Python实现控制台进度条功能
本文实例讲述了Python显示进度条的方法,是Python程序设计中非常实用的技巧。分享给大家供大家参考。具体方法如下:
首先,进度条和一般的print区别在哪里呢?
答案就是print会输出一个\n,也就是换行符,这样光标移动到了下一行行首,接着输出,之前已经通过stdout输出的东西依旧保留,而且保证我们在下面看到最新的输出结果。
进度条不然,我们必须再原地输出才能保证他是一个进度条,否则换行了怎么还叫进度条?
最简单的办法就是,再输出完毕后,把光标移动到行首,继续在那里输出更长的进度条即可实现,新的更长的进度条把旧的短覆盖,就形成了动画效果。
可以想到那个转义符了吧,那就是\ r。
转义符r就可以把光标移动到行首而不换行,转义符n就把光标移动到行首并且换行。
在python中,输出stdout(标准输出)可以使用sys.stdout.write
例如:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
j = '#'
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1,61):
j += '#'
sys.stdout.write(str(int((i/60)*100))+'% ||'+j+'->'+"\r")
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(0.5)
print
第二种思路是用转义符\b
转义符\b是退格键,也就是说把输出的光标往回退格子,这样就可以不用+=了,例如:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1,61):
sys.stdout.write('#'+'->'+"\b\b")
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(0.5)
print
光标回退2格,写个#再回退,再写,达到增长的目的了
不过写这么多似乎是废话,在耳边常常听到一句话:那就是不要重复造轮子。实际上python有丰富发lib帮你实现这个东西,你完全可以把心思放在逻辑开发上而不用注意这些小细节
下面要介绍的就是这个类“progressbar”(http://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/),使用easy_install可以方便的安装这个类库,其实就一个文件,拿过来放到文件同一个目录下面也直接可以import过来
如下图所示:
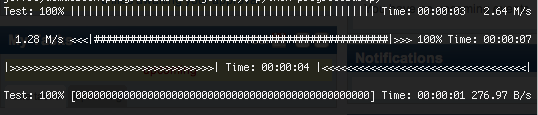
下面就是基本使用举例:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
from progressbar import *
total = 1000
#基本用法
progress = ProgressBar()
for i in progress(range(total)):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar = ProgressBar().start()
for i in range(1,1000):
pbar.update(int((i/(total-1))*100))
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.finish()
#高级用法
widgets = ['Progress: ', Percentage(), ' ', Bar(marker=RotatingMarker('>-=')),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10*i+1)
time.sleep(0.0001)
pbar.finish()
官方示例:http://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/source/browse/progressbar/examples.py
Python
# coding:utf-8
import sys
import time
from progressbar import AnimatedMarker, Bar, BouncingBar, Counter, ETA, \
FileTransferSpeed, FormatLabel, Percentage, \
ProgressBar, ReverseBar, RotatingMarker, \
SimpleProgress, Timer
examples = []
def example(fn):
try:
name = 'Example %d' % int(fn.__name__[7:])
except:
name = fn.__name__
def wrapped():
try:
sys.stdout.write('Running: %s\n' % name)
fn()
sys.stdout.write('\n')
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.stdout.write('\nSkipping example.\n\n')
examples.append(wrapped)
return wrapped
@example
def example0():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=[Percentage(), Bar()], maxval=300).start()
for i in range(300):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example1():
widgets = ['Test: ', Percentage(), ' ', Bar(marker=RotatingMarker()),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10 * i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example2():
class CrazyFileTransferSpeed(FileTransferSpeed):
"""It's bigger between 45 and 80 percent."""
def update(self, pbar):
if 45 < pbar.percentage() < 80:
return 'Bigger Now ' + FileTransferSpeed.update(self, pbar)
else:
return FileTransferSpeed.update(self, pbar)
widgets = [CrazyFileTransferSpeed(), ' <<<', Bar(), '>>> ',
Percentage(), ' ', ETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000)
# maybe do something
pbar.start()
for i in range(2000000):
# do something
pbar.update(5 * i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example3():
widgets = [Bar('>'), ' ', ETA(), ' ', ReverseBar('<')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10 * i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example4():
widgets = ['Test: ', Percentage(), ' ',
Bar(marker='0', left='[', right=']'),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=500)
pbar.start()
for i in range(100, 500 + 1, 50):
time.sleep(0.2)
pbar.update(i)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example5():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=[SimpleProgress()], maxval=17).start()
for i in range(17):
time.sleep(0.2)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example6():
pbar = ProgressBar().start()
for i in range(100):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example7():
pbar = ProgressBar() # Progressbar can guess maxval automatically.
for i in pbar(range(80)):
time.sleep(0.01)
@example
def example8():
pbar = ProgressBar(maxval=80) # Progressbar can't guess maxval.
