IN&EXISTS与NOT IN&NOT EXISTS 的优化原则小结
下面只是从理论上提出了一些建议,最好的原则是大家在上面的基础上,能够使用执行计划来分析,得出最佳的语句的写法。
1. EXISTS的执行流程select * from t1 where exists ( select null from t2 where y = x )
可以理解为:
代码如下:
for x in ( select * from t1 )
loop
if ( exists ( select null from t2 where y = x.x )
then
OUTPUT THE RECORD
end if
end loop
对于in 和 exists的性能区别:
如果子查询得出的结果集记录较少,主查询中的表较大且又有索引时应该用in,反之如果外层的主查询记录较少,子查询中的表大,又有索引时使用exists。
其实我们区分in和exists主要是造成了驱动顺序的改变(这是性能变化的关键),如果是exists,那么以外层表为驱动表,先被访问,如果是IN,那么先执行子查询,所以我们会以驱动表的快速返回为目标,那么就会考虑到索引及结果集的关系了
另外IN时不对NULL进行处理,如:
select 1 from dual where null in (0,1,2,null)
结果为空。
2. NOT IN 与NOT EXISTS:
NOT EXISTS的执行流程
代码如下:
select .....
from rollup R
where not exists ( select 'Found' from title T
where R.source_id = T.Title_ID);
可以理解为:
代码如下:
for x in ( select * from rollup )
loop
if ( not exists ( that query ) ) then
OUTPUT
end if;
end;
注意:NOT EXISTS 与 NOT IN 不能完全互相替换,看具体的需求。如果选择的列可以为空,则不能被替换。
例如下面语句,看他们的区别:
select x,y from t;
x y
------ ------
1 3
3 1
1 2
1 1
3 1
5
select * from t where x not in (select y from t t2 )
no rows
select * from t where not exists (select null from t t2
where t2.y=t.x )
x y
------ ------
5 NULL
所以要具体需求来决定
对于not in 和 not exists的性能区别:
not in 只有当子查询中,select 关键字后的字段有not null约束或者有这种暗示时用not in,另外如果主查询中表大,子查询中的表小但是记录多,则应当使用not in,并使用anti hash join.
如果主查询表中记录少,子查询表中记录多,并有索引,可以使用not exists,另外not in最好也可以用/*+ HASH_AJ */或者外连接+is null
NOT IN 在基于成本的应用中较好
比如:
代码如下:
select .....
from rollup R
where not exists ( select 'Found' from title T
where R.source_id = T.Title_ID);
改成(佳)
select ......
from title T, rollup R
where R.source_id = T.Title_id(+)
and T.Title_id is null;
或者(佳)
sql> select /*+ HASH_AJ */ ...
from rollup R
where ource_id NOT IN ( select ource_id
from title T
where ource_id IS NOT NULL )
注意:上面只是从理论上提出了一些建议,最好的原则是大家在上面的基础上,能够使用执行计划来分析,得出最佳的语句的写法。
'//=============================
exists,not exists总结
1 exists
SELECT * FROM anken_m WHERE EXISTS(
SELECT my_list_temp_m.sales_code
FROM my_list_temp_m
WHERE my_list_temp_m.sales_code=anken_m.sales_code)
说明:
1) 查询在anken_m表和my_list_temp_m表中都存在的sales_code。
2) sales_code是anken_m的主键,my_list_temp_m的外键。
注意:
1) 外层查询表anken_m是查询的对象。
2) 内层查询表my_list_temp_m是条件对象。
3) 内外层的查询表不能相同。
4) 作为关联条件的anken_m表不需要在内层查询FROM后添加。
5) my_list_temp_m.sales_code=anken_m.sales_code条件的左右顺序不影响查询结果。
2 not exists
SELECT * FROM anken_m WHERE NOT EXISTS(
SELECT my_list_temp_m.sales_code
FROM my_list_temp_m
WHERE my_list_temp_m.sales_code=anken_m.sales_code)
说明:
1) 查询在anken_m表中存在,但是在my_list_temp_m表中不存在的sales_code。
2) sales_code是anken_m的主键,my_list_temp_m的外键。
注意:
1) 外层查询表anken_m是查询的对象。
2) 内层查询表my_list_temp_m是条件对象。
3) 内外层的查询表不能相同。
4) 作为关联条件的anken_m表不需要在内层查询FROM后添加。
5) my_list_temp_m.sales_code=anken_m.sales_code条件的左右顺序不影响查询结果。
3 综合运用
UPDATE anken_m
SET(plan_type_code, branch_name, business_type_code)
=(SELECT anken.plan_type_code,anken.branch_name,anken.business_type_code
FROM anken
WHERE anken.sales_code=anken_m.sales_code)
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT anken.sales_code
FROM anken,my_list_temp_m
WHERE my_list_temp_m.sales_code=anken.sales_code
AND anken.sales_code=anken_m.sales_code
)
说明:
1) 用一个表的记录数据更新另一个表的记录数据。
2) 用一个SQL语句进行批量更新。
2) sales_code是anken,anken_m的主键,my_list_temp_m的外键。
注意:
1) set 语句中的要被更新字段必须跟数据源字段一一对应,另外数据源查询中的条件必须限定一条记录。也就是根据sales_code可以唯一确定anken的一条记录,和anken_m的一条记录,这样才能保证要被更新的记录和数据源记录的主键是相同的。
2) 根据WHERE EXISTS语句可以确定数据源记录的范围,也就是可以用anken表中哪些记录更新anken_m表。所以anken_m不需要在WHERE EXISTS语句中的FROM后添加。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Tips for using i18n to implement multi-language switching in Vue
Jun 25, 2023 am 09:33 AM
Tips for using i18n to implement multi-language switching in Vue
Jun 25, 2023 am 09:33 AM
With the continuous development of internationalization, more and more websites and applications need to support multi-language switching functions. As a popular front-end framework, Vue provides a plug-in called i18n that can help us achieve multi-language switching. This article will introduce common techniques for using i18n to implement multi-language switching in Vue. Step 1: Install the i18n plug-in First, we need to install the i18n plug-in using npm or yarn. Enter the following command at the command line: npminst
 What do out and in interfaces mean?
