Oracle数据库中段管理方式的详细介绍
用Oracle数据库10g通过回收浪费的空间、联机重组表格和评估增长的趋势,有效地在段中进行存储管理。近来,有人要求我评估一个与
用Oracle数据库10g通过回收浪费的空间、联机重组表格和评估增长的趋势,有效地在段中进行存储管理。近来,有人要求我评估一个与 Oracle 数据库竞争的RDBMS。在供应商的演示过程中,观众认为“最棒”的特性是,对联机重组的支持——该产品可以联机重新部署数据块,以使段的等价物更简洁,并且不会影响当前的用户。
那时,Oracle还没有在Oracle 9i数据库中提供这种功能。但是现在,有了Oracle数据库10g,就可以轻松地联机回收浪费的空间和压缩对象——正好适合于起步者。
不过,在检验该特性之前,让我们看一看处理这项任务的“传统的”方法。
当前惯例
考虑让我们看一个段,如一张表,其中填满了块,如图1 所示。在正常操作过程中,,删除了一些行,如图2 所示。现有就有了许多浪费的空间:(i)在表的上一个末端和现有的块之间,以及(ii)在块内部,其中还有一些没有删除的行。
图 1:分配给该表的块。用灰色正方形表示行
Oracle不会释放空间以供其他对象使用,有一条简单的理由:由于空间是为新插入的行保留的,并且要适应现有行的增长。被占用的最高空间称为最高使用标记(HWM),如图2所示:

图 2:行后面的块已经删除了;HWM 仍保持不变
但是,这种方法有两个主要的问题:
当用户发出一个全表扫描时,Oracle始终必须从段一直扫描到HWM,即使它什么也没有发现。该任务延长了全表扫描的时间。
当用直接路径插入行时 — 例如,通过直接加载插入(用APPEND提示插入)或通过SQL*Loader直接路径 — 数据块直接置于HWM之上。它下面的空间就浪费掉了。
在Oracle9i及其以前的版本中,可以通过删除表,然后重建表并重新加载数据来回收空间;或通过使用ALTER TABLE MOVE命令把表移动到一个不同的表空间中来回收空间。这两种处理方式都必须脱机进行。另外,可以使用联机表重组特性,但是这需要至少双倍的现有表空间。
在10g中,该任务已经变得微不足道了;假如您的表空间中支持自动段空间管理(ASSM),您现在可以缩小段、表和索引,以回收空闲块并把它们提供给数据库以作他用,让我们看看其中的缘由。
10g中的段管理方式
设想有一个表BOOKINGS,它保存有经由Web站点的联机登记。当一个登记确认后,就会把它存储在一个存档表BOOKINGS_HIST中,并从BOOKINGS表中删除该行。登记和确认之间的时间间隔依据客户有很大的不同,由于无法从删除的行获得足够的空间,因此许多行就插入到了表的 HWM 之上。
现在您需要回收浪费的空间。首先,准确地查明在可回收的段中浪费了多少空间。由于它是在支持ASSM的表空间中,您将不得不使用DBMS_SPACE包的SPACE_USAGE过程,如下所示:
declare
l_fs1_bytes number;
l_fs2_bytes number;
l_fs3_bytes number;
l_fs4_bytes number;
l_fs1_blocks number;
l_fs2_blocks number;
l_fs3_blocks number;
l_fs4_blocks number;
l_full_bytes number;
l_full_blocks number;
l_unformatted_bytes number;
l_unformatted_blocks number;
begin
dbms_space.space_usage(
segment_owner => user,
segment_name => 'BOOKINGS',
segment_type => 'TABLE',
fs1_bytes => l_fs1_bytes,
fs1_blocks => l_fs1_blocks,
fs2_bytes => l_fs2_bytes,
fs2_blocks => l_fs2_blocks,
fs3_bytes => l_fs3_bytes,
fs3_blocks => l_fs3_blocks,
fs4_bytes => l_fs4_bytes,
fs4_blocks => l_fs4_blocks,
full_bytes => l_full_bytes,
full_blocks=> l_full_blocks,
unformatted_blocks => l_unformatted_blocks,
unformatted_bytes => l_unformatted_bytes
);
dbms_output.put_line(' FS1 Blocks = '
||l_fs1_blocks||' Bytes = '||l_fs1_bytes);
dbms_output.put_line(' FS2 Blocks = '
||l_fs2_blocks||' Bytes = '||l_fs1_bytes);
dbms_output.put_line(' FS3 Blocks = '
||l_fs3_blocks||' Bytes = '||l_fs1_bytes);
dbms_output.put_line(' FS4 Blocks = '
||l_fs4_blocks||' Bytes = '||l_fs1_bytes);
dbms_output.put_line('Full Blocks = '
||l_full_blocks||' Bytes = ||l_full_bytes);
end;
/
输出结果如下:
FS1 Blocks = 0 Bytes = 0
FS2 Blocks = 0 Bytes = 0
FS3 Blocks = 0 Bytes = 0
FS4 Blocks = 4148 Bytes = 0
Full Blocks = 2 Bytes = 16384
这个输出结果显示有4,148个块,具有75-100%的空闲空间(FS4);没有其他空闲块可用。这里仅有两个得到完全使用的块。4,148个块都可以回收。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
The retention period of Oracle database logs depends on the log type and configuration, including: Redo logs: determined by the maximum size configured with the "LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST" parameter. Archived redo logs: Determined by the maximum size configured by the "DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST_SIZE" parameter. Online redo logs: not archived, lost when the database is restarted, and the retention period is consistent with the instance running time. Audit log: Configured by the "AUDIT_TRAIL" parameter, retained for 30 days by default.
