有关DBLINK操作的语句执行机制及优化方式
?分布式查询语句对于远程对象的查询在远程库执行,在远程可以执行的语句会通过优化器的查询转换,执行的是转换后的语句,然后结果集返回到本地,再与本地表运算。当然, 本地还是远程是相对的,我们可以通过driving_hint改变主查询计划的执行位置,但是对DML
?分布式查询语句对于远程对象的查询在远程库执行,在远程可以执行的语句会通过优化器的查询转换,执行的是转换后的语句,然后结果集返回到本地,再与本地表运算。当然,
本地还是远程是相对的,我们可以通过driving_hint改变主查询计划的执行位置,但是对DML,driving_site是失效的。另外对远程表也可以使用其他hint。
???分布式查询可能一条SQL语句中有不同远程库的表,优化分布式查询要达到3点效果:
1.访问同一个远程库的次数要尽量少,也就是同一远程库的对象应该尽量转为一条SQL运算,一次运算,运算后将结果返回给本地库
2.从远程库上返回到本地库的结果要尽量少,只访问远程对象需要的字段
3.远程库上执行的语句的计划以及远程库返回的结果与本地可以联合查询的计划应该高效
?优化分布式查询需要从以上3个方面着手。
下面的local_tab 7万多条,remote_big_tab百万条,remote_small_tab 7万多条。
?1.使用Collocated内联视图
? 也就是SQL要对引用不同远程库的表,要组织好,将相同库的表放一起组织成内联视图,这样ORACLE就很容易知道这个内联视图里的表是在同一远程库作完查询
? 后再返回给本地库,这样减少了本地库与远程库的交互次数和传输结果集的数量和次数。比如上面的查询
|
SELECT ?* FROM local_tab a ?WHERE EXISTS ?(SELECT ?1 FROM remote_big_tab@remote b,remote_small_tab@remote c ?WHERE b.object_id=c.object_id AND a.object_type=b.object_type); 执行计划 |
? 可以看出,在远程库remote上执行的语句是两个远程表关联后,并经过查询转换(全转为大写,自己取了别名A1,A2,ORACLE内部自己改造为止查询DISTINCT ??remote_big_tab.object_type),之后远程查询结果返回给本地,可以去远程库里查询实际的计划,走的是HASH JOIN。
2.了解CBO优化器对分布式查询的处理
? ?CBO对分布式查询的处理,也是尽量转为Collocated内联视图,CBO会做如下动作:
? ?1)所有可mergeable的视图会merge
? ?2 ) CBO会测试Collocated内联视图的query BLOCK
? ?3 ) 如果可以使用,就使用合并
? ?当然,CBO对分布式查询的处理,可能是不高效的,这时候得用其他的方法,比如使用HINT,改造SQL,改造分布式查询的方法(远程库用视图)等。
???特别当分布式查询包含下列情况,CBO可能是不高效的:
? ?1)有分组运算
? ?2)有子查询
? ?3)SQL很复杂
? ?
