oracle12c_Temporal Validity
创建Temporal Validity有两种方法一是自己指定列,一是让oracle自己指定 手工指定 CREATE TABLE Temporal_ValidityEMPNO NUMBER, SALARY NUMBER, DEPTID NUMBER, NAME VARCHAR2100, USER_TIME_START DATE, USER_TIME_END DATE, PERIOD FOR USER_TIME USER_TI
创建Temporal Validity有两种方法一是自己指定列,一是让oracle自己指定
- 手工指定
CREATE TABLE Temporal_Validity
(EMPNO NUMBER, SALARY NUMBER, DEPTID NUMBER,
NAME VARCHAR2(100),
USER_TIME_START DATE,
USER_TIME_END DATE,
PERIOD FOR USER_TIME
(USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END));
SQL> SELECT OWNER,TABLE_NAME,COLUMN_NAME,COLUMN_ID FROM DBA_TAB_COLS WHERE TABLE_NAME=UPPER('Temporal_Validity');
: TEMPORAL_VALIDITY
TABLE COLUMN
Owner Name COLUMN_ID
---------- ------------------------------ ---------
TRAVEL USER_TIME_END 6
TRAVEL USER_TIME_START 5
TRAVEL NAME 4
TRAVEL DEPTID 3
TRAVEL SALARY 2
TRAVEL EMPNO 1
TRAVEL USER_TIME
7 ROWS selected.
SQL> col NAME FOR a15
SQL> col DEFAULT$ FOR a10
SQL> col SPARE4 FOR a1
SQL> col SPARE5 FOR a1
SQL> col SPARE6 FOR a1
SQL> SELECT * FROM sys.col$ WHERE obj#=92087;
OBJ# COL# SEGCOL# SEGCOLLENGTH OFFSET NAME TYPE# LENGTH FIXEDSTORAGE PRECISION# SCALE NULL$ DEFLENGTH DEFAULT$ INTCOL# PROPERTY CHARSETID CHARSETFORM EVALEDITION# UNUSABLEBEFORE# UNUSABLEBEGINNING# SPARE1 SPARE2 SPARE3 S S S SPARE7 SPARE8
---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- --------------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- ------------ --------------- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- - - - ---------- ----------
92087 0 0 22 0 USER_TIME 2 22 0 0 0 9 430120635 1 65576 0 0 0 0 0 0
92087 1 1 22 0 EMPNO 2 22 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
92087 2 2 22 0 SALARY 2 22 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
92087 3 3 22 0 DEPTID 2 22 0 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
92087 4 4 100 0 NAME 1 100 0 0 5 0 873 1 0 0 0 100
92087 5 5 7 0 USER_TIME_START 12 7 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
92087 6 6 7 0 USER_TIME_END 12 7 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
7 ROWS selected.
SQL> col COLUMN_NAME FOR a20
SQL> col TABLE_NAME FOR a15
SQL> col CONSTRAINT_NAME FOR a20 USER_TIME_START ENABLED VALIDATED
SQL> col R_CONSTRAINT_NAME FOR a20
SQL> @cons
SHOW constraints ON TABLE %TEMPORAL_VALIDITY%...
OWNER TABLE_NAME CONSTRAINT_NAME CO R_CONSTRAINT_NAME COLUMN_NAME POSITION STATUS VALIDATED
------------------------------ --------------- -------------------- -- -------------------- ------------------------------ ---------- ---------------- --------------------------
TRAVEL TEMPORAL_VALIDI USER_TIMEA31EBB C USER_TIME ENABLED VALIDATED
TY
TRAVEL USER_TIMEA31EBB C USER_TIME_END ENABLED VALIDATED
TRAVEL USER_TIMEA31EBB C USER_TIME_START ENABLED VALIDATED
SQL>
SQL> @DESC TEMPORAL_VALIDITY
Name NULL? TYPE
------------------------------- -------- ----------------------------
1 EMPNO NUMBER
2 SALARY NUMBER
3 DEPTID NUMBER
4 NAME VARCHAR2(100)
5 USER_TIME_START DATE
6 USER_TIME_END DATE
手工指定是正常列,可以通过SELECT * 来查看SQL>
SQL> CREATE TABLE TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2
2 ( empno NUMBER, salary NUMBER, deptid NUMBER, name VARCHAR2(100),
3 PERIOD FOR user_time);
TABLE created.
