【OpenCV2.4】SVM处理线性不可分的例子
【原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/justany/archive/2012/11/26/2788509.html】 目的 实际事物模型中,并非所有东西都是线性可分的。 需要寻找一种方法对线性不可分数据进行划分。 原理 ,我们推导出对于线性可分数据,最佳划分超平面应满足: 现在我们想引入
【原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/justany/archive/2012/11/26/2788509.html】
目的
- 实际事物模型中,并非所有东西都是线性可分的。
- 需要寻找一种方法对线性不可分数据进行划分。
原理
,我们推导出对于线性可分数据,最佳划分超平面应满足:

现在我们想引入一些东西,来表示那些被错分的数据点(比如噪点),对划分的影响。
如何来表示这些影响呢?
被错分的点,离自己应当存在的区域越远,就代表了,这个点“错”得越严重。
所以我们引入 ,为对应样本离同类区域的距离。
,为对应样本离同类区域的距离。

接下来的问题是,如何将这种错的程度,转换为和原模型相同的度量呢?
我们再引入一个常量C,表示 和原模型度量的转换关系,用C对
和原模型度量的转换关系,用C对 进行加权和,来表征错分点对原模型的影响,这样我们得到新的最优化问题模型:
进行加权和,来表征错分点对原模型的影响,这样我们得到新的最优化问题模型:

关于参数C的选择, 明显的取决于训练样本的分布情况。 尽管并不存在一个普遍的答案,但是记住下面几点规则还是有用的:
- C比较大时分类错误率较小,但是间隔也较小。 在这种情形下, 错分类对模型函数产生较大的影响,既然优化的目的是为了最小化这个模型函数,那么错分类的情形必然会受到抑制。
- C比较小时间隔较大,但是分类错误率也较大。 在这种情形下,模型函数中错分类之和这一项对优化过程的影响变小,优化过程将更加关注于寻找到一个能产生较大间隔的超平面。
说白了,C的大小表征了,错分数据对原模型的影响程度。于是C越大,优化时越关注错分问题。反之越关注能否产生一个较大间隔的超平面。
开始使用

#include <iostream><span>
#include </span><opencv2><span>
#include </span><opencv2><span>
#include </span><opencv2>
<span>#define</span> NTRAINING_SAMPLES 100 <span>//</span><span> 每类训练样本的数量</span>
<span>#define</span> FRAC_LINEAR_SEP 0.9f <span>//</span><span> 线性可分部分的样本组成比例</span>
<span>using</span> <span>namespace</span><span> cv;
</span><span>using</span> <span>namespace</span><span> std;
</span><span>int</span><span> main(){
</span><span>//</span><span> 用于显示的数据</span>
<span>const</span> <span>int</span> WIDTH = <span>512</span>, HEIGHT = <span>512</span><span>;
Mat I </span>=<span> Mat::zeros(HEIGHT, WIDTH, CV_8UC3);
</span><span>/*</span><span> 1. 随即产生训练数据 </span><span>*/</span><span>
Mat trainData(</span><span>2</span>*NTRAINING_SAMPLES, <span>2</span><span>, CV_32FC1);
Mat labels (</span><span>2</span>*NTRAINING_SAMPLES, <span>1</span><span>, CV_32FC1);
RNG rng(</span><span>100</span>); <span>//</span><span> 生成随即数
</span><span>//</span><span> 设置线性可分的训练数据</span>
<span>int</span> nLinearSamples = (<span>int</span>) (FRAC_LINEAR_SEP *<span> NTRAINING_SAMPLES);
</span><span>//</span><span> 生成分类1的随机点</span>
Mat trainClass = trainData.rowRange(<span>0</span><span>, nLinearSamples);
</span><span>//</span><span> 点的x坐标在[0, 0.4)之间</span>
Mat c = trainClass.colRange(<span>0</span>, <span>1</span><span>);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(</span><span>1</span>), Scalar(<span>0.4</span> *<span> WIDTH));
</span><span>//</span><span> 点的y坐标在[0, 1)之间</span>
c = trainClass.colRange(<span>1</span>,<span>2</span><span>);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(</span><span>1</span><span>), Scalar(HEIGHT));
</span><span>//</span><span> 生成分类2的随机点</span>
trainClass = trainData.rowRange(<span>2</span>*NTRAINING_SAMPLES-nLinearSamples, <span>2</span>*<span>NTRAINING_SAMPLES);
</span><span>//</span><span> 点的x坐标在[0.6, 1]之间</span>
c = trainClass.colRange(<span>0</span> , <span>1</span><span>);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(</span><span>0.6</span>*<span>WIDTH), Scalar(WIDTH));
</span><span>//</span><span> 点的y坐标在[0, 1)之间</span>