for i in pbar((i for i in range(80))):
time.sleep(0.01)
@example
def example9():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=['Working: ', AnimatedMarker()])
for i in pbar((i for i in range(50))):
time.sleep(.08)
@example
def example10():
widgets = ['Processed: ', Counter(), ' lines (', Timer(), ')']
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(150))):
time.sleep(0.1)
@example
def example11():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Processed: %(value)d lines (in: %(elapsed)s)')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(150))):
time.sleep(0.1)
@example
def example12():
widgets = ['Balloon: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='.oO<a href="http://www.jobbole.com/members/weiboyes8848">@*</a> ')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
@example
def example13():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Arrows: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='←↖↑↗→↘↓↙')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError:
sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example14():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Arrows: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='◢◣◤◥')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError:
sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example15():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Wheels: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='◐◓◑◒')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError:
sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example16():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Bouncer: value %(value)d - '), BouncingBar()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(180))):
time.sleep(0.05)
@example
def example17():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Animated Bouncer: value %(value)d - '),
BouncingBar(marker=RotatingMarker())]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(180))):
time.sleep(0.05)
@example
def example18():
widgets = [Percentage(),
' ', Bar(),
' ', ETA(),
' ', AdaptiveETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=500)
pbar.start()
for i in range(500):
time.sleep(0.01 + (i < 100) * 0.01 + (i > 400) * 0.9)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example19():
pbar = ProgressBar()
for i in pbar([]):
pass
pbar.finish()
try:
for example in examples:
example()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.stdout('\nQuitting examples.\n')
再发一个类:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
class progressbarClass:
def __init__(self, finalcount, progresschar=None):
import sys
self.finalcount=finalcount
self.blockcount=0
#
# See if caller passed me a character to use on the
# progress bar (like "*"). If not use the block
# character that makes it look like a real progress
# bar.
#
if not progresschar: self.block=chr(178)
else: self.block=progresschar
#
# Get pointer to sys.stdout so I can use the write/flush
# methods to display the progress bar.
#
self.f=sys.stdout
#
# If the final count is zero, don't start the progress gauge
#
if not self.finalcount : return
self.f.write('\n------------------- % Progress -------------------\n')
return
def progress(self, count):
#
# Make sure I don't try to go off the end (e.g. >100%)
#
count=min(count, self.finalcount)
#
# If finalcount is zero, I'm done
#
if self.finalcount:
percentcomplete=int(round(100*count/self.finalcount))
if percentcomplete < 1: percentcomplete=1
else:
percentcomplete=100
#print "percentcomplete=",percentcomplete
blockcount=int(percentcomplete/2)
#print "blockcount=",blockcount
if blockcount > self.blockcount:
for i in range(self.blockcount,blockcount):
self.f.write(self.block)
self.f.flush()
if percentcomplete == 100: self.f.write("\n")
self.blockcount=blockcount
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
from time import sleep
pb=progressbarClass(8,"*")
count=0
while count<9:
count+=1
pb.progress(count)
sleep(0.2)
另外,python cookbook中11.1节也提供了一个不错的进度条类,代码如下:
Python
import sys
class progressbar(object):
def __init__(self, finalcount, block_char='.'):
self.finalcount = finalcount
self.blockcount = 0
self.block = block_char
self.f = sys.stdout
if not self.finalcount:
return
self.f.write('\n------------------ % Progress -------------------1\n')
self.f.write(' 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0\n')
self.f.write('----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0\n')
def progress(self, count):
count = min(count, self.finalcount)
if self.finalcount:
percentcomplete = int(round(100.0 * count / self.finalcount))
if percentcomplete < 1:
percentcomplete = 1
else:
percentcomplete = 100
blockcount = int(percentcomplete // 2)
if blockcount <= self.blockcount:
return
for i in range(self.blockcount, blockcount):
self.f.write(self.block)
self.f.flush()
self.blockcount = blockcount
if percentcomplete == 100:
self.f.write("\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
from time import sleep
pb = progressbar(8, "*")
for count in range(1, 9):
pb.progress(count)
sleep(0.2)
pb = progressbar(100)
pb.progress(20)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(47)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(90)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(100)
print "testing 1:"
pb = progressbar(1)
pb.progress(1)
运行结果如下图所示:
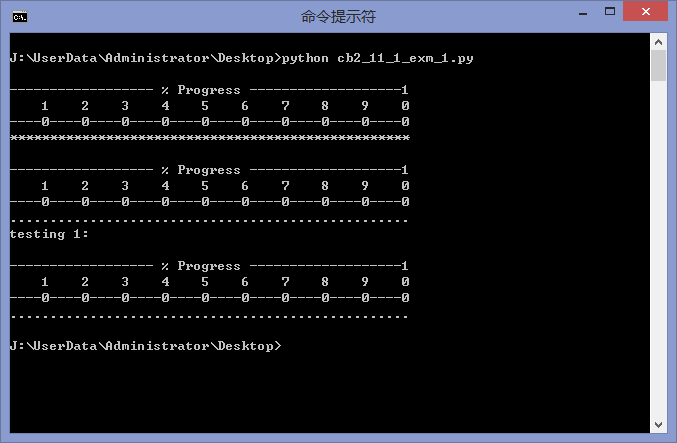
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计的学习有所帮助。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
There is no simple and direct free XML to PDF tool on mobile. The required data visualization process involves complex data understanding and rendering, and most of the so-called "free" tools on the market have poor experience. It is recommended to use computer-side tools or use cloud services, or develop apps yourself to obtain more reliable conversion effects.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Modifying XML content requires programming, because it requires accurate finding of the target nodes to add, delete, modify and check. The programming language has corresponding libraries to process XML and provides APIs to perform safe, efficient and controllable operations like operating databases.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.
 How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
XML beautification is essentially improving its readability, including reasonable indentation, line breaks and tag organization. The principle is to traverse the XML tree, add indentation according to the level, and handle empty tags and tags containing text. Python's xml.etree.ElementTree library provides a convenient pretty_xml() function that can implement the above beautification process.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.






