 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Use JavaScript to wrap text element nodes with a DIV_javascript skills
Use JavaScript to wrap text element nodes with a DIV_javascript skills
Use JavaScript to wrap text element nodes with a DIV_javascript skills
When your application relies on a specific JavaScript library, you are inadvertently trying to solve problems with the library itself, rather than with the language. Like when I try to wrap text (which may also contain HTML elements) with a DIV element. Suppose you have the following HTML:
This is some text and <a href="">a link</a>
At this time, if you want to convert it to the following:
<div>This is some text and <a href="">a link</a><div>
The simplest brute force method is that you can perform updates through the .innerHTML property on the parent element, but the problem is that all bound event listeners will be invalid because using innerHTML will recreate an HTML element. What a big glass! So at this time, we can only use JavaScript to achieve it - the ruler is short and the inch is long. The following is the implementation code:
var newWrapper = document.createElement('div');
while(existingParent.firstChild) {
// 移动DOM元素,不会创建新元素
newWrapper.appendChild(existingParent.firstChild);
}For loop cannot be used here, because childNodes is a collection of dynamic nodes, and moving a node will affect its index value. We use a while loop to keep checking the firstChild of the parent element. If it returns a value representing false, then you know that all nodes have been moved to the new parent!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Wrapping C/C++ into Python using SWIG
Aug 25, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
Wrapping C/C++ into Python using SWIG
Aug 25, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
There are several ways to encapsulate existing C or C++ functionality in Python. In this section, we will see how to use SWIG to wrap C/C++ functionality. Here are other options for wrapping C/C++ functionality in python. Manual wrapping uses Pyrex to wrap C code. CtypesSIPBoostPythonSWIG (Simple Wrapper Interface Generator) is capable of working with many other languages including Perl, Python, PHP, Ruby, Tcl, C#, CommonLisp (CLISP, Allegro, CL, UFFI, CFFI), Java, Modula-3, and OCAML. Swig also Supports multiple interpretations and compilations
 Query the minimum weight in the subtree starting from node X and distance at most D
Aug 25, 2023 am 11:25 AM
Query the minimum weight in the subtree starting from node X and distance at most D
Aug 25, 2023 am 11:25 AM
When doing computer programming, sometimes it is necessary to find the minimum weight of a subtree originating from a specific node, provided that the subtree cannot contain nodes that are more than D units away from the specified node. This problem arises in various fields and applications, including graph theory, tree-based algorithms, and network optimization. A subtree is a subset of a larger tree structure, with the specified node serving as the root node of the subtree. A subtree contains all descendants of the root node and their connecting edges. A node's weight refers to a specific value assigned to that node, which can represent its importance, significance, or other relevant metrics. In this problem, the goal is to find the minimum weight among all nodes in a subtree while limiting the subtree to nodes that are at most D units away from the root node. In the following article, we will delve into the complexity of mining minimum weights from subtrees
 How to implement the node copy and cut functions of mind maps through Vue and jsmind?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
How to implement the node copy and cut functions of mind maps through Vue and jsmind?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
How to implement the node copy and cut functions of mind maps through Vue and jsmind? Mind map is a common thinking tool that can help us organize our thoughts and sort out our thinking logic. The node copy and cut functions are commonly used operations in mind maps, which allow us to reuse existing nodes more conveniently and improve the efficiency of thinking organization. In this article, we will use the two tools Vue and jsmind to implement the node copy and cut functions of the mind map. First, we need to install Vue and jsmind and create
 What is the method to delete node in js
Sep 01, 2023 pm 05:00 PM
What is the method to delete node in js
Sep 01, 2023 pm 05:00 PM
The methods for deleting nodes in js are: 1. The removeChild() method is used to remove the specified child node from the parent node. It requires two parameters. The first parameter is the child node to be deleted, and the second parameter is the parent node. Node; 2. The parentNode.removeChild() method can be called directly through the parent node to delete the child node; 3. The remove() method can directly delete the node without specifying the parent node; 4. The innerHTML attribute is used to delete the node. content.
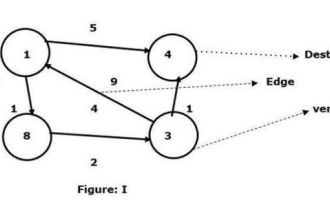 Find the shortest path between any two nodes using the Floyd-Warshal algorithm
Sep 20, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Find the shortest path between any two nodes using the Floyd-Warshal algorithm
Sep 20, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
C++ has a macro, which is defined as a piece of code or an expected value, and it will be reused whenever the user needs it. The Floyd-Walshall algorithm is the process of finding the shortest path between all pairs of vertices in a given weighted graph. The algorithm follows a dynamic programming approach to find the minimum weight graph. Let us understand the meaning of Floyd-Walshall algorithm through a diagram - take vertex 1 as the source and vertex 4 as the destination and find the shortest path between them. We have seen that there are two paths that can be connected to the target vertex 4. 1->4 – the edge has a weight of 51->8->3->4 – the edge weight (1+2+1) is 4. In the given graph I, we see the smallest edge connecting two vertices. So here the vertex
 How to create, delete, append and replace element nodes in js (with code examples)
Aug 06, 2022 pm 05:26 PM
How to create, delete, append and replace element nodes in js (with code examples)
Aug 06, 2022 pm 05:26 PM
This article mainly introduces how to create, delete, append and replace element nodes in js. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!
 Checks whether the path between two nodes in the given graph represents the shortest path
Sep 07, 2023 pm 06:57 PM
Checks whether the path between two nodes in the given graph represents the shortest path
Sep 07, 2023 pm 06:57 PM
To check if a given path between two centers of a graph conforms to the shortest path, this can be calculated by comparing the entire edge weight along the given path to the shortest distance between combinations of the same centers using a reliable shortest path method, such as Dijkstra's calculation or Floyd−Warshall calculation. If all edge weights on a given path match the most limited deletion, then it represents the simplest path. Also: If the overall edge weight is more prominent than the shortest distance, it indicates that there is a short distance between the two centers in the graph. Methods Used Dijkstra's Algorithm Floyd−Warshall Algorithm with Edge Reversal Cost Greedy Algorithm Dijkstra's calculation may be a popular graph traversal calculation
 In the C program, translate the following content into Chinese: Program to find the nth node from the bottom of a linked list
Sep 13, 2023 pm 03:13 PM
In the C program, translate the following content into Chinese: Program to find the nth node from the bottom of a linked list
Sep 13, 2023 pm 03:13 PM
Given n nodes, the task is to print the nth node at the end of the linked list. The program must not change the order of the nodes in the list, but should only print the nth node from the last node of the linked list. Example Input-:102030405060 N=3Output-:40 In the above example, starting from the first node, traverse to count-n nodes, that is, 10,2030,40,50,60, so the third to last node is 40. Instead of traversing the entire list so efficiently the approach you can follow - get a temporary pointer to, say, temp of node type set this temporary pointer to the first node that the head pointer points to set the counter to the one in the list