 The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The Oracle database startup sequence is: 1. Check the preconditions; 2. Start the listener; 3. Start the database instance; 4. Wait for the database to open; 5. Connect to the database; 6. Verify the database status; 7. Enable the service (if necessary ); 8. Test the connection.
 How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
The amount of memory required by Oracle depends on database size, activity level, and required performance level: for storing data buffers, index buffers, executing SQL statements, and managing the data dictionary cache. The exact amount is affected by database size, activity level, and required performance level. Best practices include setting the appropriate SGA size, sizing SGA components, using AMM, and monitoring memory usage.
 How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
To find the number of occurrences of a character in Oracle, perform the following steps: Get the total length of a string; Get the length of the substring in which a character occurs; Count the number of occurrences of a character by subtracting the substring length from the total length.
 Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements: Processor: multi-core, with a main frequency of at least 2.5 GHz. For large databases, 32 cores or more are recommended. Memory: At least 8GB for small databases, 16-64GB for medium sizes, up to 512GB or more for large databases or heavy workloads. Storage: SSD or NVMe disks, RAID arrays for redundancy and performance. Network: High-speed network (10GbE or higher), dedicated network card, low-latency network. Others: Stable power supply, redundant components, compatible operating system and software, heat dissipation and cooling system.
 70B model generates 1,000 tokens in seconds, code rewriting surpasses GPT-4o, from the Cursor team, a code artifact invested by OpenAI
Jun 13, 2024 pm 03:47 PM
70B model generates 1,000 tokens in seconds, code rewriting surpasses GPT-4o, from the Cursor team, a code artifact invested by OpenAI
Jun 13, 2024 pm 03:47 PM
70B model, 1000 tokens can be generated in seconds, which translates into nearly 4000 characters! The researchers fine-tuned Llama3 and introduced an acceleration algorithm. Compared with the native version, the speed is 13 times faster! Not only is it fast, its performance on code rewriting tasks even surpasses GPT-4o. This achievement comes from anysphere, the team behind the popular AI programming artifact Cursor, and OpenAI also participated in the investment. You must know that on Groq, a well-known fast inference acceleration framework, the inference speed of 70BLlama3 is only more than 300 tokens per second. With the speed of Cursor, it can be said that it achieves near-instant complete code file editing. Some people call it a good guy, if you put Curs
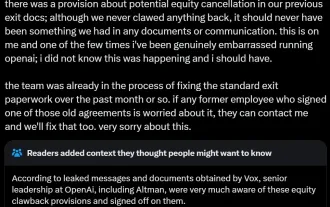 AI startups collectively switched jobs to OpenAI, and the security team regrouped after Ilya left!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
AI startups collectively switched jobs to OpenAI, and the security team regrouped after Ilya left!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
Last week, amid the internal wave of resignations and external criticism, OpenAI was plagued by internal and external troubles: - The infringement of the widow sister sparked global heated discussions - Employees signing "overlord clauses" were exposed one after another - Netizens listed Ultraman's "seven deadly sins" Rumors refuting: According to leaked information and documents obtained by Vox, OpenAI’s senior leadership, including Altman, was well aware of these equity recovery provisions and signed off on them. In addition, there is a serious and urgent issue facing OpenAI - AI safety. The recent departures of five security-related employees, including two of its most prominent employees, and the dissolution of the "Super Alignment" team have once again put OpenAI's security issues in the spotlight. Fortune magazine reported that OpenA
 How to read dbf file in oracle
May 10, 2024 am 01:27 AM
How to read dbf file in oracle
May 10, 2024 am 01:27 AM
Oracle can read dbf files through the following steps: create an external table and reference the dbf file; query the external table to retrieve data; import the data into the Oracle table.