SQL> @DESC TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2
Name NULL? TYPE
------------------------------- -------- ----------------------------
1 EMPNO NUMBER
2 SALARY NUMBER
3 DEPTID NUMBER
4 NAME VARCHAR2(100)
SQL>
SQL> col TABLE_NAME FOR a25
SQL> col OWNER FOR a10
SQL> SELECT OWNER,TABLE_NAME,COLUMN_NAME,COLUMN_ID FROM DBA_TAB_COLS WHERE TABLE_NAME=UPPER('Temporal_Validity2');
OWNER TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME COLUMN_ID
---------- ------------------------- -------------------- ----------
TRAVEL TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 NAME 4
TRAVEL DEPTID 3
TRAVEL SALARY 2
TRAVEL EMPNO 1
TRAVEL USER_TIME
TRAVEL USER_TIME_END
TRAVEL USER_TIME_START
7 ROWS selected.
SQL>
SQL> @o TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2
owner object_name object_type STATUS OID D_OID CREATED LAST_DDL_TIME
------------------------- ------------------------------ ------------------ --------- ---------- ---------- ----------------- -----------------
TRAVEL TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 TABLE VALID 92089 92089 20140526 22:41:37 20140526 22:41:37
SQL> SELECT * FROM sys.col$ WHERE obj#=92089;
OBJ# COL# SEGCOL# SEGCOLLENGTH OFFSET NAME TYPE# LENGTH FIXEDSTORAGE PRECISION# SCALE NULL$ DEFLENGTH DEFAULT$ INTCOL# PROPERTY CHARSETID CHARSETFORM EVALEDITION# UNUSABLEBEFORE# UNUSABLEBEGINNING# SPARE1 SPARE2 SPARE3 S S S SPARE7 SPARE8
---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- --------------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- ------------ --------------- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- - - - ---------- ----------
92089 0 1 13 0 USER_TIME_START 181 13 0 6 0 1 32 0 0 0 6 0 0
92089 0 2 13 0 USER_TIME_END 181 13 0 6 0 2 32 0 0 0 6 0 0
92089 0 0 22 0 USER_TIME 2 22 0 0 0 9 430191669 3 65576 0 0 0 0 0 0
92089 1 3 22 0 EMPNO 2 22 0 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
92089 2 4 22 0 SALARY 2 22 0 0 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
92089 3 5 22 0 DEPTID 2 22 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
92089 4 6 100 0 NAME 1 100 0 0 7 0 873 1 0 0 0 100
7 ROWS selected.
SQL> @cons
SHOW constraints ON TABLE %TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2%...
OWNER TABLE_NAME CONSTRAINT_NAME CO R_CONSTRAINT_NAME COLUMN_NAME POSITION STATUS VALIDATED
------------------------------ ------------------------- -------------------- -- -------------------- ------------------------------ ---------- ---------------- --------------------------
TRAVEL TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 USER_TIMEA43435 C USER_TIME_END ENABLED VALIDATED
TRAVEL USER_TIMEA43435 C USER_TIME_START ENABLED VALIDATED
SQL>系统自动创建了2个隐藏列USER_TIME_START,USER_TIME_END
插入数据
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (101,1900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2000-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2004-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (102,2900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2001-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2005-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (103,3900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2002-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2006-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (104,4900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2003-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2007-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (105,5900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2004-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2008-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (106,6900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2005-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2009-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (107,7900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2006-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2010-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (108,8900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2007-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2011-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (109,9900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2008-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2012-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (110,1900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2009-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2014-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (111,2900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2010-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2011-05-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (112,3900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2011-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2011-08-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (113,4900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2012-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2013-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (114,5900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2013-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2014-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (115,6900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2014-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2015-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));