? ?比如下面语句含有子查询:
|
SELECT ?* FROM local_tab a,remote_big_tab@remote b,remote_small_tab@remote c ?WHERE b.object_id=c.object_id AND a.object_type=b.object_type ?AND a.object_id IN (SELECT object_id from sub); 执行计划 ———————————————————- Plan hash value: 252158753 ———————————————————————————————————- | Id ?| Operation ? ? ? ? ? ? | Name ? ? ? ? ? ? | Rows ?| Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time ? ? | Inst ? |IN-OUT| ———————————————————————————————————- | ? 0 | SELECT STATEMENT ? ? ?| ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ? ?79M| ? ?20G| ?3843 ?(46)| 00:00:47 | ? ? ? ?| ? | |* ?1 | ?HASH JOIN ? ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ? ?79M| ? ?20G| ?3843 ?(46)| 00:00:47 | ? ? ? ?| ? | | ? 2 | ??REMOTE ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| REMOTE_SMALL_TAB?| ?5320 | ? 431K| ? ? 8 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | REMOTE | R->S | |* ?3 | ? HASH JOIN ? ? ? ? ? | ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ? 172M| ? ?31G| ?2978 ?(31)| 00:00:36 | ? ? ? ?| ? | |* ?4 | ? ?HASH JOIN ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ?5260 | ? 565K| ? 303 ? (2)| 00:00:04 | ? ? ? ?| ? | | ? 5 | ? ? SORT UNIQUE ? ? ? | ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ?5320 | 69160 | ? ? 5 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | ? ? ? ?| ? | | ? 6 | ? ? ?TABLE ACCESS FULL| SUB ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ?5320 | 69160 | ? ? 5 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | ? ? ? ?| ? | | ? 7 | ? ? TABLE ACCESS FULL | LOCAL_TAB ? ? ? ?| 73985 | ?7008K| ? 296 ? (1)| 00:00:04 | ? ? ? ?| ? | | ? 8 | ???REMOTE ? ? ? ? ? ? | REMOTE_BIG_TAB?? | ?1479K| ? 119M| ?1819 ? (2)| 00:00:22 | REMOTE | R->S | ———————————————————————————————————- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): ————————————————— ? ?1 – access(“B”.”OBJECT_ID”=”C”.”OBJECT_ID”) ? ?3 – access(“A”.”OBJECT_TYPE”=”B”.”OBJECT_TYPE”) ? ?4 – access(“A”.”OBJECT_ID”=”OBJECT_ID”) Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): ???2 – SELECT “OBJECT_NAME”,”SUBOBJECT_NAME”,”OBJECT_ID”,”DATA_OBJECT_ID”,”OBJECT_TYPE”,”CREATED”, ? ?8 – SELECT “OWNER”,”OBJECT_NAME”,”SUBOBJECT_NAME”,”OBJECT_ID”,”DATA_OBJECT_ID”,”OBJECT_TYPE”,”C ? |
?通过计划可以看到REMOTE有两个,两张远程表无法做Collocated inline VIEW运算。
?
? 再比如下面的语句,有分组运算:
|
SELECT ?* FROM local_tab a,remote_big_tab@remote b,(SELECT max(object_id) object_id FROM remote_small_tab@remote c GROUP BY c.object_type) c WHERE b.object_id=c.object_id AND a.object_type=b.object_type; 执行计划 Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): |
?? 通过计划看出,将远程表进行分组运算后,传输给本地库,然后大表传输给本地库,之后做HASH JOIN,这是不高效的。运行时间:已用时间: ?00: 02: 12.22
?可以改造分布式查询,手动组织Collocated inline VIEW,在远程库建立view:
|
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW v_remote AS SELECT ?b.* FROM remote_big_tab b,(SELECT max(object_id) object_id FROM remote_small_tab c GROUP BY c.object_type) c WHERE b.object_id=c.object_id;? 查询改为: 执行计划 |
?通过计划可以看出,现在是远程表做整体操作之后才返回到本地了。
?3.使用HINT,特别是driving_site HINT
? 对远程表可以使用hint,比如parallel,use_nl,use_hash,FULL等。
? driving_site hint能够指定执行计划在远程还是本地做,比如下面使用driving_site(b),那么原来的远程表就相当于本地表,本地表要传输给remote库,主计划在remote库上执行
??
|
SELECT/*+driving_site(b)*/ ?* FROM local_tab a,remote_big_tab@remote b,(SELECT max(object_id) object_id FROM remote_small_tab@remote c GROUP BY c.object_type) c WHERE b.object_id=c.object_id AND a.object_type=b.object_type; |
? ?当然,如果是driving_site(a)那么就是本地驱动的,默认的是本地驱动的。
? ?
? ?使用driving_site,特别是本地小结果集,远程大结果集的时候,总体结果集较小,希望计划在远程驱动,这样远程执行完毕,将结果集传输到本地,这样避免大结果集的传输。
? ?
