 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Sharing an AJAX function encapsulated in native Javascript_javascript skills
Sharing an AJAX function encapsulated in native Javascript_javascript skills
Sharing an AJAX function encapsulated in native Javascript_javascript skills
My recent work involves a lot of ajax operations, and I have to do the things that should be done in the background. The ajax function used now is encapsulated by a background person - but it is based on jquery's ajax. So the function without jquery is useless. And I think that the ajax method of jquery is very complete and can be used directly. If you already have jquery, then its ajax will not be used in vain. What I am missing is An ajax method that can be used without jquery.
So I also spent a day writing one. The parameters and calling method are similar to jquery's ajax. Let's call it xhr, because xhr=XMLHttpRequest.
/*
* Name: xhr,AJAX wrapper function
* Description: An ajax calling encapsulation class, imitating jquery’s ajax calling method
* Author: Ten Years Lamp
*/
var xhr = function () {
var
ajax = function () {
return ('XMLHttpRequest' in window) ? function () {
return new XMLHttpRequest();
} : function () {
return new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
}(),
formatData= function (fd) {
var res = '';
for(var f in fd) {
res = f '=' fd[f] '&';
}
return res.slice(0,-1);
},
AJAX = function(ops) {
root = this,
req = ajax();
root.url = ops.url;
root.type = ops.type || 'responseText';
root.method = ops.method || 'GET';
root.async = ops.async || true;
root.data = ops.data || {};
root.complete = ops.complete || function () {};
root.success = ops.success || function(){};
root.error = ops.error || function (s) { alert(root.url '->status:' s 'error!')};
root.abort = req.abort;
root.setData = function (data) {
for(var d in data) {
root.data[d] = data[d];
}
}
root.send = function () {
var datastring = formatData(root.data),
sendstring,get = false,
async = root.async,
complete = root.complete,
method = root.method,
type=root.type;
If(method === 'GET') {
root.url ='?' datastring;
get = true;
}
req.open(method,root.url,async);
if(!get) {
req.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
sendstring = datastring;
//Reset the onreadystatechange method before send, otherwise a new synchronization request will occur and two successful callbacks will be executed (chrome, etc. will also execute onreadystatechange during synchronization requests)
req.onreadystatechange = async ? function () {
// console.log('async true');
If (req.readyState ==4){
complete();
If(req.status == 200) {
root.success(req[type]);
} else {
Root.error(req.status);
}
} : null;
req.send(sendstring);
if(!async) {
//console.log('async false');
complete();
root.success(req[type]);
}
}
root.url && root.send();
};
Return function(ops) {return new AJAX(ops);}
}();
1.url: Request address. If you don’t fill it in, the request will not be initiated. But if you don’t fill it in and force send, you don’t blame me if something goes wrong
2.method: ‘GET’ or ‘POST’, all capital letters, default GET
3.data: The data to be sent is attached, the format is an object
4.async: Whether to be asynchronous, default true
5.type: The returned data type is only responseText or responseXML. The default is responseText
6.complete: Function executed when the request is completed
7.success: Function executed when the request is successful
8.error: Function executed when the request fails
Note: The type parameter is not as rich as jquery's dataType. It only has responseText or responseXML in native AJAX. If json data is returned, you need to process it yourself in the success function to convert text into json.
Function description:
An instantiated xhr object has two functions available, one is send, the calling method is: xhr.send(), no parameters, its function is to initiate the request process. If there is no url during initialization, it will not be executed. send method, so that you can add the url later and initiate the send manually - if there is no url when sending, the request will fail and I did not handle this error. You will only find the error yourself.
Another method is setData. The calling method is xhr.setData(data_obj), and its parameter is an object. The function of the setData method is to partially replace the value in the data attribute of xhr. For example, there is already a page in xhr.data: 1. You can use xhr.setData({page:2}) to update its value without affecting other attribute values that already exist in data.
Calling method:
var a1 = xhr({
data:{ 'username':'lix', 'password':'123456',
'gender':'male',
'interset':'play'
},
async:false,
Method:'GET',
Success: function (data) {
var obj = JSON.parse(data);
//....
}
});
Note: No need to write new
After this period of project experience, I found that an ajax class should have a very common feature: to facilitate repeated requests. For example, when I wrote pagination ajax in the project, a request had to be sent every time the page was turned, but Except for the current page number and the number of items per page, the other data will not change. If you make multiple such requests, you have to repeatedly define those unchanged parameters, which is undoubtedly a waste of resources.
So this xhr function has already considered this function. Taking the example of paging, we can initialize an xhr object when the page is loaded and save it as variable a1. When a page turning request is initiated, other None of the parameters have changed, but the pageNumber has changed. At this time, you can call the setData method of xhr to change the pageNumber.
Note: The parameter of setData is also an object.
a1.data = {…};
Not just data, you can make more changes to the instantiated xhr object a1, such as changing the url, changing the success function, GET to POST, synchronous to asynchronous... After changing, call again a1.send() method, it will initiate the request again according to your settings.
Of course, if it is another ajax request that is completely unrelated, there is no need to use this ready-made a1. We can instantiate another xhr and call it a2 or something.
If you are not satisfied with the name xhr, then you have to change it yourself.
A compressed and encrypted version is also provided. The uncompressed version is about 2kb with comments removed, and the compressed version is 1.00kb.
There must be some imperfections in xhr. If found in future use, I will correct them in time. If you are not happy with it or find it insufficient, please feel free to provide suggestions for improvement.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
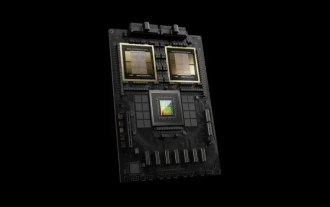 TrendForce: Nvidia's Blackwell platform products drive TSMC's CoWoS production capacity to increase by 150% this year
Apr 17, 2024 pm 08:00 PM
TrendForce: Nvidia's Blackwell platform products drive TSMC's CoWoS production capacity to increase by 150% this year
Apr 17, 2024 pm 08:00 PM
According to news from this site on April 17, TrendForce recently released a report, believing that demand for Nvidia's new Blackwell platform products is bullish, and is expected to drive TSMC's total CoWoS packaging production capacity to increase by more than 150% in 2024. NVIDIA Blackwell's new platform products include B-series GPUs and GB200 accelerator cards integrating NVIDIA's own GraceArm CPU. TrendForce confirms that the supply chain is currently very optimistic about GB200. It is estimated that shipments in 2025 are expected to exceed one million units, accounting for 40-50% of Nvidia's high-end GPUs. Nvidia plans to deliver products such as GB200 and B100 in the second half of the year, but upstream wafer packaging must further adopt more complex products.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 AMD 'Strix Halo” FP11 package size exposed: equivalent to Intel LGA1700, 60% larger than Phoenix
Jul 18, 2024 am 02:04 AM
AMD 'Strix Halo” FP11 package size exposed: equivalent to Intel LGA1700, 60% larger than Phoenix
Jul 18, 2024 am 02:04 AM
This website reported on July 9 that the AMD Zen5 architecture "Strix" series processors will have two packaging solutions. The smaller StrixPoint will use the FP8 package, while the StrixHalo will use the FP11 package. Source: videocardz source @Olrak29_ The latest revelation is that StrixHalo’s FP11 package size is 37.5mm*45mm (1687 square millimeters), which is the same as the LGA-1700 package size of Intel’s AlderLake and RaptorLake CPUs. AMD’s latest Phoenix APU uses an FP8 packaging solution with a size of 25*40mm, which means that StrixHalo’s F