1 ROW created.
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (116,7900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2002-04-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2002-06-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'));om
2
SQL> INSERT INTO TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 (empno , salary , deptid , name , USER_TIME_START, USER_TIME_END) VALUES (116,7900,90,'ADAM',to_date('2002-04-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ,to_date('2002-06-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd'))
2 ;
1 ROW created.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
SQL> SELECT * FROM TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2;
EMPNO SALARY DEPTID NAME
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------------
101 1900 90 ADAM
101 1900 90 ADAM
102 2900 90 ADAM
103 3900 90 ADAM
104 4900 90 ADAM
105 5900 90 ADAM
106 6900 90 ADAM
107 7900 90 ADAM
108 8900 90 ADAM
109 9900 90 ADAM
110 1900 90 ADAM
111 2900 90 ADAM
112 3900 90 ADAM
113 4900 90 ADAM
114 5900 90 ADAM
115 6900 90 ADAM
116 7900 90 ADAM
SQL> SELECT NAME,
2 to_char(USER_TIME_START, 'yyyy-mm-dd'), to_char(USER_TIME_END, 'yyyy-mm-dd')
3 FROM TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 ORDER BY 2;
NAME TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_ST TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_EN
--------------- -------------------- --------------------
ADAM 2000-01-01 2011-12-31
ADAM 2000-01-01 2004-01-01
ADAM 2001-01-01 2005-01-01
ADAM 2002-01-01 2006-01-01
ADAM 2002-04-01 2002-06-01
ADAM 2003-01-01 2007-01-01
ADAM 2004-01-01 2008-01-01
ADAM 2005-01-01 2009-01-01
ADAM 2006-01-01 2010-01-01
ADAM 2007-01-01 2011-01-01
ADAM 2008-01-01 2012-01-01
ADAM 2009-01-01 2014-01-01
ADAM 2010-01-01 2011-05-01
ADAM 2011-01-01 2011-08-01
ADAM 2012-01-01 2013-01-01
ADAM 2013-01-01 2014-01-01
ADAM 2014-01-01 2015-01-01- 示例1

SQL> SELECT NAME,
2 to_char(USER_TIME_START, 'yyyy-mm-dd'), to_char(USER_TIME_END, 'yyyy-mm-dd')
3 FROM TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 AS OF PERIOD FOR USER_TIME
4 to_date('2004-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd') ORDER BY 2;
NAME TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_ST TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_EN
--------------- -------------------- --------------------
ADAM 2000-01-01 2011-12-31
ADAM 2001-01-01 2005-01-01
ADAM 2002-01-01 2006-01-01
ADAM 2003-01-01 2007-01-01
ADAM 2004-01-01 2008-01-01The query displays all whose

SQL> SELECT NAME,
2 to_char(USER_TIME_START, 'yyyy-mm-dd'), to_char(USER_TIME_END, 'yyyy-mm-dd')
3 FROM TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 versions PERIOD FOR USER_TIME
4 BETWEEN to_date('2004-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
5 AND to_date('2008-01-01', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
6 ORDER BY 2;
NAME TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_ST TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_EN
--------------- -------------------- --------------------
ADAM 2000-01-01 2011-12-31
ADAM 2001-01-01 2005-01-01
ADAM 2002-01-01 2006-01-01
ADAM 2003-01-01 2007-01-01
ADAM 2004-01-01 2008-01-01
ADAM 2005-01-01 2009-01-01
ADAM 2006-01-01 2010-01-01
ADAM 2007-01-01 2011-01-01
ADAM 2008-01-01 2012-01-01The query displays all whose USER_TIME_START is less than or equal to ‘2004-01-01′ and USER_TIME_END greater than or equal to ‘2008-01-01′‘.