? ?例1:
?? ? ? ??小表9998条,大表3169376条记录,远程大表sub_id,acc_id上联合索引
|
SQL> ?SELECT ?COUNT(*) ?FROM small_tab_local a, big_tab_remote@remote b ? 2 ? WHERE a.sub_id=b.sub_id AND a.acc_id=b.acc_id; ? ??? ? ?859 已用时间: ?00: 00: 50.76 执行计划 Predicate Information (identified by operation id): Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): ? ?3 – SELECT “SUB_ID”,”ACC_ID” FROM “BIG_TAB_REMOTE” “B” ORDER BY “SUB_ID”,”ACC_ID” |
? ? 查询876条数据,耗时50s,显然将大结果集拉到本地做运算是不好的,因为本地表很小,远程大表有索引,如果能在远端执行,并走nl,那么显然效率非常好。使用driving_site hint改造查询如下:
??
|
SELECT/*+driving_site(b) ?ordered use_nl(b)*/ ?COUNT(*) FROM small_tab_local a, big_tab_remote@remote b ?WHERE a.sub_id=b.sub_id AND a.acc_id=b.acc_id; 计划如下: Predicate Information (identified by operation id): Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): |
? ? ?现在主计划是在远端remote上执行的,本地表small_tab_local变成了远程表,会讲small_tab_local结果集送到远端,只查询了sub_id,acc_id,然后作为驱动表,与远端表做nl运算,
计划里可以看到远端表走索引了,最后将远端结果返回到本地。(事实上这里的远端库与本地库换了)
? driving_site hint注意点:
??driving_site对dml无效,dml以目标表所在库驱动SQL计划。比如下面的driving_site失效,后面的hint还是有效的。
? ?
|
? CREATE TABLE test_cnt (cnt NUMBER); ? INSERT INTO test_cnt ? SELECT/*+driving_site(b) ordered use_nl(b)*/ ?COUNT(*) FROM small_tab_local a, big_tab_remote@remote b ? WHERE a.sub_id=b.sub_id AND a.acc_id=b.acc_id; 已用时间:??00: 01: 31.48 执行计划 Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): ? ?5 – SELECT?/*+ OPAQUE_TRANSFORM USE_NL (“B”) */?”SUB_ID”,”ACC_ID” FROM “BIG_TAB_REMOTE” “B” |
? 语句执行1分31s,driving_site hint失效,但是后面的NL没有失效,可以从计划中看出类似绑定变量的东西,这实际对于每个small_tab_local的结果集的行,将sub_id,acc_id传给远端表big_tab_remote,也就是:1,:2,这样本地的表筛选出多少行,远程语句?SELECT?/*+ OPAQUE_TRANSFORM USE_NL (“B”) */?”SUB_ID”,”ACC_ID” FROM “BIG_TAB_REMOTE” “B”
?WHERE?:1=”SUB_ID” AND :2=”ACC_ID” 就执行多少次。
?这里本地表9998条,无过滤条件,因此远程表语句运行了9998次,虽然远程查询也是走索引的,但是SQL被执行了9998次,是非常影响性能的。可以去远程库查询下:
?
|
SQL> SELECT sql_text,executions FROM v$sql WHERE sql_text LIKE ‘%SELECT /*+ USE_NL (“B”) */ “SUB_ID”,”ACC_ID” FROM “BIG_TAB_REMOTE”%’ ? 2 ?/ ? SQL_TEXT ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? EXECUTIONS ——————————————————————————– ————————————————————– SELECT /*+ USE_NL (“B”) */ “SUB_ID”,”ACC_ID” FROM “BIG_TAB_REMOTE” “B” WHERE :1= ? ??? 9998 |
? ?这里driving_site失效,但是后面的nl还有效,远程表执行的次数是small_tab_local表的数量(因为这里没有谓词过滤small_tab_local),可以使用其他hint,比如。
? INSERT INTO test_cnt
? SELECT/*+ordered use_hash(b)*/ ? COUNT(*) FROM small_tab_local a, big_tab_remote@remote b
? WHERE a.sub_id=b.sub_id AND a.acc_id=b.acc_id;
??
