数据库数据在Java占用内存简单估算
数据库数据在Java占用内存简单估算 结论: 1.数据库记录放在JAVA里,用对象(ORM一般的处理方式)需要4倍左右的内存空间,用HashMap这种KV保存需要10倍空间; 2.如果你主要数据是text大文本,那空间一般可以按2倍估算。 以上是一个通用数据测试结论,估大家参考
数据库数据在Java占用内存简单估算
结论:
1.数据库记录放在JAVA里,用对象(ORM一般的处理方式)需要4倍左右的内存空间,用HashMap这种KV保存需要10倍空间;
2.如果你主要数据是text大文本,那空间一般可以按2倍估算。
以上是一个通用数据测试结论,估大家参考。
数据库记录占用的空间大小比较好算,比如一个int占用4字节,bigint占用8字节,date占用3字节,datetime占用8字节,varchar是变长字节等。如果不想精确计算,在数据库中通过统计信息也可以比较轻松的知道表总共占用的空间及每条记录平均行长。
当我们用JDBC访问数据库时,经常会被问到内存溢出的问题,由于java是面向对象的语言,用JVM来自动内存回收,不能按普通方法计算内存,本文给出一个估算内存的思路和参考答案
先给出普通JDBC中数据库对象与内存的映射关系
|
MySQL |
Oracle |
JDBC |
|
Int |
Integer |
|
|
Int unsigned |
Long |
|
|
BigInt |
Long |
|
|
BigInt unsigned |
BigInteger |
|
|
Decimal |
Number |
BigDecimal |
|
Varchar |
Varchar2 |
String |
|
Date |
Date |
|
|
Datetime |
Date |
Timestamp |
|
Timestamp |
Timestamp |
Timestamp |
|
Clob |
Clob |
String |
|
Blob |
blob |
Byte[] |
|
Text |
Clob |
String |
|
float |
binary_float |
float |
|
double |
binary_double |
double |
上面这个比较好理解,接下来我们需要JAVA常用对象的内存占用空间,这个可以通过JDK 5 开始提供的Instrumentation 接口来完成,也可以通过开源的sizeOf.jar 来测试,笔者是通过sizeOf.jar验证的。测试结果数据如下:
|
对象 |
64位 JVM 压缩指针 |
64位 JVM 非压缩指针 |
|
Integer |
16 |
24 |
|
Long |
24 |
24 |
|
Object |
16 |
16 |
|
Date |
24 |
32 |
|
Timestamp |
32 |
40 |
|
String_0 |
48 |
64 |
|
String_1 |
56 |
72 |
|
String_10 |
72 |
88 |
|
String_100 |
248 |
264 |
|
StringBuilder |
24 |
32 |
|
BigDecimal |
40 |
48 |
|
BigInteger |
64 |
80 |
|
HashMap |
128 |
216 |
|
HashMap_0 |
72 |
96 |
|
HashMap_100 |
576 |
1112 |
|
HashMap_10000 |
65600 |
131160 |
|
ArrayList |
80 |
144 |
|
ArrayList_0 |
40 |
64 |
|
ArrayList_100 |
440 |
864 |
|
ArrayList_10000 |
40040 |
80064 |
|
LinkedList |
48 |
80 |
|
LinkedHashMap |
96 |
144 |
|
ClassA |
32 |
40 |
|
ClassB |
40 |
48 |
|
ClassC |
40 |
56 |
由于现在主机一般都是64位, 64位JVM从JDK1.6.45开始,当JVM最大内存小于32GB时,自动打开压缩指针特性,这样对象的内存占用空间少很多,由上表可以看出,至少减少1/3的空间。
下面我们结合数据库数据来测试
假如mysql数据库有一张emp表,结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `emp` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `modify_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL, `address` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL, `age` smallint(6) DEFAULT NULL, `height` decimal(10,2) DEFAULT NULL, `weight` decimal(10,2) DEFAULT NULL, `phone` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
样本数据如下:
hm.put("id", 1988);
hm.put("createTime", new Date());
hm.put("modifyTime", new Date());
hm.put("name", "张三丰");
hm.put("address","浙江杭州市西湖大道188号808室");
hm.put("age",88);
hm.put("weight",new BigDecimal(88));
hm.put("height",new BigDecimal(188));
hm.put("phone","1388888888");按上面样本数据计算,有效数据约80字节,在MySQL里占用空间约120字节
在java里转换为HashMap和Emp对象测试空间如下
|
对象 |
64位 JVM 压缩指针 |
64位 JVM 非压缩指针 |
|
HashMap_empty |
128 |
216 |
|
HashMap_full |
1360 |
1832 |
|
Emp_empty |
72 |
112 |
|
Emp_full |
464 |
600 |
从上面测试结果看,数据到JAVA里占用的空间增加了许多,在64位压缩指针下,如果存到HashMap,需要1360字节,空间是数据库约11.3倍,如果存为Emp普通对象,需要464字节,是数据库的3.8倍。
如果我们是一个分页从数据库读取emp信息,每页显示50条记录,用List保存,HashMap需要68KB,emp对象需要23KB。
根据这个简单测试,我们可以总结一个结论:
数据库记录放在JAVA里,用对象(ORM一般的处理方式)需要4倍左右的内存空间,用HashMap这种KV保存需要10倍空间。
如果你的数据和参考数据差异非常大,如主要数据text大文本,那空间一般可以简单的按2倍估算。
以上是一个通用数据测试结论,估大家参考。
下面是测试代码:
import net.sourceforge.sizeof.SizeOf;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.util.*;
public class TestSize {
static {
SizeOf.skipStaticField(true); //java.sizeOf will not compute static fields
//SizeOf.skipFinalField(true); //java.sizeOf will not compute final fields
//SizeOf.skipFlyweightObject(true); //java.sizeOf will not compute well-known flyweight objects
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, IllegalAccessException {
TestSize ts=new TestSize();
ts.testObjectSize();
ts.testDataSize();
System.out.println("ok");
}
public void testObjectSize() {
System.out.println("Integer:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new Integer(56)));
System.out.println("Long:"+SizeOf.sizeOf(new Long(56L)));
System.out.println("Object:"+SizeOf.sizeOf(new Object()));
System.out.println("Date:"+SizeOf.sizeOf(new Date()));
System.out.println("Timestamp:"+SizeOf.sizeOf(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())));
System.out.println("String_0:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new String()));