SQL> EXEC DBMS_FLASHBACK_ARCHIVE.ENABLE_AT_VALID_TIME('CURRENT')
PL/SQL PROCEDURE successfully completed.
SQL> SELECT NAME,
2 to_char(USER_TIME_START, 'yyyy-mm-dd'), to_char(USER_TIME_END, 'yyyy-mm-dd')
3 FROM TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 ORDER BY 2;
NAME TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_ST TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_EN
--------------- -------------------- --------------------
ADAM 2014-01-01 2015-01-01SQL> EXEC DBMS_FLASHBACK_ARCHIVE.ENABLE_AT_VALID_TIME('ALL')
PL/SQL PROCEDURE successfully completed.
SQL> SELECT NAME,
2 to_char(USER_TIME_START, 'yyyy-mm-dd'), to_char(USER_TIME_END, 'yyyy-mm-dd')
3 FROM TEMPORAL_VALIDITY2 ORDER BY 2;
NAME TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_ST TO_CHAR(USER_TIME_EN
--------------- -------------------- --------------------
ADAM 2000-01-01 2011-12-31
ADAM 2000-01-01 2004-01-01
ADAM 2001-01-01 2005-01-01
ADAM 2002-01-01 2006-01-01
ADAM 2002-04-01 2002-06-01
ADAM 2003-01-01 2007-01-01
ADAM 2004-01-01 2008-01-01
ADAM 2005-01-01 2009-01-01
ADAM 2006-01-01 2010-01-01
ADAM 2007-01-01 2011-01-01
ADAM 2008-01-01 2012-01-01
ADAM 2009-01-01 2014-01-01
ADAM 2010-01-01 2011-05-01
ADAM 2011-01-01 2011-08-01
ADAM 2012-01-01 2013-01-01
ADAM 2013-01-01 2014-01-01
ADAM 2014-01-01 2015-01-01
17 ROWS selected.原文地址:oracle12c_Temporal Validity, 感谢原作者分享。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to create a cumulative curve graph in Python?
Aug 23, 2023 pm 08:33 PM
How to create a cumulative curve graph in Python?
Aug 23, 2023 pm 08:33 PM
The ogive graph graphically represents the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a set of data, sometimes called a cumulative frequency curve. It is used to examine data distribution and discover patterns and trends. Matplotlib, Pandas, and Numpy are some of the libraries and tools provided by Python for creating otive graphics. In this tutorial, we will look at how to use Matplotlib to generate ogive graphics in Python. To create a cumulative curve chart, we need to import the required libraries. In this example we will use Matplotlib, Pandas and Numpy. Matplotlib is a popular data visualization library for creating in Python
 How to create a constant in Python?
Aug 29, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
How to create a constant in Python?