Sep 28, 2021 pm 04:39 PM
What do out and in interfaces mean?
Sep 28, 2021 pm 04:39 PM
The out interface refers to the output interface, and the in interface refers to the input interface. The out interface generally represents the audio source line output interface, which is used to connect loads, such as speakers, headphones, etc.; while the in interface generally represents the audio source line input interface, which is used to connect CD players, mobile phones, MP3 players, computers, etc.
 How to use the File.Exists function in C# to determine whether a file exists
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:25 AM
How to use the File.Exists function in C# to determine whether a file exists
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:25 AM
How to use the File.Exists function in C# to determine whether a file exists. In C# file operations, determining whether a file exists is a basic functional requirement. The File.Exists function is a method in C# used to determine whether a file exists. This article will introduce how to use the File.Exists function in C# to determine whether a file exists and provide specific code examples. Reference the namespace Before you start writing code, you first need to reference the System.IO namespace, which
 What is the difference between on, in, as, and where in Mysql?
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:37 AM
What is the difference between on, in, as, and where in Mysql?
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:37 AM
The difference between Mysqlon, in, as, and where Answer: Where query conditions, use on for internal and external connections, as as an alias, in to query whether a certain value creates 2 tables in a certain condition: student, scorestudent: score: whereSELECT*FROMstudentWHEREs_sex=' Male'For example: onSELECT*FROMstudentLEFTJOINscoreonstudent.s_id=score.s_id; combination of on and where: SELECT*FROMstudentLEFTJOINs
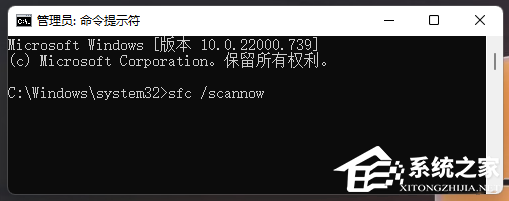 Five ways to fix Thread Stuck in Device Driver blue screen
Mar 25, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
Five ways to fix Thread Stuck in Device Driver blue screen
Mar 25, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
Some users reported that after installing Microsoft's March Win11 update patch KB5035853, a blue screen of death error occurred, with "ThreadStuckinDeviceDriver" displayed on the system page. It is understood that this error may be caused by hardware or driver issues. Here are five fixes that will hopefully resolve your computer blue screen problem quickly. Method 1: Run system file check. Run the [sfc/scannow] command in the command prompt, which can be used to detect and repair system file integrity issues. The purpose of this command is to scan and repair any missing or damaged system files, helping to ensure system stability and normal operation. Method 2: 1. Download and open the "Blue Screen Repair Tool"
 How to do multi-language processing in Vue?
Jun 11, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
How to do multi-language processing in Vue?
Jun 11, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
In actual development, multi-language support for websites or applications has become a necessary feature. As a popular JavaScript framework, Vue also supports multiple languages. This article will introduce the scheme and implementation details of multi-language processing in Vue. Solution Selection There are many multi-language support solutions, including but not limited to the following: 1.1. Front-end integrated implementation of multi-language functions on the front end, supported through the vue-i18n plug-in. Introducing the corresponding language pack as an independent component can display different
 Take stock of some practical Linux tips
Mar 12, 2024 pm 01:49 PM
Take stock of some practical Linux tips
Mar 12, 2024 pm 01:49 PM
Linux is a powerful operating system with many useful commands and tips to help you use it more efficiently. 1. Check the file check value. During the file copying or transmission process, the file may be damaged or modified. In this case, the check value can be used for verification. Usually, we need to use some interface programs provided by other teams in our work. Whenever the running results of these programs are not as expected, we will compare the md5 check values of both parties to confirm the consistency of the data. There are many ways to generate the check value of a file. Commonly used ones include md5sum check, crc check, sum check, etc. The commands are: md5sumfile_namecksumfile_namesum algorithm parameter file
 How to use i18n in CakePHP?
Jun 04, 2023 pm 12:10 PM
How to use i18n in CakePHP?
Jun 04, 2023 pm 12:10 PM
CakePHP is an open source PHP framework that supports the integration of multi-language internationalization (i18n). i18n can make your application multilingual, making it easier for you to attract international audiences and better serve local users. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the usage of CakePHPi18n. Getting Started First, you need to enable CakePHP’s multilingual capabilities. To do this, update the configuration file config/bootstrap.php and add the following code to your application