??当然效率不一定很好,因为这里由远程驱动效率最好,为了不想driving_site失效,可以使用PL/SQL(这里是只查询数量,如果查询结果集可以使用PL/SQL批处理插入)。
|
BEGIN ? ? FOR i IN (SELECT/*+driving_site(b) ordered use_nl(b)*/ ?COUNT(*) cnt FROM small_tab_local a, big_tab_remote@remote b ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?WHERE a.sub_id=b.sub_id AND a.acc_id=b.acc_id) ? ?LOOP ? ? ?INSERT INTO test_cnt VALUES(i.cnt); ? END LOOP; ? COMMIT; END; 已用时间:??00: 00: 00.89 |
? ? ?
? 例2:
? ? ? 查询语句:
|
SELECT * FROM?v_remote?WHERE object_id IN ( ??SELECT c.object_id FROM c WHERE c.object_name ? ? ? ? ?? IN (SELECT d.object_name FROM d WHERE d.object_id=11) ); |
?比较慢,返回32行,需要10来秒。其中v_remote是个视图,此视图连接到远程表,其中远程的两张表的object_id都有索引:
|
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW v_remote AS SELECT object_name,object_id,object_type FROM a@remote ? UNION ALL SELECT ?object_name,object_id,object_type FROM b@remote; 两表记录数如下: |
? c和d是本地表,d.object_id以及c.object_name有索引。单独查询很快,
|
–单独本地语句消耗时间00: 00: 00.01 SQL> SELECT c.object_id FROM c WHERE c.object_name IN (SELECT d.object_name FROM d WHERE d.object_id=11); 已用时间: ?00: 00: 00.01 执行计划 ———————————————————- Plan hash value: 2528799293 —————————————————————————————- | Id ?| Operation ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| Name ?| Rows ?| Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time ? ? | —————————————————————————————- | ? 0 | SELECT STATEMENT ? ? ? ? ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? 2 | ? ?94 | ? ? 6 ?(17)| 00:00:01 | | ? 1 | ?NESTED LOOPS ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? ? ?| | ? 2 | ? NESTED LOOPS ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? 2 | ? ?94 | ? ? 6 ?(17)| 00:00:01 | | ? 3 | ? ?SORT UNIQUE ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? 1 | ? ?17 | ? ? 2 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | | ? 4 | ? ? TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| D ? ? | ? ? 1 | ? ?17 | ? ? 2 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | |* ?5 | ? ? ?INDEX RANGE SCAN ? ? ? ? ?| IDX_D | ? ? 1 | ? ? ? | ? ? 1 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | |* ?6 | ? ?INDEX RANGE SCAN ? ? ? ? ? ?| IDX_C | ? ? 2 | ? ? ? | ? ? 2 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | | ? 7 | ? TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID ?| C ? ? | ? ? 2 | ? ?60 | ? ? 3 ? (0)| 00:00:01 | —————————————————————————————- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): ————————————————— ? ?5 – access(“D”.”OBJECT_ID”=11) ? ?6 – access(“C”.”OBJECT_NAME”=”D”.”OBJECT_NAME”) –单独远程语句消耗时间?00: 00: 00.06 Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): Predicate Information (identified by operation id): Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): ? |
? ? ?单独查询很快,为什么联合查询就慢了呢?原因在于:
?
| 单独执行远程查询 | 本地与远程混合查询 |
| 直接执行视图,并将OBJECT_ID=11谓词推入到视图中,走索引,最后只将32行结果返回给本地 | 从计划中可以看到,本地查询与远程查询做HASH JOIN,但是访问远程的SQL是没有谓词的,这样必然全表从远程拉到本地,因为行数较多,所以慢 |
?