c = trainClass.colRange(<span>1</span>,<span>2</span><span>);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(</span><span>1</span><span>), Scalar(HEIGHT));
</span><span>/*</span><span> 设置非线性可分的训练数据 </span><span>*/</span>
<span>//</span><span> 生成分类1和分类2的随机点</span>
trainClass = trainData.rowRange( nLinearSamples, <span>2</span>*NTRAINING_SAMPLES-<span>nLinearSamples);
</span><span>//</span><span> 点的x坐标在[0.4, 0.6)之间</span>
c = trainClass.colRange(<span>0</span>,<span>1</span><span>);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(</span><span>0.4</span>*WIDTH), Scalar(<span>0.6</span>*<span>WIDTH));
</span><span>//</span><span> 点的y坐标在[0, 1)之间</span>
c = trainClass.colRange(<span>1</span>,<span>2</span><span>);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(</span><span>1</span><span>), Scalar(HEIGHT));
</span><span>/*</span><span>*/</span><span>
labels.rowRange( </span><span>0</span>, NTRAINING_SAMPLES).setTo(<span>1</span>); <span>//</span><span> Class 1</span>
labels.rowRange(NTRAINING_SAMPLES, <span>2</span>*NTRAINING_SAMPLES).setTo(<span>2</span>); <span>//</span><span> Class 2</span>
<span>/*</span><span> 设置支持向量机参数 </span><span>*/</span><span>
CvSVMParams </span><span>params</span><span>;
</span><span>params</span>.svm_type =<span> SVM::C_SVC;
</span><span>params</span>.C = <span>0.1</span><span>;
</span><span>params</span>.kernel_type =<span> SVM::LINEAR;
</span><span>params</span>.term_crit = TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, (<span>int</span>)1e7, 1e-<span>6</span><span>);
</span><span>/*</span><span> 3. 训练支持向量机 </span><span>*/</span><span>
cout </span>"<span>Starting training process</span><span>"</span> endl;
CvSVM svm;
svm.train(trainData, labels, Mat(), Mat(), <span>params</span><span>);
cout </span>"<span>Finished training process</span><span>"</span> endl;
<span>/*</span><span> 4. 显示划分区域 </span><span>*/</span><span>
Vec3b green(</span><span>0</span>,<span>100</span>,<span>0</span>), blue (<span>100</span>,<span>0</span>,<span>0</span><span>);
</span><span>for</span> (<span>int</span> i = <span>0</span>; i i)
<span>for</span> (<span>int</span> j = <span>0</span>; j j){
Mat sampleMat = (Mat_float>(<span>1</span>,<span>2</span>) i, j);
<span>float</span> response =<span> svm.predict(sampleMat);
</span><span>if</span> (response == <span>1</span>) I.at<vec3b>(j, i) =<span> green;
</span><span>else</span> <span>if</span> (response == <span>2</span>) I.at<vec3b>(j, i) =<span> blue;
}
</span><span>/*</span><span> 5. 显示训练数据 </span><span>*/</span>
<span>int</span> thick = -<span>1</span><span>;
</span><span>int</span> lineType = <span>8</span><span>;
</span><span>float</span><span> px, py;
</span><span>//</span><span> 分类1</span>
<span>for</span> (<span>int</span> i = <span>0</span>; i i){
px = trainData.atfloat>(i,<span>0</span><span>);
py </span>= trainData.atfloat>(i,<span>1</span><span>);
circle(I, Point( (</span><span>int</span>) px, (<span>int</span>) py ), <span>3</span>, Scalar(<span>0</span>, <span>255</span>, <span>0</span><span>), thick, lineType);
