Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 HTML Tutorial
HTML Tutorial
 Explanation of the difference between the location of Js placed in the HTML file
Explanation of the difference between the location of Js placed in the HTML file
Explanation of the difference between the location of Js placed in the HTML file
This question has always been a confusion for beginners. First understand where js can be placed in HTML, namely head and body. Most people put it in the head. When I was learning it, I confusedly followed it and put it in the head. I don’t know why? Today, let’s talk about the difference between these two places:
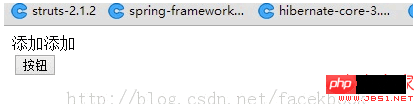
Let’s look at a piece of html code first:
<html> <head> <title> New Document </title> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8"> <script type="text/javascript" src="test.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="target"> </div> <button id="btn">按钮</button> </body> </html>
var test = function(){
var span = document.createElement("span");
span.innerHTML="添加";
document.getElementById("target").appendChild(span);
}
document.getElementById("btn").onclick=test;If this code is placed in the head, it will not run. Why?
This is about the running order of HTML. To be more precise, it is not the running order of HTML, but the running order of js. When HTML is run from above to , it enters the test.js file. The previous one will not run, that is, the one wrapped by function will not be run. At this time, the last sentence will be executed. Go to the page and get the element whose element ID is btn. But at this time, the HTML page has not been loaded. It is definitely not possible to get the element with id btn. An error will be reported. At this time, someone said that it can be changed to the following code:
document.body.onload = function(){
document.getElementById("btn").onclick=test;
};But it is not as good as writing it this way, writing it in front of