? ??因此,优化此混合查询的语句可以由多种办法(比如本地查询的数量较少,可以采用上面的方法,本地与远程查询拆分为2条语句),另外就是可以使用driving_site hint,将主计划推到远程库去执行,本地的结果集少,推到远程,远程视图走索引,效率高。如下:
|
–耗时已用时间: ?00: 00: 00.08 SQL> SELECT/*+driving_site(v_remote.a)*/ * FROM v_remote WHERE object_id IN ( ? 2 ?SELECT c.object_id FROM c WHERE c.object_name IN (SELECT d.object_name FROM d WHERE d.object_id=11 ? 3 ?); 已选择32行。 已用时间: ?00: 00: 00.08 ————————————————————————————— | Id ?| Operation ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| Name ? ? | Rows ?| Bytes | Cost ?| Inst ? |IN-OUT| ————————————————————————————— | ? 0 | SELECT STATEMENT REMOTE ? ?| ? ? ? ? ?| ? ?15 | ?1425 | ? 109 | ? ? ? ?| ? ? ?| | ? 1 | NESTED LOOPS ? ? ? ? ? ? ? | ? ? ? ? ?| ? ?15 | ?1425 | ? 109 | ? ? ? ?| ? ? ?| | ? 2 | SORT UNIQUE ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ? ?| ? ? ?| | ? 3 | VIEW ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? | VW_NSO_1 | ? ? 3 | ? ?39 | ? ? 8 | MZT~ | ? ? ?| | ? 4 |?REMOTE ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? | ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ?! | R->S?| | ? 5 | VIEW ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? | ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? 5 | ? 410 | ? ?33 | ? ? ? ?| ? ? ?| | ? 6 |?UNION-ALL PARTITION ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? ? ?| ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ? | ? ? ? ?| ? ? ?| | ? 7 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| A ? ? ? ?| ? ?32 | ? 960 | ? ?35 |MZT~ | ? ? ?| |* ?8 | INDEX RANGE SCAN ? ? ? ? ? | IDX_A ? ?| ? ?32 | ? ? ? | ? ? 3 |MZT~ | ? ? ?| | ? 9 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| B ? ? ? ?| ? ? 1 | ? ?32 | ? ? 2 | MZT~ | ? ? ?| |* 10 | INDEX RANGE SCAN ? ? ? ? ? | IDX_B ? ?| ? ? 1 | ? ? ? | ? ? 1 | MZT~ | ? ? ?| ————————————————————————————— Predicate Information (identified by operation id): Remote SQL Information (identified by operation id): |

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 Linux Deploy operation steps and precautions
Mar 14, 2024 pm 03:03 PM
Linux Deploy operation steps and precautions
Mar 14, 2024 pm 03:03 PM
LinuxDeploy operating steps and precautions LinuxDeploy is a powerful tool that can help users quickly deploy various Linux distributions on Android devices, allowing users to experience a complete Linux system on their mobile devices. This article will introduce the operating steps and precautions of LinuxDeploy in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better use this tool. Operation steps: Install LinuxDeploy: First, install
 Huawei Mate60 Pro screenshot operation steps sharing
Mar 23, 2024 am 11:15 AM
Huawei Mate60 Pro screenshot operation steps sharing
Mar 23, 2024 am 11:15 AM
With the popularity of smartphones, the screenshot function has become one of the essential skills for daily use of mobile phones. As one of Huawei's flagship mobile phones, Huawei Mate60Pro's screenshot function has naturally attracted much attention from users. Today, we will share the screenshot operation steps of Huawei Mate60Pro mobile phone, so that everyone can take screenshots more conveniently. First of all, Huawei Mate60Pro mobile phone provides a variety of screenshot methods, and you can choose the method that suits you according to your personal habits. The following is a detailed introduction to several commonly used interceptions:
 C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
Time complexity measures the execution time of an algorithm relative to the size of the input. Tips for reducing the time complexity of C++ programs include: choosing appropriate containers (such as vector, list) to optimize data storage and management. Utilize efficient algorithms such as quick sort to reduce computation time. Eliminate multiple operations to reduce double counting. Use conditional branches to avoid unnecessary calculations. Optimize linear search by using faster algorithms such as binary search.
 PHP string manipulation: a practical way to effectively remove spaces
Mar 24, 2024 am 11:45 AM
PHP string manipulation: a practical way to effectively remove spaces
Mar 24, 2024 am 11:45 AM
PHP String Operation: A Practical Method to Effectively Remove Spaces In PHP development, you often encounter situations where you need to remove spaces from a string. Removing spaces can make the string cleaner and facilitate subsequent data processing and display. This article will introduce several effective and practical methods for removing spaces, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the PHP built-in function trim(). The PHP built-in function trim() can remove spaces at both ends of the string (including spaces, tabs, newlines, etc.). It is very convenient and easy to use.