}
</span><span>//</span><span> 分类2</span>
<span>for</span> (<span>int</span> i = NTRAINING_SAMPLES; i 2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES; ++<span>i){
px </span>= trainData.atfloat>(i,<span>0</span><span>);
py </span>= trainData.atfloat>(i,<span>1</span><span>);
circle(I, Point( (</span><span>int</span>) px, (<span>int</span>) py ), <span>3</span>, Scalar(<span>255</span>, <span>0</span>, <span>0</span><span>), thick, lineType);
}
</span><span>/*</span><span> 6. 显示支持向量 */</span>
thick = <span>2</span><span>;
lineType </span>= <span>8</span><span>;
</span><span>int</span> x =<span> svm.get_support_vector_count();
</span><span>for</span> (<span>int</span> i = <span>0</span>; i i)
{
<span>const</span> <span>float</span>* v =<span> svm.get_support_vector(i);
circle( I, Point( (</span><span>int</span>) v[<span>0</span>], (<span>int</span>) v[<span>1</span>]), <span>6</span>, Scalar(<span>128</span>, <span>128</span>, <span>128</span><span>), thick, lineType);
}
imwrite(</span><span>"</span><span>result.png</span><span>"</span>, I); <span>//</span><span> 保存图片</span>
imshow(<span>"</span><span>SVM线性不可分数据划分</span><span>"</span>, I); <span>//</span><span> 显示给用户</span>
waitKey(<span>0</span><span>);
}</span></vec3b></vec3b></opencv2></opencv2></opencv2></iostream>
设置SVM参数
这里的参数设置可以参考一下的API。
<span>CvSVMParams</span> <span>params</span><span>;</span> <span>params</span><span>.</span><span>svm_type</span> <span>=</span> <span>SVM</span><span>::</span><span>C_SVC</span><span>;</span> <span>params</span><span>.</span><span>C</span> <span>=</span> <span>0.1</span><span>;</span> <span>params</span><span>.</span><span>kernel_type</span> <span>=</span> <span>SVM</span><span>::</span><span>LINEAR</span><span>;</span> <span>params</span><span>.</span><span>term_crit</span> <span>=</span> <span>TermCriteria</span><span>(</span><span>CV_TERMCRIT_ITER</span><span>,</span> <span>(</span><span>int</span><span>)</span><span>1e7</span><span>,</span> <span>1e-6</span><span>);</span>Copy after login
可以看到,这次使用的是C类支持向量分类机。其参数C的值为0.1。
结果
- 程序创建了一张图像,在其中显示了训练样本,其中一个类显示为浅绿色圆圈,另一个类显示为浅蓝色圆圈。
- 训练得到SVM,并将图像的每一个像素分类。 分类的结果将图像分为蓝绿两部分,中间线就是最优分割超平面。由于样本非线性可分, 自然就有一些被错分类的样本。 一些绿色点被划分到蓝色区域, 一些蓝色点被划分到绿色区域。
- 最后支持向量通过灰色边框加重显示。

被山寨的原文
Support Vector Machines for Non-Linearly Separable Data . OpenCV.org

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
1. First, we right-click the blank space of the taskbar and select the [Task Manager] option, or right-click the start logo, and then select the [Task Manager] option. 2. In the opened Task Manager interface, we click the [Services] tab on the far right. 3. In the opened [Service] tab, click the [Open Service] option below. 4. In the [Services] window that opens, right-click the [InternetConnectionSharing(ICS)] service, and then select the [Properties] option. 5. In the properties window that opens, change [Open with] to [Disabled], click [Apply] and then click [OK]. 6. Click the start logo, then click the shutdown button, select [Restart], and complete the computer restart.