System.out.println("String_1:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new String("1")));
System.out.println("String_10:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new String("0123456789")));
System.out.println("String_100:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf("0123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789"));
System.out.println("StringBuilder:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new StringBuilder()));
System.out.println("BigDecimal:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new BigDecimal("34535643.23")));
System.out.println("BigInteger:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new BigInteger("34535643")));
System.out.println("HashMap:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new HashMap()));
System.out.println("HashMap_0:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new HashMap(0)));
System.out.println("HashMap_100:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new HashMap(100)));
System.out.println("HashMap_10000:" + SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new HashMap(10000)));
System.out.println("ArrayList:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new ArrayList()));
System.out.println("ArrayList_0:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new ArrayList(0)));
System.out.println("ArrayList_100:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new ArrayList(100)));
System.out.println("ArrayList_10000:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new ArrayList(10000)));
System.out.println("LinkedList:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new LinkedList<Object>()));
System.out.println("LinkedHashMap:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new LinkedHashMap<Object,Object>()));
System.out.println("ClassA:" + SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new ClassA()));
System.out.println("ClassB:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new ClassB()));
System.out.println("ClassC:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(new ClassC()));
}
public void testDataSize() throws IOException, IllegalAccessException {
HashMap hm=new HashMap();
System.out.println("HashMap_empty:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(hm));
hm.put("id", 1988);
hm.put("createTime", new Date());
hm.put("modifyTime", new Date());
hm.put("name", "张三丰");
hm.put("address","浙江杭州市西湖大道188号808室");
hm.put("age",88);
hm.put("weight",new BigDecimal(88));
hm.put("height",new BigDecimal(188));
hm.put("phone","1388888888");
System.out.println("HashMap_full:" + SizeOf.deepSizeOf(hm));
Emp emp=new Emp();
System.out.println("Emp_empty:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(emp));
emp.setId(1988);
emp.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));
emp.setModifyTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));
emp.setName("张三丰");
emp.setAddress("浙江杭州市西湖大道188号808室");
emp.setAge(28);
emp.setWeight(new BigDecimal("88"));
emp.setHeight(new BigDecimal("188"));
emp.setPhone("13888888888");
System.out.println("Emp_full:"+SizeOf.deepSizeOf(emp));
}
class ClassA{
}
class ClassB extends ClassA{
}
class ClassC extends ClassB{
}
class Emp{
private Integer id;
private Timestamp createTime;
private Timestamp modifyTime;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer age;
private BigDecimal height;
private BigDecimal weight;
private String phone;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Timestamp getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Timestamp createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public Timestamp getModifyTime() {
return modifyTime;
}
public void setModifyTime(Timestamp modifyTime) {
this.modifyTime = modifyTime;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public BigDecimal getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(BigDecimal height) {
this.height = height;
}
public BigDecimal getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(BigDecimal weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
}
}
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
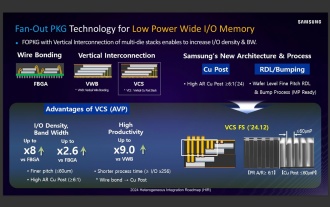 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




