Java?????????mysql??????23:00????????????
Java?????????mysql??????23:00???????????? public class DatabaseBackup { /** * * @param dbdir mysql????????????????????? * @param dbname ?????????????????? * @param backdir ??????????????? */ public static void backup(String dbdir, String db
Java?????????mysql??????23:00????????????public class DatabaseBackup {
/**
*
* @param dbdir mysql?????????????????????
* @param dbname ??????????????????
* @param backdir ???????????????
*/
public static void backup(String dbdir, String dbname, String backdir) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy_MM_dd_HHmmss");
String currentTime = dateFormat.format(calendar.getTime());
try {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process child = rt
.exec(dbdir + "/bin/mysqldump --default-character-set=utf8 -uroot -p123456 " + dbname);
InputStream in = child.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader xx = new InputStreamReader(in, "utf8");
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(new File(backdir, dbname + "_" + currentTime + ".bak"));
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fout, "utf8");
dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
writer.write("-- Dump by Microsoul at " + dateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()) + "\r\n");
String inStr;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(xx);
// ??????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????Java????????????????????????
while ((inStr = br.readLine()) != null) {
writer.write(inStr);
writer.write("\r\n");
}
writer.write("\r\n-- Use " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms\r\n");
writer.flush();
in.close();
xx.close();
br.close();
writer.close();
fout.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
PrintStream print = null;
try {
print = new PrintStream(new File(backdir, currentTime + "_backup_err.log"));
dateFormat.applyPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
currentTime = dateFormat.format(calendar.getTime());
print.println(currentTime + " backup failed.");
e.printStackTrace(print);
print.flush();
} catch (IOException e2) {
} finally {
if (print != null) {
print.close();
}
}
}
}
}?????????????????????????????
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar twentyOne = Calendar.getInstance();
twentyOne.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 23);
twentyOne.set(Calendar.MINUTE, 0);
twentyOne.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0);
new Timer().schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
DatabaseBackup.backup("/usr/local/mysql", "test", "/home/xtiger/db/");
}
}, twentyOne.getTime(), 24 * 3600 * 1000);
}
}??????????????????????????????????? Timer???????????????

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 The page is blank after PHP is connected to MySQL. What is the reason for the invalid die() function?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
The page is blank after PHP is connected to MySQL. What is the reason for the invalid die() function?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
The page is blank after PHP connects to MySQL, and the reason why die() function fails. When learning the connection between PHP and MySQL database, you often encounter some confusing things...
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
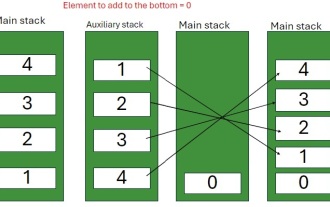 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the
 PHP PDO connection to MySQL database: How does the charset=utf8 setting affect the database character set?
Apr 01, 2025 am 11:39 AM
PHP PDO connection to MySQL database: How does the charset=utf8 setting affect the database character set?
Apr 01, 2025 am 11:39 AM
PHP...
 How to efficiently integrate Node.js or Python services under LAMP architecture?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:48 PM
How to efficiently integrate Node.js or Python services under LAMP architecture?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:48 PM
Many website developers face the problem of integrating Node.js or Python services under the LAMP architecture: the existing LAMP (Linux Apache MySQL PHP) architecture website needs...
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in IntelliJ?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:40 AM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in IntelliJ?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:40 AM
IntelliJ IDEA simplifies Spring Boot development, making it a favorite among Java developers. Its convention-over-configuration approach minimizes boilerplate code, allowing developers to focus on business logic. This tutorial demonstrates two metho