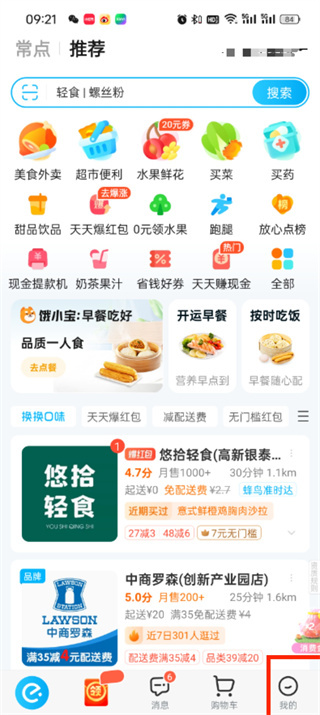 How to bind WeChat on Ele.me
Apr 01, 2024 pm 03:46 PM
How to bind WeChat on Ele.me
Apr 01, 2024 pm 03:46 PM
Ele.me is a software that brings together a variety of different delicacies. You can choose and place an order online. The merchant will make it immediately after receiving the order. Users can bind WeChat through the software. If you want to know the specific operation method , remember to check out the PHP Chinese website. Instructions on how to bind WeChat to Ele.me: 1. First open the Ele.me software. After entering the homepage, we click [My] in the lower right corner; 2. Then in the My page, we need to click [Account] in the upper left corner; 3. Then come to the personal information page where we can bind mobile phones, WeChat, Alipay, and Taobao. Here we click [WeChat]; 4. After the final click, select the WeChat account that needs to be bound in the WeChat authorization page and click Just [Allow];
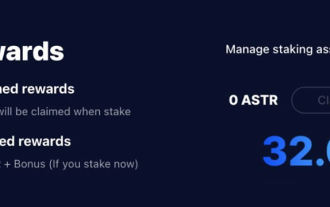 Astar staking principle, income dismantling, airdrop projects and strategies & operation nanny-level strategy
Jun 25, 2024 pm 07:09 PM
Astar staking principle, income dismantling, airdrop projects and strategies & operation nanny-level strategy
Jun 25, 2024 pm 07:09 PM
Table of Contents Astar Dapp Staking Principle Staking Revenue Dismantling of Potential Airdrop Projects: AlgemNeurolancheHealthreeAstar Degens DAOVeryLongSwap Staking Strategy & Operation "AstarDapp Staking" has been upgraded to the V3 version at the beginning of this year, and many adjustments have been made to the staking revenue rules. At present, the first staking cycle has ended, and the "voting" sub-cycle of the second staking cycle has just begun. To obtain the "extra reward" benefits, you need to grasp this critical stage (expected to last until June 26, with less than 5 days remaining). I will break down the Astar staking income in detail,
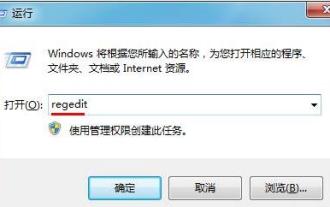 How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
1. Press the key combination (win key + R) on the desktop to open the run window, then enter [regedit] and press Enter to confirm. 2. After opening the Registry Editor, we click to expand [HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorer], and then see if there is a Serialize item in the directory. If not, we can right-click Explorer, create a new item, and name it Serialize. 3. Then click Serialize, then right-click the blank space in the right pane, create a new DWORD (32) bit value, and name it Star
 Forgot your Win8 computer startup password? This operation will restore it immediately!
Mar 27, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Forgot your Win8 computer startup password? This operation will restore it immediately!
Mar 27, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Forgetting the Win8 computer startup password is a problem that many people encounter when using computers on a daily basis. When we forget the login password, we will be unable to enter the system normally, causing inconvenience to our daily use. If you happen to encounter this problem, don’t worry. Below I will introduce some simple operations to help you quickly restore the power-on password of your Win8 computer. Method 1: Use Microsoft account password. If you use a Microsoft account to log in to your Win8 computer, you can try using the password of that account.




