SQL Server由于主外键约束导致插入失败的记录方法
你打算从 SQL Server 2000 数据库的客户表和国别表中导入客户数据到 SQL Server 2005 数据库中。你要确保在导入过程中,客户表中国家代码列的每个值在 SQL Server 2005 数据库中国别表内都有其相应的纪录。你在两个表之间定义一外键,这样,参照完整性将保证
你打算从 SQL Server 2000 数据库的客户表和国别表中导入客户数据到 SQL Server 2005 数据库中。你要确保在导入过程中,客户表中国家代码列的每个值在 SQL Server 2005 数据库中国别表内都有其相应的纪录。你在两个表之间定义一外键,这样,参照完整性将保证若国家代码值在客户表中存在, 而在国别表中不存在时导入程序失败。 你要确保国别表无记录时导入过程不失败。--创建Department(deptID,deptName)和UserInfo(userID, userName, sex, loginDate,deptid)
--其中deptID,userID是自动增长的,并且是主键。deptid是外键。并且插入测试数据
--创建序列
CREATE SEQUENCE seq_Dep
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NOMAXVALUE
NOCYCLE
CACHE 30;
--建表Department
CREATE TABLE Department
(
deptID VARCHAR2(10) PRIMARY KEY,
deptName VARCHAR2(20)
);
--插入测试数据
INSERT INTO Department VALUES ('D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL,'人事部');
INSERT INTO Department VALUES ('D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL,'技术部');
INSERT INTO Department VALUES ('D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL,'后勤部');
INSERT INTO Department VALUES ('D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL,'经理部');
INSERT INTO Department VALUES ('D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL,'销售部');
INSERT INTO Department VALUES ('D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL,'服务部');
INSERT INTO Department VALUES ('D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL,'公关部');
COMMIT;
--创建序列
CREATE SEQUENCE seq_User
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NOMAXVALUE
NOCYCLE
CACHE 30;
--建表UserInfo
CREATE TABLE UserInfo
(
userID VARCHAR2(10) PRIMARY KEY,
userName VARCHAR2(20),
sex VARCHAR2(2),
loginDate DATE,
deptid VARCHAR2(10) REFERENCES Department (deptID)
);
--插入测试数据
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Eric Schmidt','男','12-9月-07','D1');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Larry Page','男','12-10月-07','D3');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Sergey Brin','男','12-11月-07','D5');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'W. M. Coughran, Jr.','男','1-12月-07','D4');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'David C. Drummond','女','12-12月-01','D2');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Alan Eustace','男','12-9月-07','D1');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Jeff Huber','男','12-10月-07','D3');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'George Reyes','男','12-11月-07','D5');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Elliot Schrage','男','1-12月-07','D4');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Tim Armstrong','女','12-12月-01','D2');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Nikesh Arora','女','12-12月-01','D2');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Sukhinder','男','12-9月-07','D1');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Vinton G. Cerf','男','12-10月-07','D3');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'George Reyes','男','12-11月-07','D5');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Dave Girouard','男','1-12月-07','D4');
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES ('U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL,'Singh Cassidy','女','12-12月-01','D2');
COMMIT;
--3. 在deptid建立索引
CREATE INDEX deptid_index on UserInfo(deptid);
--4. 给Department和UserInfo创建同义词,名称分别是dept, sy_user
CREATE OR REPLACE SYNONYM dept FOR Department;
CREATE OR REPLACE SYNONYM sy_user FOR UserInfo;
/*
5. 通过同义词dept, user来创建视图,
视图要求能查询出“部门名称,部门编号,用户名,性别,注册时间”
*/
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_dept_user
("部门名称","部门编号","用户名","性别","注册时间")
AS SELECT d.deptName,d.deptID,u.userName,u.sex,u.loginDate
FROM dept d ,sy_user u
WHERE d.deptID=u.deptid;
--14. 使用Instead Of触发器,往第5题创建的视图中插入数据。
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON;
INSERT INTO view_dept_user ('部门名称','部门编号','用户名','性别','注册时间')
VALUES('仓储部','D6','Dejan Perkovic','男','1-1月-08');
/*
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_dept_user
("部门名称","部门编号","用户名","性别","注册时间")
AS SELECT d.deptName,d.deptID,u.userName,u.sex,u.loginDate
FROM dept d ,sy_user u
WHERE d.deptID=u.deptid;
*/
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER dept_user_insert
INSTEAD OF INSERT ON view_dept_user
FOR EACH ROW
DECLARE
CURSOR cur_dept IS SELECT * FROM Department
WHERE Department.deptID = :NEW.deptID;
CURSOR cur_user IS SELECT * FROM sy_user
WHERE sy_user.userName = :NEW.userName;
d cur_dept%rowtype;
u cur_user%rowtype;
did dept.deptID%TYPE;
uid sy_user.userID%TYPE;
BEGIN
OPEN cur_dept;
OPEN cur_user;
FETCH cur_user INTO u;
FETCH cur_dept INTO d;
/*
如果插入的数据中部门ID不存在,则将 seq_Dep.NEXTVAL 产生的序号赋值给变量did,执行插入语句新增加一个部门。
*/
IF cur_dept%NOTFOUND THEN
did := 'D'||seq_Dep.NEXTVAL;
INSERT INTO Department(deptID,deptName) VALUES(did,:NEW.deptName);
/*
如果插入数据中的员工不存在,则执行插入语句增加一个新员工
*/
IF cur_user%NOTFOUND THEN
uid := 'U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL;
INSERT INTO UserInfo(userID,userName,sex,loginDate,deptid) VALUES(uid,:NEW.userName,:NEW.sex,:NEW.loginDate,did);
END IF;
IF cur_dept%FOUND THEN
/*
如果插入的数据中部门ID是已经存在的部门ID,则更新部门名称
*/
did:=:NEW.deptID;
UPDATE Department SET Department.deptName WHERE Department.deptID = :NEW.deptID;
/*
如果插入数据中的员工不存在,则将seq_User.NEXTVAL 产生的序号赋值给变量uid,执行插入语句增加一个新员工
*/
IF cur_user%NOTFOUND THEN
uid := 'U'||seq_User.NEXTVAL;
INSERT INTO UserInfo VALUES(uid,:NEW.userName,:NEW.sex,:NEW.loginDate,:NEW.deptID);
ELSE
/*
如果插入数据中的员工已存在,则根据部门ID、员工姓名 来更新员工的其他字段的值,员工ID为主键,不用更新。
考虑到同名员工存在的可能,但员工的ID不可能相同的特点,需要根据插入数据中的部门ID、员工姓名来查询出
符合要求的员工的ID,用员工ID来进行后续的操作
*/
SELECT userID INTO uid FROM UserInfo WHERE UserInfo.userName=:NEW.userName AND UserInfo.deptID=did;
UPDATE UserInfo SET UserInfo.sex = :NEW.sex,UserInfo.loginDate = :NEW.loginDate,UserInfo.deptID = :NEW.sex
WHERE UserInfo.userID=uid AND UserInfo.userName=:NEW.userName;