Aug 29, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
Constants and variables are used to store data values in programming. A variable usually refers to a value that can change over time. A constant is a type of variable whose value cannot be changed during program execution. There are only six built-in constants available in Python, they are False, True, None, NotImplemented, Ellipsis(...) and __debug__. Apart from these constants, Python does not have any built-in data types to store constant values. Example An example of a constant is demonstrated below - False=100 outputs SyntaxError:cannotassigntoFalseFalse is a built-in constant in Python that is used to store boolean values
 How to personalize your iPhone on the latest iOS 17
Sep 21, 2023 am 08:17 AM
How to personalize your iPhone on the latest iOS 17
Sep 21, 2023 am 08:17 AM
How to Personalize Calls on iPhone Apple’s iOS 17 introduces a new feature called Contact Posters that allows you to personalize the look of your call screen on your iPhone. This feature allows you to design a poster using selected photos, colors, fonts, and Memoji as contact cards. So when you make a call, your custom image will appear on the recipient's iPhone exactly as you envisioned. You can choose to share your unique contact poster with all your saved contacts, or choose who can see it. Likewise, during a call exchange, you will also see other people's contact posters. Additionally, Apple lets you set specific contact photos for individual contacts, making calls from those contacts
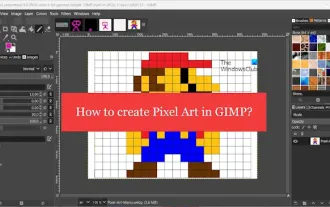 How to create pixel art in GIMP
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
How to create pixel art in GIMP
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
This article will interest you if you are interested in using GIMP for pixel art creation on Windows. GIMP is a well-known graphics editing software that is not only free and open source, but also helps users create beautiful images and designs easily. In addition to being suitable for beginners and professional designers alike, GIMP can also be used to create pixel art, a form of digital art that utilizes pixels as the only building blocks for drawing and creating. How to Create Pixel Art in GIMP Here are the main steps to create pixel pictures using GIMP on a Windows PC: Download and install GIMP, then launch the application. Create a new image. Resize width and height. Select the pencil tool. Set the brush type to pixels. set up
 How to create a family with Gree+
Mar 01, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
How to create a family with Gree+
Mar 01, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
Many friends expressed that they want to know how to create a family in Gree+ software. Here is the operation method for you. Friends who want to know more, come and take a look with me. First, open the Gree+ software on your mobile phone and log in. Then, in the options bar at the bottom of the page, click the "My" option on the far right to enter the personal account page. 2. After coming to my page, there is a "Create Family" option under "Family". After finding it, click on it to enter. 3. Next jump to the page to create a family, enter the family name to be set in the input box according to the prompts, and click the "Save" button in the upper right corner after entering it. 4. Finally, a "save successfully" prompt will pop up at the bottom of the page, indicating that the family has been successfully created.
 How to create user interface via Python?
Aug 26, 2023 am 09:17 AM
How to create user interface via Python?
Aug 26, 2023 am 09:17 AM
In this article, we will learn how to create user interface using python. What is a graphical user interface? The term "graphical user interface" (or "GUI") refers to a set of visual element items that can be interacted with in computer software to display information and interact. In response to human input, objects may change appearance characteristics such as color, size, and visibility. Graphical components such as icons, cursors, and buttons can be enhanced with audio or visual effects (such as transparency) to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs). If you want more people to use your platform, you need to make sure it has a good user interface. This is because the combination of these factors can greatly affect the quality of service provided by your app or website. Python is widely used by developers because it provides
 How to create a folder on Realme Phone?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
How to create a folder on Realme Phone?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
Title: Realme Phone Beginner’s Guide: How to Create Folders on Realme Phone? In today's society, mobile phones have become an indispensable tool in people's lives. As a popular smartphone brand, Realme Phone is loved by users for its simple and practical operating system. In the process of using Realme phones, many people may encounter situations where they need to organize files and applications on their phones, and creating folders is an effective way. This article will introduce how to create folders on Realme phones to help users better manage their phone content. No.
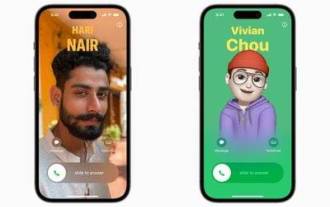 How to Create a Contact Poster for Your iPhone
Mar 02, 2024 am 11:30 AM
How to Create a Contact Poster for Your iPhone
Mar 02, 2024 am 11:30 AM
In iOS17, Apple has added a contact poster feature to its commonly used Phone and Contacts apps. This feature allows users to set personalized posters for each contact, making the address book more visual and personal. Contact posters can help users identify and locate specific contacts more quickly, improving user experience. Through this feature, users can add specific pictures or logos to each contact according to their preferences and needs, making the address book interface more vivid. Apple in iOS17 provides iPhone users with a novel way to express themselves, and added a personalizable contact poster. The Contact Poster feature allows you to display unique, personalized content when calling other iPhone users. you