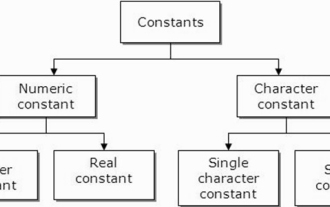 What are constants in C language? Can you give an example?
Aug 28, 2023 pm 10:45 PM
What are constants in C language? Can you give an example?
Aug 28, 2023 pm 10:45 PM
A constant is also called a variable and once defined, its value does not change during the execution of the program. Therefore, we can declare a variable as a constant referencing a fixed value. It is also called text. Constants must be defined using the Const keyword. Syntax The syntax of constants used in C programming language is as follows - consttypeVariableName; (or) consttype*VariableName; Different types of constants The different types of constants used in C programming language are as follows: Integer constants - For example: 1,0,34, 4567 Floating point constants - Example: 0.0, 156.89, 23.456 Octal and Hexadecimal constants - Example: Hex: 0x2a, 0xaa.. Octal
 Summary of frequently asked questions about importing Excel data into Mysql: How to deal with error log problems encountered when importing data?
Sep 10, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Summary of frequently asked questions about importing Excel data into Mysql: How to deal with error log problems encountered when importing data?
Sep 10, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Summary of frequently asked questions about importing Excel data into Mysql: How to deal with error log problems encountered when importing data? Importing Excel data into a MySQL database is a common task. However, during this process, we often encounter various errors and problems. One of them is the error log issue. When we try to import data, the system may generate an error log listing the specific information about the error that occurred. So, how should we deal with the error log when we encounter this situation? First, we need to know how
 A quick guide to CSV file manipulation
Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:23 PM
A quick guide to CSV file manipulation
Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:23 PM
Quickly learn how to open and process CSV format files. With the continuous development of data analysis and processing, CSV format has become one of the widely used file formats. A CSV file is a simple and easy-to-read text file with different data fields separated by commas. Whether in academic research, business analysis or data processing, we often encounter situations where we need to open and process CSV files. The following guide will show you how to quickly learn to open and process CSV format files. Step 1: Understand the CSV file format First,
 Learn how to handle special characters and convert single quotes in PHP
Mar 27, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Learn how to handle special characters and convert single quotes in PHP
Mar 27, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
In the process of PHP development, dealing with special characters is a common problem, especially in string processing, special characters are often escaped. Among them, converting special characters into single quotes is a relatively common requirement, because in PHP, single quotes are a common way to wrap strings. In this article, we will explain how to handle special character conversion single quotes in PHP and provide specific code examples. In PHP, special characters include but are not limited to single quotes ('), double quotes ("), backslash (), etc. In strings
 How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development requires specific code examples. In modern software development, XML and JSON are two widely used data formats. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language used to store and transmit data, while JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data exchange format. In C# development, we often need to process and operate XML and JSON data. This article will focus on how to use C# to process these two data formats, and attach
 How to handle java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError error in Java?
Aug 24, 2023 am 11:01 AM
How to handle java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError error in Java?
Aug 24, 2023 am 11:01 AM
The Java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError exception occurs at runtime when an attempt to access or load a native method or library fails due to a mismatch between its architecture, operating system, or library path configuration and the referenced one. It usually indicates that there is an incompatibility with the architecture, operating system configuration, or path configuration that prevents success - usually the local library referenced does not match the library installed on the system and is not available at runtime. To overcome this error, the key is to be native The library is compatible with your system and can be accessed through its library path setting. You should verify that library files exist in their specified locations and meet system requirements. java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkErrorjava.lang
 How to crawl and process data by calling API interface in PHP project?
Sep 05, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to crawl and process data by calling API interface in PHP project?
Sep 05, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to crawl and process data by calling API interface in PHP project? 1. Introduction In PHP projects, we often need to crawl data from other websites and process these data. Many websites provide API interfaces, and we can obtain data by calling these interfaces. This article will introduce how to use PHP to call the API interface to crawl and process data. 2. Obtain the URL and parameters of the API interface. Before starting, we need to obtain the URL of the target API interface and the required parameters.