END IF;
END IF;
CLOSE ecur;
CLOSE dcur;
END dept_user_insert;
/
show errors;
出现的错误提示:
警告: 创建的触发器带有编译错误。
SQL> show errors;
TRIGGER DEPT_USER_INSERT 出现错误:
LINE/COL ERROR
-------- -----------------------------------------------------------------
3/31 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.DEPTID'
5/30 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.USERNAME'
20/56 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.DEPTNAME'
26/75 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.USERNAME'
26/89 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.SEX'
26/98 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.LOGINDATE'
33/10 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.DEPTID'
34/4 PL/SQL: SQL Statement ignored
34/46 PL/SQL: ORA-00927: 缺少等号
34/72 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.DEPTID'
40/37 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.USERNAME'
LINE/COL ERROR
-------- -----------------------------------------------------------------
40/51 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.SEX'
40/60 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.LOGINDATE'
40/75 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.DEPTID'
47/66 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.USERNAME'
49/40 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.SEX'
49/70 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.LOGINDATE'
49/103 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.SEX'
50/53 PLS-00049: 错误的赋值变量 'NEW.USERNAME'
55/5 PLS-00103: 出现符号 "DEPT_USER_INSERT"在需要下列之一时:
if

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
HQL and SQL are compared in the Hibernate framework: HQL (1. Object-oriented syntax, 2. Database-independent queries, 3. Type safety), while SQL directly operates the database (1. Database-independent standards, 2. Complex executable queries and data manipulation).
 Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
"Usage of Division Operation in OracleSQL" In OracleSQL, division operation is one of the common mathematical operations. During data query and processing, division operations can help us calculate the ratio between fields or derive the logical relationship between specific values. This article will introduce the usage of division operation in OracleSQL and provide specific code examples. 1. Two ways of division operations in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operations can be performed in two different ways.
 Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Oracle and DB2 are two commonly used relational database management systems, each of which has its own unique SQL syntax and characteristics. This article will compare and differ between the SQL syntax of Oracle and DB2, and provide specific code examples. Database connection In Oracle, use the following statement to connect to the database: CONNECTusername/password@database. In DB2, the statement to connect to the database is as follows: CONNECTTOdataba
 What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What is Identity in SQL? Specific code examples are needed. In SQL, Identity is a special data type used to generate auto-incrementing numbers. It is often used to uniquely identify each row of data in a table. The Identity column is often used in conjunction with the primary key column to ensure that each record has a unique identifier. This article will detail how to use Identity and some practical code examples. The basic way to use Identity is to use Identit when creating a table.
 Using the MINUS operator in SQL
Feb 18, 2024 pm 04:53 PM
Using the MINUS operator in SQL
Feb 18, 2024 pm 04:53 PM
Usage of MINUS in SQL and specific code examples In SQL, MINUS is an operator used to perform a difference operation between two result sets. It is used to delete the same rows from the first result set as in the second result set. The result set returned by the MINUS operator will contain rows that exist only in the first result set. The following uses specific code examples to demonstrate the usage of MINUS: Assume there are two tables - "table1" and "table2", their structures are as follows: Table name: table1 field
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
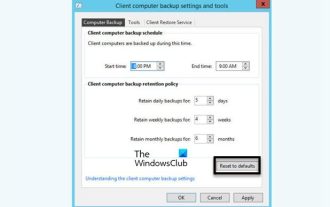 How to install, uninstall, and reset Windows server backup
Mar 06, 2024 am 10:37 AM
How to install, uninstall, and reset Windows server backup
Mar 06, 2024 am 10:37 AM
WindowsServerBackup is a function that comes with the WindowsServer operating system, designed to help users protect important data and system configurations, and provide complete backup and recovery solutions for small, medium and enterprise-level enterprises. Only users running Server2022 and higher can use this feature. In this article, we will explain how to install, uninstall or reset WindowsServerBackup. How to Reset Windows Server Backup If you are experiencing problems with your server backup, the backup is taking too long, or you are unable to access stored files, then you may consider resetting your Windows Server backup settings. To reset Windows
 How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Solution: 1. Check whether the logged-in user has sufficient permissions to access or operate the database, and ensure that the user has the correct permissions; 2. Check whether the account of the SQL Server service has permission to access the specified file or folder, and ensure that the account Have sufficient permissions to read and write the file or folder; 3. Check whether the specified database file has been opened or locked by other processes, try to close or release the file, and rerun the query; 4. Try as administrator Run Management Studio as etc.






