pattern ...] { COMMANDS ; }
Eine andere Möglichkeit besteht darin, den folgenden Befehl zu verwenden:
compgen -b compgen -b | more
Führen Sie Folgendes aus, um detaillierte Informationen zu erhalten:
help command help read
Um nur eine Liste aller integrierten Befehle mit einer kurzen Beschreibung zu erhalten, gehen Sie wie folgt vor:
$ help -d
Verwenden Sie die folgende Syntax, um weitere verwandte integrierte Befehle herauszufinden:
help name help cd help fg help for help read help :
Beispielausgabe:
:: : Null command. No effect; the command does nothing. Exit Status: Always succeeds
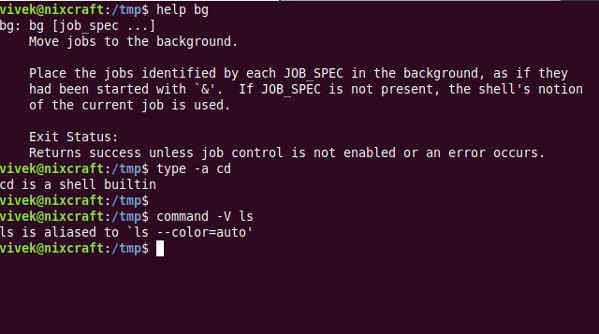
Verwenden Sie den Befehlstyp oder den Befehlsbefehl:
type -a command-name-here type -a cd type -a uname type -a : type -a ls
oder:
type -a cd uname : ls uname
Beispielausgabe:
cd is a shell builtin
uname is /bin/uname
: is a shell builtin
ls is aliased to `ls --color=auto'
ls is /bin/ls
l is a function
l ()
{
ls --color=auto
}oder:
command -V ls command -V cd command -V foo
Autor: Vivek Gite
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonListen Sie alle in die Bash-Shell integrierten Befehle auf. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

Video Face Swap
Tauschen Sie Gesichter in jedem Video mühelos mit unserem völlig kostenlosen KI-Gesichtstausch-Tool aus!

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Notepad++7.3.1
Einfach zu bedienender und kostenloser Code-Editor

SublimeText3 chinesische Version
Chinesische Version, sehr einfach zu bedienen

Senden Sie Studio 13.0.1
Leistungsstarke integrierte PHP-Entwicklungsumgebung

Dreamweaver CS6
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

SublimeText3 Mac-Version
Codebearbeitungssoftware auf Gottesniveau (SublimeText3)

Heiße Themen
 So laden Sie GIT -Projekte auf lokale Herd herunter
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
So laden Sie GIT -Projekte auf lokale Herd herunter
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
Um Projekte lokal über Git herunterzuladen, befolgen Sie die folgenden Schritte: Installieren Sie Git. Navigieren Sie zum Projektverzeichnis. Klonen des Remote-Repositorys mit dem folgenden Befehl: Git Clone https://github.com/username/repository-name.git.git
 So aktualisieren Sie den Code in Git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
So aktualisieren Sie den Code in Git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
Schritte zur Aktualisierung von Git -Code: CODEHOUSSCHAFTEN:
 Wie man Git Commit benutzt
Apr 17, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
Wie man Git Commit benutzt
Apr 17, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
Git Commit ist ein Befehl, mit dem Dateien Änderungen an einem Git -Repository aufgezeichnet werden, um einen Momentaufnahme des aktuellen Status des Projekts zu speichern. So verwenden Sie dies wie folgt: Fügen Sie Änderungen in den temporären Speicherbereich hinzu, schreiben Sie eine prägnante und informative Einreichungsnachricht, um die Einreichungsnachricht zu speichern und zu beenden, um die Einreichung optional abzuschließen: Fügen Sie eine Signatur für die Einreichungs -Git -Protokoll zum Anzeigen des Einreichungsinhalts hinzu.
 Was tun, wenn der Git -Download nicht aktiv ist
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Was tun, wenn der Git -Download nicht aktiv ist
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Auflösung: Wenn die Git -Download -Geschwindigkeit langsam ist, können Sie die folgenden Schritte ausführen: Überprüfen Sie die Netzwerkverbindung und versuchen Sie, die Verbindungsmethode zu wechseln. Optimieren Sie die GIT-Konfiguration: Erhöhen Sie die Post-Puffer-Größe (GIT-Konfiguration --global http.postbuffer 524288000) und verringern Sie die Niedriggeschwindigkeitsbegrenzung (GIT-Konfiguration --global http.lowSpeedLimit 1000). Verwenden Sie einen GIT-Proxy (wie Git-Proxy oder Git-LFS-Proxy). Versuchen Sie, einen anderen Git -Client (z. B. Sourcetree oder Github Desktop) zu verwenden. Überprüfen Sie den Brandschutz
 Wie man Code in Git zusammenfasst
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
Wie man Code in Git zusammenfasst
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
Git -Code -Merge -Prozess: Ziehen Sie die neuesten Änderungen an, um Konflikte zu vermeiden. Wechseln Sie in die Filiale, die Sie zusammenführen möchten. Initiieren Sie eine Zusammenführung und geben Sie den Zweig an, um zusammenzuarbeiten. Merge -Konflikte auflösen (falls vorhanden). Inszenierung und Bekämpfung verschmelzen, liefern die Botschaft.
 Linux -Architektur: Enthüllung der 5 Grundkomponenten
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux -Architektur: Enthüllung der 5 Grundkomponenten
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Die fünf grundlegenden Komponenten des Linux -Systems sind: 1. Kernel, 2. Systembibliothek, 3. System Utilities, 4. Grafische Benutzeroberfläche, 5. Anwendungen. Der Kernel verwaltet Hardware -Ressourcen, die Systembibliothek bietet vorkompilierte Funktionen, Systemversorgungsunternehmen werden für die Systemverwaltung verwendet, die GUI bietet visuelle Interaktion und Anwendungen verwenden diese Komponenten, um Funktionen zu implementieren.
 So löschen Sie ein Repository von Git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
So löschen Sie ein Repository von Git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
Befolgen Sie die folgenden Schritte, um ein Git -Repository zu löschen: Bestätigen Sie das Repository, das Sie löschen möchten. Lokale Löschen des Repositorys: Verwenden Sie den Befehl rm -RF, um seinen Ordner zu löschen. Löschen Sie ein Lager aus der Ferne: Navigieren Sie zu den Lagereinstellungen, suchen Sie die Option "Lager löschen" und bestätigen Sie den Betrieb.
 Wie löste ich das effiziente Suchproblem in PHP -Projekten? Typense hilft Ihnen, es zu erreichen!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
Wie löste ich das effiziente Suchproblem in PHP -Projekten? Typense hilft Ihnen, es zu erreichen!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
Bei der Entwicklung einer E-Commerce-Website habe ich auf ein schwieriges Problem gestoßen: Wie kann ich effiziente Suchfunktionen in großen Mengen an Produktdaten erzielen? Herkömmliche Datenbanksuche sind ineffizient und haben eine schlechte Benutzererfahrung. Nach einigen Nachforschungen entdeckte ich den Suchmaschinen-Artensense und löste dieses Problem durch seine offizielle PHP-Client-Artense-/Artense-Php, die die Suchleistung erheblich verbesserte.






